1. What is Refrigerant Capillary Tube Resizer Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the new length (\( \text{NL} \)) of a capillary tube when resizing it to a new inside diameter (\( \text{New ID} \)), based on the original length (\( \text{OL} \)) and original inside diameter (\( \text{Orig ID} \)).
Purpose: It is used in refrigeration system design to adjust capillary tube dimensions, ensuring proper refrigerant flow and system performance.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula:
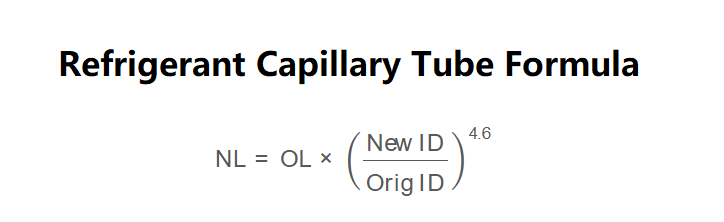
Formula:
\[
\text{NL} = \text{OL} \times \left( \frac{\text{New ID}}{\text{Orig ID}} \right)^{4.6}
\]
Where:
- \( \text{NL} \): New length of the capillary tube (m, cm, mm, in, ft)
- \( \text{OL} \): Original length of the capillary tube (m, cm, mm, in, ft)
- \( \text{New ID} \): New inside diameter of the tube (m, cm, mm, in)
- \( \text{Orig ID} \): Original inside diameter of the capillary tube (m, cm, mm, in)
Unit Conversions:
- Length (\( \text{OL} \), \( \text{NL} \)) and Diameter (\( \text{Orig ID} \), \( \text{New ID} \)):
- 1 m = 1 m
- 1 cm = 0.01 m
- 1 mm = 0.001 m
- 1 in = 0.0254 m
- 1 ft = 0.3048 m
Steps:
- Enter the original length (\( \text{OL} \)) with its respective unit (m, cm, mm, in, ft).
- Enter the original inside diameter (\( \text{Orig ID} \)) with its respective unit (m, cm, mm, in).
- Enter the new inside diameter (\( \text{New ID} \)) with its respective unit (m, cm, mm, in).
- Convert all inputs to meters.
- Calculate the new length (\( \text{NL} \)) using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit and display it, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Capillary Tube Resizing
Resizing capillary tubes is crucial for:
- Refrigeration Efficiency: Ensuring the correct flow rate of refrigerant to maintain optimal cooling performance.
- System Design: Adapting capillary tubes to new system requirements or replacement parts with different diameters.
- Cost Optimization: Adjusting tube length to avoid over- or under-sizing, which can affect system efficiency and energy consumption.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Calculate the new length of a capillary tube with an original length of 2 m, original inside diameter of 0.5 mm, and new inside diameter of 0.6 mm, with the result in meters:
- Enter \( \text{OL} = 2 \) m.
- Enter \( \text{Orig ID} = 0.5 \) mm.
- Convert to m: \( \text{Orig ID} = 0.5 \times 0.001 = 0.0005 \, \text{m} \)
- Enter \( \text{New ID} = 0.6 \) mm.
- Convert to m: \( \text{New ID} = 0.6 \times 0.001 = 0.0006 \, \text{m} \)
- New length: \( \text{NL} = 2 \times \left( \frac{0.0006}{0.0005} \right)^{4.6} = 2 \times (1.2)^{4.6} = 2 \times 1.9875 = 3.9750 \, \text{m} \)
- Result: \( \text{NL} = 3.9750 \, \text{m} \)
- Example 2: Calculate the new length of a capillary tube with an original length of 50 in, original inside diameter of 0.02 in, and new inside diameter of 0.015 in, with the result in inches:
- Enter \( \text{OL} = 50 \) in.
- Convert to m: \( \text{OL} = 50 \times 0.0254 = 1.27 \, \text{m} \)
- Enter \( \text{Orig ID} = 0.02 \) in.
- Convert to m: \( \text{Orig ID} = 0.02 \times 0.0254 = 0.000508 \, \text{m} \)
- Enter \( \text{New ID} = 0.015 \) in.
- Convert to m: \( \text{New ID} = 0.015 \times 0.0254 = 0.000381 \, \text{m} \)
- New length: \( \text{NL} = 1.27 \times \left( \frac{0.000381}{0.000508} \right)^{4.6} = 1.27 \times (0.75)^{4.6} = 1.27 \times 0.2768 = 0.3515 \, \text{m} \)
- Convert to in: \( \text{NL} = 0.3515 \div 0.0254 = 13.8386 \, \text{in} \)
- Result: \( \text{NL} = 13.8386 \, \text{in} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a capillary tube in refrigeration?
A: A capillary tube is a narrow tube used in refrigeration systems to control the flow of refrigerant, acting as an expansion device to reduce pressure and temperature.
Q: Why is the exponent 4.6 used in the formula?
A: The exponent 4.6 accounts for the relationship between the tube's diameter and flow resistance, derived from empirical data and the Hagen-Poiseuille equation adjusted for refrigerant flow dynamics.
Q: Can this calculator be used for any refrigerant?
A: Yes, the formula is generally applicable to capillary tubes in refrigeration systems, but the accuracy may depend on the specific refrigerant properties and system conditions.
Refrigerant Capillary Tube Resizer Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back