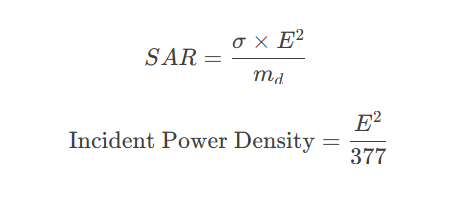1. What is SAR RF Exposure?
Definition: Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) is a measure of the rate at which radio frequency (RF) energy is absorbed by the body when exposed to an electric field. It is expressed in watts per kilogram (W/kg). Incident Power Density measures the power per unit area of the RF field, expressed in watts per square meter (W/m²).
Purpose: This calculator determines the SAR and Incident Power Density, which are critical for assessing RF exposure levels and ensuring compliance with safety standards for wireless devices.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas for RF exposure parameters:
Specific Absorption Rate (SAR):
\[
\text{Specific Absorption Rate (SAR)} = \frac{\sigma \times E^2}{m_d}
\]
Incident Power Density:
\[
\text{Incident Power Density} = \frac{E^2}{377}
\]
Where:
- SAR: Specific Absorption Rate (in W/kg)
- Incident Power Density: In W/m²
- \( E \): Electric field strength (in V/m, RMS)
- \( \sigma \): Conductivity of the material (in S/m)
- \( m_d \): Mass density of the material (in kg/m³)
- 377: Free-space impedance (in ohms, \( \Omega \))
Steps:
- Enter the electric field strength \( E \), conductivity \( \sigma \), and mass density \( m_d \).
- Click "Calculate" to compute the SAR and Incident Power Density.
- Results are displayed with 4 decimal places, or in scientific notation if less than 0.001.
3. Importance of SAR RF Exposure Calculations
SAR RF exposure calculations are essential for:
- Safety Compliance: Ensures wireless devices meet regulatory RF exposure limits to protect human health.
- Device Design: Helps engineers design devices with safe RF emission levels.
- Health Risk Assessment: Evaluates potential biological effects of RF exposure, such as thermal effects or tissue heating.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Typical Human Tissue Exposure
- \( E = 5 \, \text{V/m} \), \( \sigma = 1 \, \text{S/m} \), \( m_d = 1300 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \)
- SAR: \( \frac{1 \times 5^2}{1300} = \frac{25}{1300} \approx 0.0192 \, \text{W/kg} \)
- Incident Power Density: \( \frac{5^2}{377} = \frac{25}{377} \approx 0.0663 \, \text{W/m}^2 \)
- Example 2: Higher Electric Field
- \( E = 10 \, \text{V/m} \), \( \sigma = 0.33 \, \text{S/m} \), \( m_d = 1000 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \)
- SAR: \( \frac{0.33 \times 10^2}{1000} = \frac{33}{1000} = 0.0330 \, \text{W/kg} \)
- Incident Power Density: \( \frac{10^2}{377} = \frac{100}{377} \approx 0.2653 \, \text{W/m}^2 \)
- Example 3: Low Conductivity Material
- \( E = 2 \, \text{V/m} \), \( \sigma = 0.0042 \, \text{S/m} \), \( m_d = 1500 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \)
- SAR: \( \frac{0.0042 \times 2^2}{1500} = \frac{0.0168}{1500} \approx 0.0000 \, \text{W/kg} \ (1.1200 \times 10^{-5}) \)
- Incident Power Density: \( \frac{2^2}{377} = \frac{4}{377} \approx 0.0106 \, \text{W/m}^2 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Specific Absorption Rate (SAR)?
A: SAR is a measure of the rate at which RF energy is absorbed by the body, expressed in W/kg. It is used to assess the safety of RF exposure from devices like mobile phones.
Q: What does Incident Power Density represent?
A: Incident Power Density measures the power of the RF field per unit area, in W/m², and is used to evaluate the intensity of RF exposure at a given point.
Q: Why is the free-space impedance 377 ohms?
A: The value 377 ohms is the impedance of free space, derived from the relationship between electric and magnetic fields in a vacuum, calculated as \( \sqrt{\mu_0 / \epsilon_0} \), where \(\mu_0\) and \(\epsilon_0\) are the permeability and permittivity of free space, respectively.
SAR RF Exposure Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back