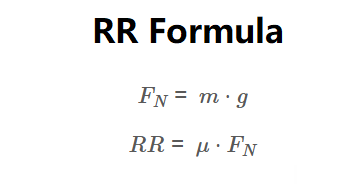1. What is a Rolling Resistance Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the rolling resistance force (\( RR \)) of an object, which is the force opposing the motion of a rolling object due to friction between the object and the surface.
Purpose: It is used in physics and engineering to analyze the energy losses due to rolling resistance, aiding in vehicle design, tire selection, and efficiency calculations.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Normal Force (used internally):
\[
F_N = m \cdot g
\]
Rolling Resistance Force:
\[
RR = \mu \cdot F_N
\]
Where:
- \( RR \): Rolling resistance force (N, lbf)
- \( m \): Mass of the object (kg, lb)
- \( g \): Gravitational acceleration (m/s², ft/s²)
- \( \mu \): Coefficient of friction (dimensionless)
Predefined Coefficients of Friction (μ):
- Asphalt and Concrete (Dry): 0.85
- Asphalt (Wet): 0.60
- Concrete (Wet): 0.80
- Gravel: 0.60
- Earth Road (Dry): 0.68
- Earth Road (Wet): 0.55
- Snow (Hard-Packed): 0.20
- Ice: 0.10
Unit Conversions:
- Mass Units (m): kg, lb
- Gravity Units (g): m/s², ft/s²
- Force Units (RR): N, lbf
Steps:
- Enter the mass of the object (\( m \)), selecting the unit (kg or lb)
- Enter the gravitational acceleration (\( g \)), selecting the unit (m/s² or ft/s², default is 9.81 m/s²)
- Select the coefficient of friction (\( \mu \)) source: either from a predefined road surface or a custom input
- Convert mass to kg and gravity to m/s²
- Calculate the rolling resistance force (\( RR \))
- Select the desired unit for the force and view the result
3. Importance of Rolling Resistance Calculation
Calculating rolling resistance is crucial for:
- Vehicle Efficiency: Understanding energy losses due to rolling resistance in tires, aiding in fuel efficiency improvements.
- Engineering Design: Selecting materials and tire designs to minimize rolling resistance.
- Physics Education: Studying the forces acting on rolling objects under gravity.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (Predefined μ): Mass = 1000 kg, Gravity = 9.81 m/s², Road Surface = Asphalt and Concrete (Dry) (μ = 0.85):
- Normal Force (internal) = \( 1000 \times 9.81 = 9810.000 \, \text{N} \)
- Rolling Resistance = \( 0.85 \times 9810 = 8338.500 \, \text{N} \)
- Example 2 (Custom μ): Mass = 2000 lb (907.185 kg), Gravity = 32.174 ft/s² (9.807 m/s²), Custom μ = 0.02:
- Normal Force (internal) = \( 907.185 \times 9.807 = 8896.763 \, \text{N} \)
- Rolling Resistance = \( 0.02 \times 8896.763 = 177.935 \, \text{N} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is rolling resistance?
A: Rolling resistance (\( RR \)) is the force opposing the motion of a rolling object, caused by friction between the object (e.g., a tire) and the surface.
Q: What factors affect rolling resistance?
A: Rolling resistance depends on the coefficient of friction (\( \mu \)), the mass of the object (\( m \)), and gravitational acceleration (\( g \)), as well as surface conditions and tire properties.
Q: Why is rolling resistance important for vehicles?
A: Rolling resistance affects fuel efficiency and energy consumption in vehicles, making it a key factor in tire design and vehicle performance optimization.
Rolling Resistance Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back