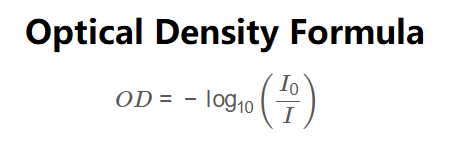1. What is Optical Density Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the optical density (OD), absorbance (A), and transmittance (%) of a medium based on the incident and transmitted light intensities, using the optical density formula.
Purpose: It is used in optics and spectroscopy to quantify how much light is absorbed or transmitted by a material, such as in filters, solutions, or biological samples.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Optical Density Formula:
\[
OD = -\log_{10}\left(\frac{I_0}{I}\right)
\]
Absorbance Formula:
\[
A = \log_{10}\left(\frac{I_0}{I}\right) = -OD
\]
Transmittance Formula:
\[
\text{Transmittance} (\%) = \left(\frac{I}{I_0}\right) \times 100
\]
Where:
- \( OD \): Optical density (unitless)
- \( A \): Absorbance (unitless)
- \( I_0 \): Incident light intensity (W/m², mW/m², μW/m², nW/m²)
- \( I \): Transmitted light intensity (W/m², mW/m², μW/m², nW/m²)
- \( \text{Transmittance} \): Percentage of light transmitted (%)
Unit Conversions:
- Intensity (\( I_0 \), \( I \)): W/m², mW/m² (1 mW/m² = \( 10^{-3} \) W/m²), μW/m² (1 μW/m² = \( 10^{-6} \) W/m²), nW/m² (1 nW/m² = \( 10^{-9} \) W/m²)
Steps:
- Enter the incident light intensity (\( I_0 \)) and transmitted light intensity (\( I \)), and select their units.
- Convert both intensities to W/m².
- Calculate the optical density: \( OD = -\log_{10}\left(\frac{I_0}{I}\right) \).
- Calculate the absorbance: \( A = -OD \).
- Calculate the transmittance: \( \text{Transmittance} (\%) = \left(\frac{I}{I_0}\right) \times 100 \).
- Display the results, using scientific notation for OD and absorbance values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places. Transmittance is displayed with 2 decimal places.
3. Importance of Optical Density Calculation
Calculating optical density, absorbance, and transmittance is crucial for:
- Spectroscopy: Measuring the concentration of substances in solutions (e.g., in UV-Vis spectroscopy).
- Optical Filters: Designing filters for photography, microscopy, or laser systems.
- Biological Research: Quantifying the density of bacterial cultures or the absorbance of biomolecules.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( I_0 = 25 \, \text{W/m²} \), \( I = 12 \, \text{W/m²} \):
- Calculate: \( OD = -\log_{10}\left(\frac{25}{12}\right) \approx -0.3188 \)
- Absorbance: \( A = -OD \approx 0.3188 \)
- Transmittance: \( \text{Transmittance} (\%) = \left(\frac{12}{25}\right) \times 100 = 48 \, \% \)
- Example 2: For \( I_0 = 100 \, \text{mW/m²} \), \( I = 10 \, \text{mW/m²} \):
- Convert: \( I_0 = 100 \times 10^{-3} = 0.1 \, \text{W/m²} \), \( I = 10 \times 10^{-3} = 0.01 \, \text{W/m²} \)
- Calculate: \( OD = -\log_{10}\left(\frac{0.1}{0.01}\right) = -\log_{10}(10) = -1 \)
- Absorbance: \( A = -OD = 1 \)
- Transmittance: \( \text{Transmittance} (\%) = \left(\frac{0.01}{0.1}\right) \times 100 = 10 \, \% \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is optical density?
A: Optical density (OD) is a measure of how much light is absorbed by a medium, defined as the negative logarithm of the ratio of incident to transmitted light intensity.
Q: How is absorbance different from optical density?
A: Absorbance (A) is the negative of optical density (OD). While OD is typically negative in this context, absorbance is positive, reflecting the amount of light absorbed.
Q: Why must the transmitted intensity be less than or equal to the incident intensity?
A: Physically, a medium cannot transmit more light than it receives. If \( I > I_0 \), it would imply an unphysical gain of light, which is not possible without an external energy source.
Optical Density Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back