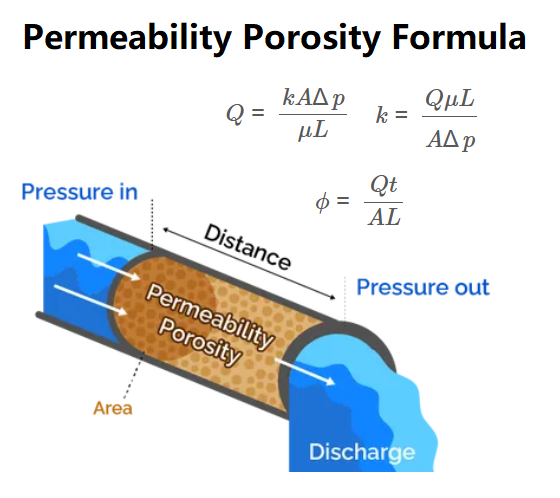
1. What is Permeability and Porosity Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the permeability (\( k \)) and porosity (\( \phi \)) of a material based on the discharge rate (\( Q \)), cross-sectional area (\( A \)), dynamic viscosity (\( \mu \)), distance (\( L \)), pressure difference (\( \Delta p \)), and time (\( t \)).
Purpose: It is used in geology, hydrology, and engineering to characterize porous materials, such as in groundwater flow, oil reservoir analysis, and filtration systems.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Formulas:
\[
Q = \frac{k A \Delta p}{\mu L}
\]
\[
k = \frac{Q \mu L}{A \Delta p}
\]
\[
\phi = \frac{Q t}{A L}
\]
Where:
- \( Q \): Discharge rate (m³/s, L/s, m³/min, ft³/s, ft³/min)
- \( k \): Permeability (m², cm², mm², Darcy)
- \( A \): Cross-sectional area (m², cm², mm², in²)
- \( \mu \): Dynamic viscosity (Pa·s, P, cP)
- \( L \): Distance (m, cm, mm, in)
- \( \Delta p \): Pressure difference (Pa, kPa, bar, psi)
- \( \phi \): Porosity (dimensionless, as a fraction)
- \( t \): Time (s, min, h)
Unit Conversions:
- Discharge Rate (\( Q \)):
- 1 m³/s = 1 m³/s
- 1 L/s = 0.001 m³/s
- 1 m³/min = \( \frac{1}{60} \) m³/s
- 1 ft³/s = \( (0.3048)^3 \) m³/s
- 1 ft³/min = \( \frac{(0.3048)^3}{60} \) m³/s
- Cross-Sectional Area (\( A \)):
- 1 m² = 1 m²
- 1 cm² = 0.0001 m²
- 1 mm² = 0.000001 m²
- 1 in² = 0.00064516 m²
- Dynamic Viscosity (\( \mu \)):
- 1 Pa·s = 1 Pa·s
- 1 P = 0.1 Pa·s
- 1 cP = 0.001 Pa·s
- Distance (\( L \)):
- 1 m = 1 m
- 1 cm = 0.01 m
- 1 mm = 0.001 m
- 1 in = 0.0254 m
- Pressure Difference (\( \Delta p \)):
- 1 Pa = 1 Pa
- 1 kPa = 1000 Pa
- 1 bar = 100000 Pa
- 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa
- Time (\( t \)):
- 1 s = 1 s
- 1 min = 60 s
- 1 h = 3600 s
- Permeability (\( k \)):
- 1 m² = 1 m²
- 1 cm² = 0.0001 m²
- 1 mm² = 0.000001 m²
- 1 Darcy ≈ 9.86923 × 10⁻¹³ m² (1 m² ≈ 1.01325 × 10¹² Darcy)
Steps:
- Enter the discharge rate (\( Q \)) with its respective unit (m³/s, L/s, m³/min, ft³/s, ft³/min).
- Enter the cross-sectional area (\( A \)) with its respective unit (m², cm², mm², in²).
- Enter the dynamic viscosity (\( \mu \)) with its respective unit (Pa·s, P, cP).
- Enter the distance (\( L \)) with its respective unit (m, cm, mm, in).
- Enter the pressure difference (\( \Delta p \)) with its respective unit (Pa, kPa, bar, psi).
- Enter the time (\( t \)) with its respective unit (s, min, h).
- Convert all inputs to SI units (m³/s for \( Q \), m² for \( A \), Pa·s for \( \mu \), m for \( L \), Pa for \( \Delta p \), s for \( t \)).
