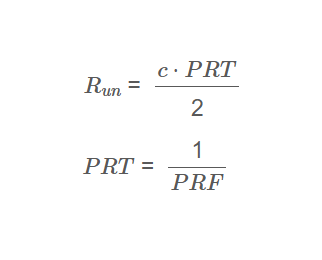1. What is a Maximum Unambiguous Range Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the maximum unambiguous range \( R_{un} \) of a radar system, which is the maximum distance at which a target can be detected without range ambiguity, based on the pulse repetition frequency (PRF) or pulse repetition time (PRT).
Purpose: It helps radar engineers and system designers evaluate the operational range of a radar system, ensuring accurate target detection without overlap from multiple pulses.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula to compute the maximum unambiguous range:
Maximum Unambiguous Range \( R_{un} \):
\[
R_{un} = \frac{c \cdot PRT}{2}
\]
Where:
\[
PRT = \frac{1}{PRF}
\]
Where:
- \( R_{un} \): Maximum unambiguous range in meters
- \( c \): Speed of light (\( 3 \times 10^8 \) m/s)
- \( PRT \): Pulse repetition time in seconds
- \( PRF \): Pulse repetition frequency in Hz
Unit Conversions:
- Input PRF:
- 1 kHz = 1000 Hz
- 1 MHz = \( 10^6 \) Hz
- Input PRT:
- 1 ms = \( 10^{-3} \) s
- 1 μs = \( 10^{-6} \) s
- Output Range (\( R_{un} \)):
- 1 km = 1000 m
- 1 mile = 1609.34 m
Steps:
- Select whether to input PRF or PRT.
- Enter the PRF (in Hz, kHz, or MHz) or PRT (in s, ms, or μs), selecting the appropriate unit.
- Click "Calculate" to compute \( R_{un} \).
- The result is initially displayed in meters (m).
- Select a different unit for \( R_{un} \) (m, km, or miles) from the dropdown after the result to convert the displayed value.
3. Importance of Maximum Unambiguous Range Calculation
Calculating the maximum unambiguous range is essential for:
- Radar Performance: Ensures accurate target detection without range ambiguity, critical for applications like air traffic control, military radar, and weather monitoring.
- System Design: Helps radar engineers select an appropriate PRF or PRT to meet operational range requirements.
- Range Optimization: Balances range and resolution in radar systems by adjusting pulse timing.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: PRF = 1 kHz, Result in meters
- Convert: PRF = \( 1 \times 1000 = 1000 \, \text{Hz} \)
- PRT: \( \frac{1}{1000} = 0.001 \, \text{s} \)
- \( R_{un} = \frac{3 \times 10^8 \times 0.001}{2} = 150000 \, \text{m} \)
- Example 2: PRT = 1 ms, Result in km
- Convert: PRT = \( 1 \times 10^{-3} = 0.001 \, \text{s} \)
- Same as Example 1: \( R_{un} = 150000 \, \text{m} \)
- Result in km: \( R_{un} = 150000 \div 1000 = 150 \, \text{km} \)
- Example 3: PRF = 1000 Hz, Result in miles
- PRT: \( \frac{1}{1000} = 0.001 \, \text{s} \)
- Same as Example 1: \( R_{un} = 150000 \, \text{m} \)
- Result in miles: \( R_{un} = 150000 \div 1609.34 \approx 93.2057 \, \text{miles} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is maximum unambiguous range?
A: Maximum unambiguous range is the greatest distance a radar can detect a target without range ambiguity, determined by the time between transmitted pulses (PRT) or the pulse repetition frequency (PRF).
Q: Why does PRF affect the unambiguous range?
A: A higher PRF (shorter PRT) means pulses are sent more frequently, reducing the time for echoes to return before the next pulse, thus decreasing the unambiguous range.
Q: Can this calculator be used for all radar systems?
A: The formula applies to pulsed radar systems. For continuous wave (CW) or frequency-modulated radars, different methods are needed to determine range ambiguity.
Maximum Unambiguous Range Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back