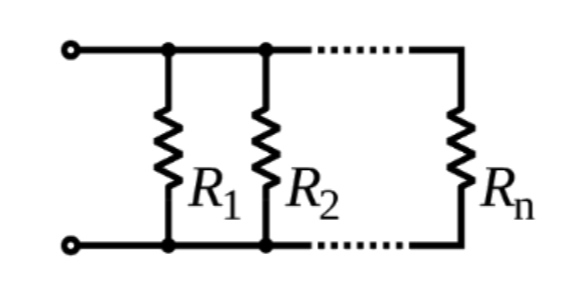
1. What is Parallel Resistor Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the equivalent resistance (\( R_{\text{eq}} \)) of multiple resistors connected in parallel.
Purpose: It is used in electronics to determine the total resistance in a parallel circuit, which is essential for designing circuits like voltage dividers, power distribution systems, and LED circuits.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the formula for resistors in parallel:
- \( \frac{1}{R_{\text{eq}}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \cdots + \frac{1}{R_n} \)
- \( R_{\text{eq}} = \frac{1}{\frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \cdots + \frac{1}{R_n}} \)
Where:
- \( R_{\text{eq}} \): Equivalent resistance (Ω)
- \( R_1, R_2, \ldots, R_n \): Resistance of each resistor (Ω)
Steps:
- Select the number of resistors.
- Enter the resistance values for each resistor with their units.
- Convert all inputs to ohms (Ω).
- Calculate the sum of the inverses of the resistances.
- Compute the equivalent resistance by taking the inverse of the sum.
- Convert the result to the selected output unit.
- Display the result with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Parallel Resistor Calculation
Calculating the equivalent resistance of resistors in parallel is crucial for:
- Circuit Design: Managing current distribution in circuits like power supplies, amplifiers, and digital logic circuits.
- Component Selection: Choosing resistors to achieve a desired total resistance when a specific value is unavailable.
- Power Distribution: Ensuring even power distribution across multiple components, as parallel resistors share the same voltage.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the equivalent resistance of four resistors in parallel with \( R_1 = 2 \, \text{kΩ} \), \( R_2 = 5 \, \text{kΩ} \), \( R_3 = 6 \, \text{kΩ} \), and \( R_4 = 200 \, \text{Ω} \):
- Resistance Values:
- \( R_1 = 2 \, \text{kΩ} = 2 \times 10^3 \, \text{Ω} \)
- \( R_2 = 5 \, \text{kΩ} = 5 \times 10^3 \, \text{Ω} \)
- \( R_3 = 6 \, \text{kΩ} = 6 \times 10^3 \, \text{Ω} \)
- \( R_4 = 200 \, \text{Ω} \)
- Sum of inverses: \( \frac{1}{R_{\text{eq}}} = \frac{1}{2 \times 10^3} + \frac{1}{5 \times 10^3} + \frac{1}{6 \times 10^3} + \frac{1}{200} \)
- \( \frac{1}{R_{\text{eq}}} = 0.0005 + 0.0002 + 0.0001667 + 0.005 \approx 0.0058667 \, \text{Ω}^{-1} \)
- Equivalent resistance: \( R_{\text{eq}} = \frac{1}{0.0058667} \approx 170.45 \, \text{Ω} \)
- Result: \( R_{\text{eq}} = 170.4500 \, \text{Ω} \)
Example 2: Calculate the equivalent resistance of two resistors in parallel with \( R_1 = 10 \, \text{Ω} \) and \( R_2 = 20 \, \text{Ω} \):
- Resistance Values:
- \( R_1 = 10 \, \text{Ω} \)
- \( R_2 = 20 \, \text{Ω} \)
- Sum of inverses: \( \frac{1}{R_{\text{eq}}} = \frac{1}{10} + \frac{1}{20} \)
- \( \frac{1}{R_{\text{eq}}} = 0.1 + 0.05 = 0.15 \, \text{Ω}^{-1} \)
- Equivalent resistance: \( R_{\text{eq}} = \frac{1}{0.15} \approx 6.6667 \, \text{Ω} \)
- Result: \( R_{\text{eq}} = 6.6667 \, \text{Ω} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why is the equivalent resistance in parallel less than the smallest individual resistance?
A: In parallel, the current has multiple paths, increasing the total conductance (inverse of resistance). This results in a lower equivalent resistance, as adding more resistors provides more pathways for current flow.
Q: How does current distribute across resistors in parallel?
A: The current through each resistor is inversely proportional to its resistance: \( I_i = \frac{V}{R_i} \), where \( V \) is the common voltage across all resistors. The total current is the sum of individual currents.
Q: Can I use this calculator for resistors in series?
A: No, this calculator is specifically for resistors in parallel. For resistors in series, the equivalent resistance is the sum of individual resistances: \( R_{\text{eq}} = R_1 + R_2 + \cdots + R_n \).
Parallel Resistor Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back