 Home
Home
 Back
Back
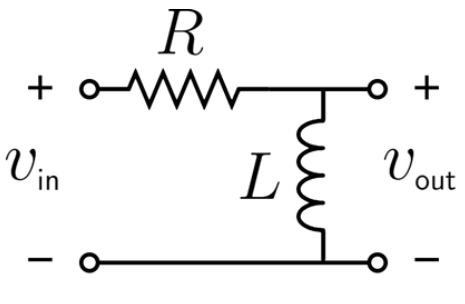
Definition: This calculator computes the cutoff frequency (\( f_c \)) for an RL high-pass filter, a basic electronic circuit that allows high-frequency signals to pass while attenuating low-frequency signals.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to design RL high-pass filters for applications like signal processing, noise filtering, and RF circuits, where low-frequency signals need to be removed.
The calculator uses the following formula:
Where:
Steps:
Calculating the cutoff frequency of an RL high-pass filter is crucial for:
Example 1: Calculate the cutoff frequency for an RL high-pass filter with \( R = 100 \, \text{Ω} \) and \( L = 10 \, \text{mH} \):
Example 2 (Demonstrating Scientific Notation): Calculate the cutoff frequency for an RL high-pass filter with \( R = 1 \, \text{kΩ} \) and \( L = 1 \, \text{µH} \):
Q: What is an RL high-pass filter?
A: An RL high-pass filter is a simple electronic circuit consisting of a resistor (\( R \)) and an inductor (\( L \)) that allows high-frequency signals to pass while attenuating low-frequency signals below a certain cutoff frequency.
Q: Why is the cutoff frequency important?
A: The cutoff frequency (\( f_c \)) determines the point at which the filter starts to attenuate low-frequency signals. It is critical for ensuring the filter performs as intended in applications where low-frequency noise needs to be removed.
Q: How does the inductor’s impedance affect the filter’s performance?
A: The inductor’s impedance (\( Z_L \)) increases with frequency, making it act like an open circuit for high-frequency signals and a short circuit for low-frequency signals. This allows high-frequency signals to pass through the resistor to the output while low-frequency signals are shunted through the inductor.