 Home
Home
 Back
Back
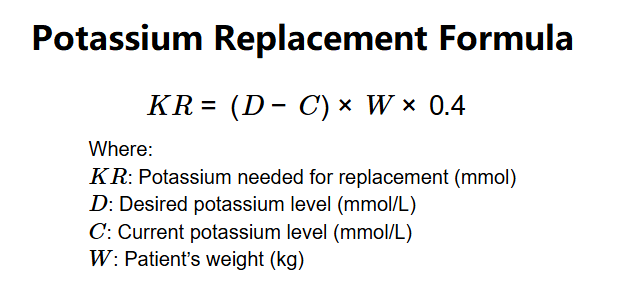
Definition: The Potassium Replacement Calculator determines the amount of potassium needed to correct hypokalemia using the formula \( KR = (D - C) \times W \times 0.4 \), based on the desired potassium level (\( D \)), current potassium level (\( C \)), and patient’s weight (\( W \)).
Purpose: Assists healthcare professionals in calculating safe potassium replacement doses for patients with low potassium levels, aiding in the management of hypokalemia to maintain heart, nerve, and muscle function.
Warning: This calculator is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Potassium replacement should be administered under medical supervision due to risks of overcorrection. Consult a healthcare provider for clinical decisions.
The calculator computes the potassium replacement using the following formula:
Formula:
Steps:
Calculating potassium replacement is crucial for:
Example: Desired potassium level = 4.2 mmol/L, Current potassium level = 3.8 mmol/L, Patient’s weight = 70 kg:
This shows that 11.2 mmol of potassium is needed to raise the patient’s potassium level from 3.8 to 4.2 mmol/L.
Q: What is hypokalemia?
A: Hypokalemia is a condition where blood potassium levels are below 3.5 mmol/L, potentially causing muscle weakness, cramps, or arrhythmias.
Q: Why is the constant 0.4 used in the formula?
A: The constant 0.4 represents the approximate extracellular fluid volume factor, as only about 2% of total body potassium is extracellular, and a 1 mmol/L deficit corresponds to a significant total body potassium loss.
Q: Is this calculator safe for clinical use?
A: This calculator provides estimates and should not replace medical judgment. Potassium replacement must be monitored closely due to risks of overcorrection. Consult a healthcare provider.