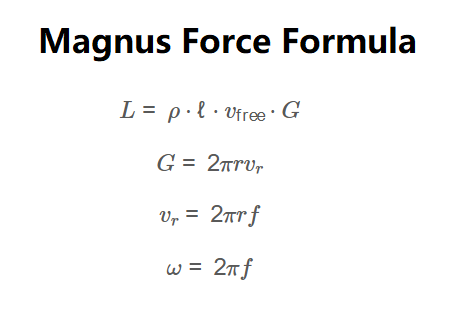1. What is Magnus Force Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the Magnus force (\( L \)), a force exerted on a spinning object moving through a fluid, based on the Kutta-Joukowski equation. It also calculates the angular velocity (\( \omega \)), rotational speed (\( v_r \)), and vortex strength (\( G \)).
Purpose: It is used in aerodynamics and fluid dynamics to analyze the lift generated by spinning objects, such as in sports (e.g., soccer balls, tennis balls) or engineering applications (e.g., Flettner rotors).
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Formulas:
\[
L = \rho \cdot \ell \cdot v_{\text{free}} \cdot G
\]
\[
G = 2 \pi r v_r
\]
\[
v_r = 2 \pi r f
\]
\[
\omega = 2 \pi f
\]
Where:
- \( L \): Magnus force (N, kN, mN, MN, lbf, kgf)
- \( \rho \): Fluid density (kg/m³, g/cm³, kg/cm³, lb/ft³, slug/ft³)
- \( \ell \): Length of the cylinder (m, cm, mm, ft, in)
- \( v_{\text{free}} \): Free stream velocity (m/s, km/h, mph, ft/s, km/min, ft/min, mile/min)
- \( G \): Vortex strength (m²/s, in²/s, ft²/s, cm²/s, mm²/s)
- \( r \): Radius of the cylinder (m, cm, mm, ft, in)
- \( v_r \): Rotational speed (m/s, ft/s, ft/min, mph, km/s, km/h)
- \( f \): Rate of rotation (rev/s, rev/min)
- \( \omega \): Angular velocity (rad/s)
Predefined Substances:
- Air: 1.225 kg/m³ (at sea level, 15°C)
- Water: 1000 kg/m³ (pure water at 4°C, max density)
- Hydrazine: 798 kg/m³ (at 20°C)
- Nitrogen (N₂): 1.165 kg/m³ (gas at 0°C, 1 atm)
- Oxygen (O₂): 1.381 kg/m³ (gas at 0°C, 1 atm)
- Ethanol: 785.1 kg/m³ (at 20°C)
- Methanol: 786.5 kg/m³ (at 20°C)
- Ammonia: 823.5 kg/m³
- Castor Oil: 952 kg/m³ (at 20°C)
- Poppy Seed Oil: 916 kg/m³ (varies with refinement)
- Helium (He): 0.1664 kg/m³ (gas at 0°C, 1 atm)
- Methane (CH₄): 0.668 kg/m³ (gas at 0°C, 1 atm)
Unit Conversions:
- Fluid Density (\( \rho \)):
- 1 kg/m³ = 1 kg/m³
- 1 g/cm³ = 1000 kg/m³
- 1 kg/cm³ = 1000000 kg/m³
- 1 lb/ft³ = 16.0185 kg/m³
- 1 slug/ft³ = 515.379 kg/m³
- Radius (\( r \)) and Length (\( \ell \)):
- 1 m = 1 m
- 1 cm = 0.01 m
- 1 mm = 0.001 m
- 1 ft = 0.3048 m
- 1 in = 0.0254 m
- Rate of Rotation (\( f \)):
- 1 rev/s = 1 rev/s
- 1 rev/min = 1/60 rev/s
- Free Stream Velocity (\( v_{\text{free}} \)):
- 1 m/s = 1 m/s
- 1 km/h = 0.277778 m/s
- 1 mph = 0.44704 m/s
- 1 ft/s = 0.3048 m/s
- 1 km/min = 16.6667 m/s
- 1 ft/min = 0.00508 m/s
- 1 mile/min = 26.8223 m/s
- Rotational Speed (\( v_r \)):
- 1 m/s = 1 m/s
- 1 ft/s = 0.3048 m/s
- 1 ft/min = 0.00508 m/s
- 1 mph = 0.44704 m/s
- 1 km/s = 1000 m/s
- 1 km/h = 0.277778 m/s
- Vortex Strength (\( G \)):
- 1 m²/s = 1 m²/s
- 1 in²/s = 0.00064516 m²/s
- 1 ft²/s = 0.092903 m²/s
- 1 cm²/s = 0.0001 m²/s
- 1 mm²/s = 0.000001 m²/s
- Magnus Force (\( L \)):
- 1 N = 1 N
- 1 kN = 1000 N
- 1 mN = 0.001 N
- 1 MN = 1000000 N
- 1 lbf = 4.44822 N
- 1 kgf = 9.80665 N
Steps:
- Select a substance from the dropdown or choose "Custom" to enter your own density.
- If a predefined substance is selected, the density field will auto-fill and become read-only.
- Specify the density unit (kg/m³, g/cm³, kg/cm³, lb/ft³, slug/ft³).
- Enter the radius (\( r \)) with its respective unit (m, cm, mm, ft, in).
- Enter the length (\( \ell \)) with its respective unit (m, cm, mm, ft, in).
- Enter the rate of rotation (\( f \)) with its respective unit (rev/s, rev/min).
- Enter the free stream velocity (\( v_{\text{free}} \)) with its respective unit (m/s, km/h, mph, ft/s, km/min, ft/min, mile/min).