- Calculate the permeability (\( k \)) and porosity (\( \phi \)) using the formulas.
- Convert the permeability to the selected unit and display the results, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Permeability and Porosity Calculation
Calculating permeability and porosity is crucial for:
- Groundwater Flow: Assessing the flow of water through aquifers for water resource management.
- Oil and Gas Extraction: Evaluating reservoir properties to optimize extraction processes.
- Filtration Systems: Designing filters and membranes for industrial and environmental applications.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Calculate the permeability and porosity of a material with a discharge rate of 0.001 L/s, cross-sectional area of 10 cm², dynamic viscosity of 0.001 Pa·s, distance of 1 m, pressure difference of 1000 Pa, and time of 100 s, with permeability in Darcy:
- Enter \( Q = 0.001 \) L/s.
- Convert to m³/s: \( Q = 0.001 \times 0.001 = 1 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m³/s} \)
- Enter \( A = 10 \) cm².
- Convert to m²: \( A = 10 \times 0.0001 = 0.001 \, \text{m²} \)
- Enter \( \mu = 0.001 \) Pa·s.
- Enter \( L = 1 \) m.
- Enter \( \Delta p = 1000 \) Pa.
- Enter \( t = 100 \) s.
- Permeability: \( k = \frac{(1 \times 10^{-6}) \times 0.001 \times 1}{0.001 \times 1000} = 1 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m²} \)
- Convert to Darcy: \( k = 1 \times 10^{-6} \times 1.01325 \times 10^{12} = 1.01325 \times 10^6 \, \text{Darcy} \)
- Porosity: \( \phi = \frac{(1 \times 10^{-6}) \times 100}{0.001 \times 1} = 0.1 \)
- Result: \( k = 1.01325 \times 10^6 \, \text{Darcy} \), \( \phi = 0.1000 \)
- Example 2: Calculate the permeability and porosity of a material with a discharge rate of 0.01 ft³/min, cross-sectional area of 1 in², dynamic viscosity of 1 cP, distance of 10 cm, pressure difference of 0.1 bar, and time of 1 min, with permeability in cm²:
- Enter \( Q = 0.01 \) ft³/min.
- Convert to m³/s: \( Q = 0.01 \times \frac{(0.3048)^3}{60} = 4.7195 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m³/s} \)
- Enter \( A = 1 \) in².
- Convert to m²: \( A = 1 \times 0.00064516 = 0.00064516 \, \text{m²} \)
- Enter \( \mu = 1 \) cP.
- Convert to Pa·s: \( \mu = 1 \times 0.001 = 0.001 \, \text{Pa·s} \)
- Enter \( L = 10 \) cm.
- Convert to m: \( L = 10 \times 0.01 = 0.1 \, \text{m} \)
- Enter \( \Delta p = 0.1 \) bar.
- Convert to Pa: \( \Delta p = 0.1 \times 100000 = 10000 \, \text{Pa} \)
- Enter \( t = 1 \) min.
- Convert to s: \( t = 1 \times 60 = 60 \, \text{s} \)
- Permeability: \( k = \frac{(4.7195 \times 10^{-6}) \times 0.001 \times 0.1}{0.00064516 \times 10000} = 7.3135 \times 10^{-11} \, \text{m²} \)
- Convert to cm²: \( k = 7.3135 \times 10^{-11} \times 10000 = 7.3135 \times 10^{-7} \, \text{cm²} \)
- Porosity: \( \phi = \frac{(4.7195 \times 10^{-6}) \times 60}{0.00064516 \times 0.1} = 4.3894 \)
- Result: \( k = 7.3135 \times 10^{-7} \, \text{cm²} \), \( \phi = 4.3894 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is permeability (\( k \))?
A: Permeability (\( k \)) measures a material's ability to allow fluid to pass through it, typically in units of m² or Darcy, and is crucial for understanding flow through porous media.
Q: What is porosity (\( \phi \))?
A: Porosity (\( \phi \)) is the fraction of the material's volume that is void space, indicating how much fluid the material can hold. It is dimensionless and typically ranges from 0 to 1, though experimental values may exceed 1 if assumptions are not met.
Q: Why might porosity exceed 1 in calculations?
A: Porosity values greater than 1 can occur if the experimental setup or assumptions (e.g., steady-state flow, uniform material) do not hold, or if there are measurement errors.
Permeability and Porosity Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back