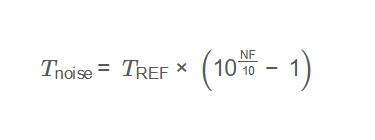1. What is Noise Temperature Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the noise temperature (\( T_{\text{noise}} \)) of a system based on the reference temperature (\( T_{\text{REF}} \)) and noise figure (\( \text{NF} \)).
Purpose: It is used in RF engineering and telecommunications to quantify the noise performance of amplifiers, receivers, and other RF components, which is critical for signal-to-noise ratio analysis.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula:
Formula:
\[
T_{\text{noise}} = T_{\text{REF}} \times \left( 10^{\frac{\text{NF}}{10}} - 1 \right)
\]
Where:
- \( T_{\text{noise}} \): Noise Temperature (K)
- \( T_{\text{REF}} \): Reference Temperature (K, typically 290 K)
- \( \text{NF} \): Noise Figure (dB)
Unit Conversions:
- Reference Temperature (\( T_{\text{REF}} \)): Measured in Kelvin (K), no conversion needed
- Noise Figure (\( \text{NF} \)): Measured in decibels (dB), no conversion needed
- Noise Temperature (\( T_{\text{noise}} \)): Measured in Kelvin (K), no conversion needed
Steps:
- Enter the reference temperature (\( T_{\text{REF}} \)) in Kelvin (default is 290 K).
- Enter the noise figure (\( \text{NF} \)) in decibels (dB).
- Calculate \( T_{\text{noise}} = T_{\text{REF}} \times \left( 10^{\frac{\text{NF}}{10}} - 1 \right) \).
- Display the result, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Noise Temperature Calculation
Calculating noise temperature is crucial for:
- RF Engineering: Evaluating the noise performance of RF components like low-noise amplifiers (LNAs).
- Telecommunications: Improving the signal-to-noise ratio in receivers for better communication quality.
- Satellite Systems: Designing systems that operate in low-noise environments, such as satellite receivers.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( T_{\text{REF}} = 290 \, \text{K} \), \( \text{NF} = 3 \, \text{dB} \):
- \( T_{\text{noise}} = 290 \times \left( 10^{\frac{3}{10}} - 1 \right) \)
- \( 10^{\frac{3}{10}} \approx 1.9953 \)
- \( T_{\text{noise}} = 290 \times (1.9953 - 1) \approx 288.6228 \, \text{K} \)
- Example 2: For \( T_{\text{REF}} = 290 \, \text{K} \), \( \text{NF} = 0 \, \text{dB} \):
- \( T_{\text{noise}} = 290 \times \left( 10^{\frac{0}{10}} - 1 \right) \)
- \( 10^{\frac{0}{10}} = 1 \)
- \( T_{\text{noise}} = 290 \times (1 - 1) = 0 \, \text{K} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is noise temperature?
A: Noise temperature (\( T_{\text{noise}} \)) is a measure of the noise power introduced by a system, expressed as an equivalent temperature in Kelvin.
Q: Why is the reference temperature typically 290 K?
A: 290 K (approximately 17°C) is a standard reference temperature used in noise calculations, representing typical ambient conditions.
Q: How is noise temperature used in real life?
A: It is used in designing low-noise systems for applications like radio astronomy, satellite communications, and high-sensitivity receivers.
Noise Temperature Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back