- Convert all inputs to SI units (kg/m³ for density, m for radius and length, rev/s for rotation rate, m/s for velocity).
- Calculate the angular velocity using \( \omega = 2 \pi f \).
- Calculate the rotational speed using \( v_r = 2 \pi r f \).
- Calculate the vortex strength using \( G = 2 \pi r v_r \).
- Calculate the Magnus force using \( L = \rho \cdot \ell \cdot v_{\text{free}} \cdot G \).
- Display the results, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
- Select the desired units for \( v_r \), \( G \), and \( L \) from the dropdowns to convert the results.
3. Importance of Magnus Force Calculation
Calculating the Magnus force is crucial for:
- Sports Dynamics: Understanding the trajectory of spinning balls in sports like soccer, tennis, and baseball.
- Engineering Applications: Designing rotating cylinders (e.g., Flettner rotors) for propulsion in ships or aircraft.
- Fluid Dynamics Research: Analyzing lift forces in rotating objects moving through fluids, aiding in the study of aerodynamics and hydrodynamics.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Calculate the Magnus force for a soccer ball with a radius of 11 cm, length of 22 cm (diameter), spinning at 10 rev/s, moving through air (1.225 kg/m³) with a free stream velocity of 20 m/s, displaying \( v_r \) in mph, \( G \) in cm²/s, and \( L \) in lbf:
- Select "Air" (auto-fills \( \rho = 1.225 \) kg/m³).
- Enter \( r = 11 \) cm.
- Convert to m: \( r = 11 \times 0.01 = 0.11 \, \text{m} \)
- Enter \( \ell = 22 \) cm.
- Convert to m: \( \ell = 22 \times 0.01 = 0.22 \, \text{m} \)
- Enter \( f = 10 \) rev/s.
- Enter \( v_{\text{free}} = 20 \) m/s.
- \( \omega = 2 \pi \times 10 = 62.8319 \, \text{rad/s} \)
- \( v_r = 2 \pi \times 0.11 \times 10 = 6.9115 \, \text{m/s} \)
- Convert \( v_r \) to mph: \( v_r = 6.9115 / 0.44704 = 15.4606 \, \text{mph} \)
- \( G = 2 \pi \times 0.11 \times 6.9115 = 4.7818 \, \text{m²/s} \)
- Convert \( G \) to cm²/s: \( G = 4.7818 / (0.01 \times 0.01) = 47818.0365 \, \text{cm²/s} \)
- \( L = 1.225 \times 0.22 \times 20 \times 4.7818 = 25.7647 \, \text{N} \)
- Convert \( L \) to lbf: \( L = 25.7647 / 4.44822 = 5.7925 \, \text{lbf} \)
- Result: \( \omega = 62.8319 \, \text{rad/s} \), \( v_r = 15.4606 \, \text{mph} \), \( G = 47818.0365 \, \text{cm²/s} \), \( L = 5.7925 \, \text{lbf} \)
- Example 2: Calculate the Magnus force for a spinning cylinder in water (1000 kg/m³) with a radius of 5 in, length of 2 ft, spinning at 300 rev/min, with a free stream velocity of 50 ft/s, displaying \( v_r \) in km/h, \( G \) in ft²/s, and \( L \) in kgf:
- Select "Water" (auto-fills \( \rho = 1000 \) kg/m³).
- Enter \( r = 5 \) in.
- Convert to m: \( r = 5 \times 0.0254 = 0.127 \, \text{m} \)
- Enter \( \ell = 2 \) ft.
- Convert to m: \( \ell = 2 \times 0.3048 = 0.6096 \, \text{m} \)
- Enter \( f = 300 \) rev/min.
- Convert to rev/s: \( f = 300 / 60 = 5 \, \text{rev/s} \)
- Enter \( v_{\text{free}} = 50 \) ft/s.
- Convert to m/s: \( v_{\text{free}} = 50 \times 0.3048 = 15.24 \, \text{m/s} \)
- \( \omega = 2 \pi \times 5 = 31.4159 \, \text{rad/s} \)
- \( v_r = 2 \pi \times 0.127 \times 5 = 3.9908 \, \text{m/s} \)
- Convert \( v_r \) to km/h: \( v_r = 3.9908 / 0.277778 = 14.3669 \, \text{km/h} \)
- \( G = 2 \pi \times 0.127 \times 3.9908 = 3.1846 \, \text{m²/s} \)
- Convert \( G \) to ft²/s: \( G = 3.1846 / (0.3048 \times 0.3048) = 34.2865 \, \text{ft²/s} \)
- \( L = 1000 \times 0.6096 \times 15.24 \times 3.1846 = 29587.3619 \, \text{N} \)
- Convert \( L \) to kgf: \( L = 29587.3619 / 9.80665 = 3017.0686 \, \text{kgf} \)
- Result: \( \omega = 31.4159 \, \text{rad/s} \), \( v_r = 14.3669 \, \text{km/h} \), \( G = 34.2865 \, \text{ft²/s} \), \( L = 3017.0686 \, \text{kgf} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the Magnus effect?
A: The Magnus effect is the phenomenon where a spinning object moving through a fluid experiences a force perpendicular to its direction of motion, caused by the pressure difference created by the spin.
Q: Why is the Magnus force important in sports?
A: In sports like soccer and tennis, the Magnus force affects the trajectory of a spinning ball, allowing players to curve shots or add spin to control the ball's path.
Q: Can the Magnus force be negative?
A: Yes, the Magnus force can be negative depending on the direction of the spin relative to the free stream velocity, indicating a downward or opposite force.
Magnus Force Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back