 Home
Home
 Back
Back
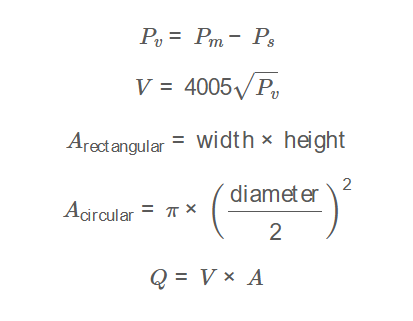
Note: This is an estimate based on standard conditions (70°F, 29.92 in Hg). For precise measurements, use a calibrated sensor like Setra’s SRIMV and account for duct friction and non-uniform velocity. Consult an HVAC professional for critical applications.
Definition: This calculator estimates air velocity (feet per minute, FPM) and volumetric flow (cubic feet per minute, CFM) in a duct based on pressure measurements and duct dimensions.
Purpose: It helps HVAC professionals and engineers determine airflow characteristics for system design, maintenance, and optimization, ensuring efficient ventilation and air quality.
The calculator uses the following method, based on Pitot tube measurements:
Formulas: \[ P_v = P_m - P_s \] \[ V = 4005 \sqrt{P_v} \] \[ A_{\text{rectangular}} = \text{width} \times \text{height} \] \[ A_{\text{circular}} = \pi \times \left(\frac{\text{diameter}}{2}\right)^2 \] \[ Q = V \times A \] Where:
Unit Conversions:
Steps:
Accurate airflow measurements are crucial for:
Examples:
Q: Why measure both measured and static pressure?
A: Measured pressure includes both static and velocity components. Subtracting static pressure gives velocity pressure, which is used to calculate air velocity.
Q: Why is an averaging Pitot tube recommended?
A: Air velocity varies across a duct due to friction at the walls. An averaging Pitot tube with multiple sensing points provides a more accurate average velocity.
Q: Can this calculator replace professional equipment?
A: No, this is an estimate. For precise measurements, use calibrated sensors like Setra’s SRIMV and consult HVAC professionals for system design.
https://www.setra.com/blog/how-to-measure-velocity-and-flow