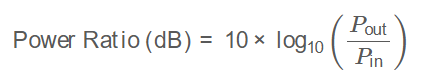1. What is RF Power Ratio Conversion Calculator?
Definition: This calculator converts the ratio of Output Power to Input Power into a decibel (dB) value, allowing different units for each power.
Purpose: It is used in RF engineering and telecommunications to quantify the gain or loss of a system, such as an amplifier or attenuator.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula:
Formula:
\[
\text{Power Ratio (dB)} = 10 \times \log_{10}\left(\frac{P_{\text{out}}}{P_{\text{in}}}\right)
\]
Where:
- \( P_{\text{out}} \): Output Power (converted to watts)
- \( P_{\text{in}} \): Input Power (converted to watts)
Unit Conversions:
- Input/Output Power:
- 1 W = 1 Watt
- 1 mW = 0.001 W
- 1 kW = 1,000 W
- 1 μW = 0.000001 W
- Power Ratio: Measured in dB, no conversion needed
Steps:
- Enter the Input Power (positive value) and select its unit (W, mW, kW, μW).
- Enter the Output Power (non-negative value) and select its unit (W, mW, kW, μW).
- Convert both powers to watts.
- Calculate \( \text{Power Ratio (dB)} = 10 \times \log_{10}\left(\frac{P_{\text{out}}}{P_{\text{in}}}\right) \).
- Display the result, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of RF Power Ratio Conversion Calculation
Calculating the Power Ratio in dB is crucial for:
- RF Engineering: Measuring the gain or loss of RF components like amplifiers and attenuators.
- Telecommunications: Analyzing signal strength changes in communication systems.
- Electronics: Evaluating the performance of power-related circuits and systems.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( P_{\text{in}} = 1 \, \text{mW} \), \( P_{\text{out}} = 10 \, \text{mW} \):
- Convert to watts: \( P_{\text{in}} = 0.001 \, \text{W} \), \( P_{\text{out}} = 0.01 \, \text{W} \)
- \( \text{Power Ratio (dB)} = 10 \times \log_{10}\left(\frac{0.01}{0.001}\right) \)
- \( \log_{10}(10) = 1 \)
- \( \text{Power Ratio (dB)} = 10 \times 1 = 10.0000 \, \text{dB} \)
- Example 2: For \( P_{\text{in}} = 100 \, \text{W} \), \( P_{\text{out}} = 50 \, \text{kW} \):
- Convert to watts: \( P_{\text{in}} = 100 \, \text{W} \), \( P_{\text{out}} = 50,000 \, \text{W} \)
- \( \text{Power Ratio (dB)} = 10 \times \log_{10}\left(\frac{50,000}{100}\right) \)
- \( \frac{50,000}{100} = 500 \)
- \( \log_{10}(500) \approx 2.6990 \)
- \( \text{Power Ratio (dB)} = 10 \times 2.6990 \approx 26.9897 \, \text{dB} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does a positive dB value indicate?
A: A positive dB value indicates a power gain, meaning the output power is greater than the input power.
Q: What does a negative dB value indicate?
A: A negative dB value indicates a power loss, meaning the output power is less than the input power.
Q: Why can I select different units for Input and Output Power?
A: The calculator converts both powers to watts before computing the ratio, allowing flexibility in unit selection.
RF Power Ratio Conversion Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back