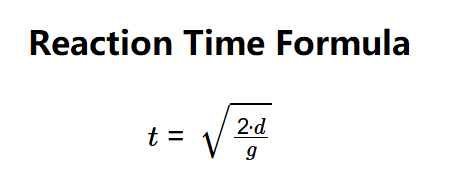1. What is the Reaction Time Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the reaction time (\( t \)) based on the distance (\( d \)) a ruler falls before being caught, using the equation \( t = \sqrt{\frac{2 \cdot d}{g}} \). It also calculates the average reaction time across multiple attempts.
Purpose: It is used in physics experiments to measure a person's reaction time by dropping a ruler and catching it, providing insight into human reflexes.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equation:
- \( t = \sqrt{\frac{2 \cdot d}{g}} \)
Where:
- \( d \): Distance the ruler falls (cm, m, in, ft);
- \( g \): Acceleration due to gravity (\( 9.81 \, \text{m/s}^2 \));
- \( t \): Reaction time (s, ms).
Steps:
- Enter the distance (\( d \)) for each attempt with its unit.
- Add more attempts as needed using the "Add Another Attempt" button.
- Convert each distance to meters.
- Calculate the reaction time for each attempt: \( t = \sqrt{\frac{2 \cdot d}{g}} \).
- Convert the reaction times to the selected output unit (seconds or milliseconds).
- Calculate the average reaction time across all attempts.
- Display the reaction times and the average, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Reaction Time Calculation
Calculating reaction time is crucial for:
- Physics Education: Teaching concepts of free fall and reaction time measurement.
- Human Performance: Assessing reflexes in sports, gaming, or medical studies.
- Safety: Understanding reaction times for activities like driving or operating machinery.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the reaction time for a ruler caught after falling 25 inches:
- Distance: \( d = 25 \, \text{in} = 25 \times 0.0254 = 0.635 \, \text{m} \);
- Reaction Time: \( t = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 0.635}{9.81}} \approx \sqrt{0.1295} \approx 0.3599 \, \text{s} = 359.9 \, \text{ms} \);
- Result: \( t = 359.9000 \, \text{ms} \).
Example 2 (Multiple Attempts): Calculate the average reaction time for two attempts with distances 20 cm and 30 cm:
- Attempt 1 Distance: \( d_1 = 20 \, \text{cm} = 0.2 \, \text{m} \);
- Attempt 1 Reaction Time: \( t_1 = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 0.2}{9.81}} \approx \sqrt{0.0408} \approx 0.2020 \, \text{s} = 202.0 \, \text{ms} \);
- Attempt 2 Distance: \( d_2 = 30 \, \text{cm} = 0.3 \, \text{m} \);
- Attempt 2 Reaction Time: \( t_2 = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 0.3}{9.81}} \approx \sqrt{0.0612} \approx 0.2474 \, \text{s} = 247.4 \, \text{ms} \);
- Average Reaction Time: \( \text{Average} = \frac{202.0 + 247.4}{2} = 224.7 \, \text{ms} \);
- Result: Average \( t = 224.7000 \, \text{ms} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why use a ruler drop to measure reaction time?
A: The ruler drop test is a simple and effective way to measure reaction time using basic physics principles, requiring only a ruler and gravity.
Q: Why is the acceleration due to gravity set to 9.81 m/s²?
A: This is the standard value of gravitational acceleration on Earth's surface, suitable for most reaction time experiments conducted under normal conditions.
Q: Can I use this calculator for other reaction time experiments?
A: This calculator is specifically designed for the ruler drop test. Other reaction time experiments may require different methods or formulas.
Reaction Time Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back