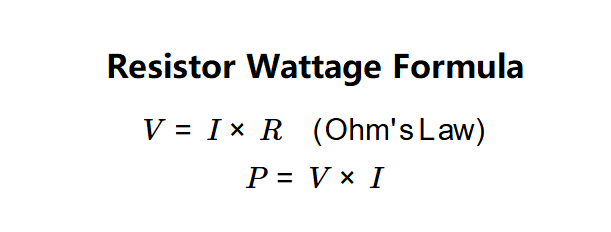1. What is Resistor Wattage Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the voltage (\( V \)) across a resistor and the power (\( P \)) dissipated by it due to the flow of current.
Purpose: It is used in electronics to determine the power rating required for a resistor to ensure it can handle the electrical power without overheating, which is essential for circuit design and safety.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas for resistor wattage:
- \( V = I \times R \quad (\text{Ohm's Law}) \)
- \( P = V \times I \)
- Alternatively: \( P = I^2 \times R \quad \text{or} \quad P = \frac{V^2}{R} \)
Where:
- \( V \): Voltage across the resistor (V);
- \( I \): Current through the resistor (A);
- \( R \): Resistance (Ω);
- \( P \): Power dissipated (W).
Steps:
- Enter the resistance (\( R \)) and either the voltage (\( V \)) or current (\( I \)).
- Convert resistance to ohms, voltage to volts, and current to amperes.
- If voltage is provided, calculate current using \( I = V / R \). If current is provided, calculate voltage using \( V = I \times R \).
- Calculate power using \( P = V \times I \).
- Convert the voltage and power to the selected output units (V/mV for voltage, W/mW for power).
- Display results in scientific notation if their absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Resistor Wattage Calculation
Calculating the voltage and power dissipated by a resistor is crucial for:
- Circuit Safety: Ensuring the resistor’s power rating exceeds the calculated power to prevent overheating and damage.
- Component Selection: Choosing a resistor with an appropriate power rating for the circuit’s requirements.
- Efficiency: Understanding power dissipation to optimize energy usage in electronic designs.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the voltage and power for a resistor with \( R = 10 \, \text{Ω} \) and \( I = 2 \, \text{A} \):
- Input Values:
- \( R = 10 \, \text{Ω} \);
- \( I = 2 \, \text{A} \);
- Voltage: \( V = I \times R = 2 \times 10 = 20 \, \text{V} \);
- Power: \( P = V \times I = 20 \times 2 = 40 \, \text{W} \);
- Result: \( V = 20.0000 \, \text{V} \), \( P = 40.0000 \, \text{W} \).
Example 2: Calculate the voltage and power for a resistor with \( R = 1 \, \text{kΩ} \) and \( V = 5 \, \text{mV} \):
- Input Values:
- \( R = 1 \, \text{kΩ} = 1000 \, \text{Ω} \);
- \( V = 5 \, \text{mV} = 5 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{V} \);
- Current: \( I = V / R = (5 \times 10^{-3}) / 1000 = 5 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{A} \);
- Power: \( P = V \times I = (5 \times 10^{-3}) \times (5 \times 10^{-6}) = 2.5 \times 10^{-8} \, \text{W} = 2.5 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{mW} \);
- Result: \( V = 5.0000 \, \text{mV} \), \( P = 2.5000e-5 \, \text{mW} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is the power rating of a resistor important?
A: The power rating indicates the maximum power a resistor can dissipate without overheating or failing. Exceeding this rating can cause the resistor to burn out, potentially damaging the circuit.
Q: How does resistance affect power dissipation?
A: For a fixed voltage, higher resistance reduces current (\( I = V / R \)), leading to lower power (\( P = V \times I \)). For a fixed current, higher resistance increases power (\( P = I^2 \times R \)).
Q: Can this calculator be used for resistors in series or parallel?
A: This calculator is designed for a single resistor. For series or parallel circuits, you need to calculate the equivalent resistance first and then apply the formulas.
Resistor Wattage Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back