 Home
Home
 Back
Back
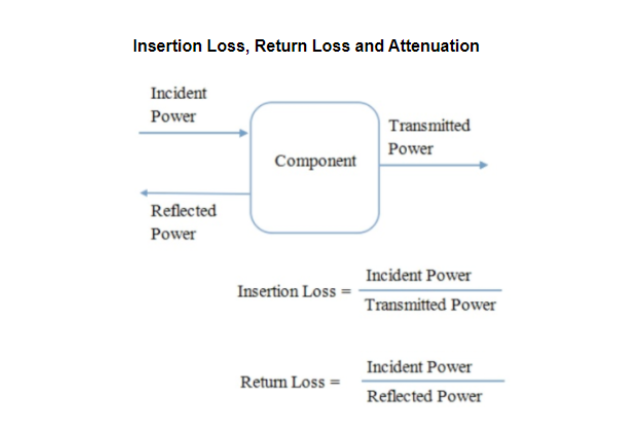
Definition: This calculator computes the Return Loss of an RF system given the magnitude of the reflection coefficient (\( |\Gamma| \)), which measures the amount of power reflected due to an impedance mismatch.
Purpose: It assists RF engineers, technicians, and students in evaluating signal reflection in RF systems, helping to optimize impedance matching and improve power transfer efficiency.
The calculator uses the formula:
\( \text{Return Loss} = -20 \log |\Gamma| \)
Where:
Steps:
Calculating return loss is essential for:
Example 1: Calculate return loss for a perfectly matched system:
Example 2: Calculate return loss for a typical mismatch:
Example 3: Calculate return loss for total reflection:
Q: Why is the reflection coefficient magnitude limited to 0 to 1?
A: Physically, the magnitude of the reflection coefficient cannot exceed 1, as it represents the ratio of reflected to incident power, and reflected power cannot exceed incident power.
Q: Why do I get an error for a reflection coefficient of 0?
A: A reflection coefficient of 0 causes a numerical issue because the logarithm of zero is undefined.
Q: What does a return loss of 0 dB mean?
A: A return loss of 0 dB indicates total reflection (\( |\Gamma| = 1 \)), meaning all power is reflected back, typically due to an open or short circuit.
Q: Why is the result formatted in scientific notation?
A: Values less than 0.001 or greater than 10000 are displayed in scientific notation for readability.