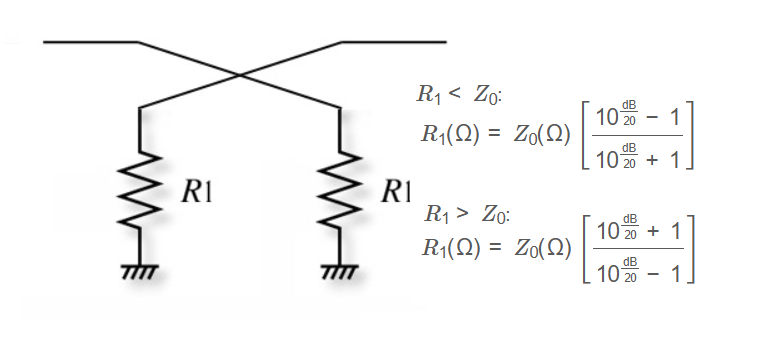
1. What is a Reflection Attenuator Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the resistor value \( R_1 \) for a reflection attenuator circuit based on the desired attenuation and the characteristic impedance \( Z_0 \). It provides two possible values for \( R_1 \): one where \( R_1 < Z_0 \) and another where \( R_1 > Z_0 \).
Purpose: It helps RF engineers and designers select an appropriate resistor value for a reflection attenuator to control signal amplitude and manage reflections in RF systems, ensuring proper impedance matching.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas to compute the resistor value \( R_1 \):
If \( R_1 < Z_0 \):
\[
R_1(\Omega) = Z_0(\Omega) \left[ \frac{10^{\frac{\text{dB}}{20}} - 1}{10^{\frac{\text{dB}}{20}} + 1} \right]
\]
If \( R_1 > Z_0 \):
\[
R_1(\Omega) = Z_0(\Omega) \left[ \frac{10^{\frac{\text{dB}}{20}} + 1}{10^{\frac{\text{dB}}{20}} - 1} \right]
\]
Where:
- \( R_1 \): Resistor value in ohms for the reflection attenuator circuit
- \( Z_0 \): Characteristic impedance in ohms (e.g., 50 ohms for typical RF systems)
- dB: Attenuation in decibels
Unit Conversions:
- Attenuation:
- 1 Np = 8.686 dB
- Impedance and Resistor (\( R_1 \)):
- 1 kΩ = 1000 Ω
- 1 mΩ = 0.001 Ω
Steps:
- Enter the desired attenuation and select the unit (dB or Np).
- Enter the characteristic impedance \( Z_0 \) and select the unit (ohms, kΩ, or mΩ).
- Click "Calculate" to compute \( R_1 \) for both cases (\( R_1 < Z_0 \) and \( R_1 > Z_0 \)).
- The results are initially displayed in ohms.
- Select a different unit for each result (ohms, kΩ, or mΩ) from the dropdowns after each result to convert the displayed values.
3. Importance of Reflection Attenuator Calculation
Calculating the resistor value for a reflection attenuator is essential for:
- Signal Control: Attenuators reduce signal amplitude without distorting the waveform, critical in RF systems.
- Reflection Management: Helps manage signal reflections due to impedance mismatches, reducing power loss and interference.
- Design Flexibility: Provides two resistor options (\( R_1 < Z_0 \) or \( R_1 > Z_0 \)), allowing designers to choose based on circuit constraints.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Attenuation = 10 dB, \( Z_0 \) = 50 ohms, Results in ohms
- \( 10^{\frac{10}{20}} = 10^{0.5} \approx 3.162 \)
- \( R_1 < Z_0 = 50 \times \frac{3.162 - 1}{3.162 + 1} \approx 25.98 \, \text{ohms} \)
- \( R_1 > Z_0 = 50 \times \frac{3.162 + 1}{3.162 - 1} \approx 96.23 \, \text{ohms} \)
- Example 2: Attenuation = 0.691 Np, \( Z_0 \) = 0.075 kΩ, Results in mΩ
- Convert: Attenuation = \( 0.691 \times 8.686 \approx 6 \, \text{dB} \), \( Z_0 = 0.075 \times 1000 = 75 \, \text{ohms} \)
- \( 10^{\frac{6}{20}} = 10^{0.3} \approx 1.995 \)
- \( R_1 < Z_0 = 75 \times \frac{1.995 - 1}{1.995 + 1} \approx 24.92 \, \text{ohms} \)
- \( R_1 > Z_0 = 75 \times \frac{1.995 + 1}{1.995 - 1} \approx 225.75 \, \text{ohms} \)
- Results in mΩ: \( R_1 < Z_0 = 24920 \, \text{mΩ} \), \( R_1 > Z_0 = 225750 \, \text{mΩ} \)
- Example 3: Attenuation = 3 dB, \( Z_0 \) = 60000 mΩ, Results in kΩ
- Convert: \( Z_0 = 60000 \times 0.001 = 60 \, \text{ohms} \)
- \( 10^{\frac{3}{20}} = 10^{0.15} \approx 1.4125 \)
- \( R_1 < Z_0 = 60 \times \frac{1.4125 - 1}{1.4125 + 1} \approx 10.24 \, \text{ohms} \)
- \( R_1 > Z_0 = 60 \times \frac{1.4125 + 1}{1.4125 - 1} \approx 351.27 \, \text{ohms} \)
- Results in kΩ: \( R_1 < Z_0 = 0.0102 \, \text{kΩ} \), \( R_1 > Z_0 = 0.3513 \, \text{kΩ} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a reflection attenuator?
A: A reflection attenuator is a circuit used in RF systems to reduce signal power and manage reflections due to impedance mismatches, typically using a single resistor \( R_1 \).
Q: Why are there two values for \( R_1 \)?
A: The calculator provides two values for \( R_1 \): one where \( R_1 < Z_0 \) and another where \( R_1 > Z_0 \), offering flexibility in design based on circuit requirements and resistor availability.
Q: What if the calculated resistor value is not standard?
A: In practice, select the closest standard resistor value (e.g., E12 or E24 series) or use a combination of resistors to approximate the calculated value.
Reflection Attenuator Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back