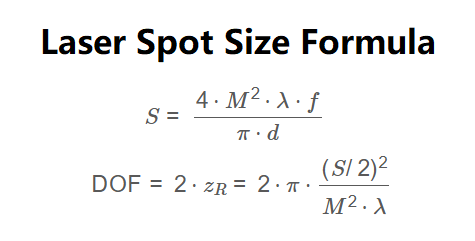1. What is Laser Spot Size Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the spot size (\( S \)) of a laser beam at the focal length of a lens, which is the minimum diameter of the focused beam, and the depth of focus (\( \text{DOF} \)), which measures the distance over which the beam remains focused.
Purpose: It is used in optics to determine the focusing characteristics of a laser beam, essential for applications like laser cutting, microscopy, and optical communication.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Spot Size Formula:
\[
S = \frac{4 \cdot M^2 \cdot \lambda \cdot f}{\pi \cdot d}
\]
Depth of Focus Formula:
\[
\text{DOF} = 2 \cdot z_R = 2 \cdot \pi \cdot \frac{(S/2)^2}{M^2 \cdot \lambda}
\]
Where:
- \( S \): Spot size at the focal length (nm, μm, mm, cm, m, in, ft, yd)
- \( \text{DOF} \): Depth of focus (nm, μm, mm, cm, m, in, ft, yd)
- \( z_R \): Rayleigh range (half of the depth of focus)
- \( M^2 \): Beam quality parameter (dimensionless)
- \( \lambda \): Wavelength of the laser (nm, μm, mm, cm, m, in, ft, yd)
- \( f \): Focal length of the lens (nm, μm, mm, cm, m, in, ft, yd)
- \( d \): Diameter of the beam at the lens surface (nm, μm, mm, cm, m, in, ft, yd)
Unit Conversions:
- Wavelength (\( \lambda \)), Focal Length (\( f \)), Diameter (\( d \)), Spot Size (\( S \)), Depth of Focus (\( \text{DOF} \)): nm (1 nm = \( 10^{-9} \) m), μm (1 μm = \( 10^{-6} \) m), mm (1 mm = 0.001 m), cm (1 cm = 0.01 m), m, in (1 in = 0.0254 m), ft (1 ft = 0.3048 m), yd (1 yd = 0.9144 m)
Steps:
- Enter the beam quality parameter (\( M^2 \)), wavelength (\( \lambda \)), focal length (\( f \)), and beam diameter at the lens surface (\( d \)), and select their units.
- Convert all length inputs to meters.
- Calculate the spot size using \( S = \frac{4 \cdot M^2 \cdot \lambda \cdot f}{\pi \cdot d} \).
- Calculate the depth of focus using \( \text{DOF} = 2 \cdot \pi \cdot \frac{(S)^2}{M^2 \cdot \lambda} \).
- Convert the results to the selected units (nm, μm, mm, cm, m, in, ft, yd).
- Display the results, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Laser Spot Size and Depth of Focus Calculation
Calculating the spot size and depth of focus of a laser beam is crucial for:
- Laser Applications: Achieving precise focusing for cutting, welding, or medical procedures.
- Optical Systems: Designing systems where the spot size and depth of focus affect resolution and performance, such as in microscopy or lithography.
- Education: Understanding the focusing properties of Gaussian beams in optics.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( M^2 = 1 \), \( \lambda = 500 \, \text{nm} \), \( f = 100 \, \text{mm} \), \( d = 2 \, \text{mm} \), spot size in μm, depth of focus in mm:
- Convert: \( \lambda = 500 \times 10^{-9} = 5 \times 10^{-7} \, \text{m} \), \( f = 100 \times 0.001 = 0.1 \, \text{m} \), \( d = 2 \times 0.001 = 0.002 \, \text{m} \)
- Spot Size: \( S = \frac{4 \times 1 \times 5 \times 10^{-7} \times 0.1}{\pi \times 0.002} \approx 3.1831 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{m} \), in μm: \( 3.1831 \times 10^{-5} \times 10^6 \approx 31.8310 \, \text{μm} \)
- Depth of Focus: \( \text{DOF} = 2 \times \pi \times \frac{(3.1831 \times 10^{-5})^2}{1 \times 5 \times 10^{-7}} \approx 0.0127 \, \text{m} \), in mm: \( 0.0127 \times 1000 \approx 12.7324 \, \text{mm} \)
- Example 2: For \( M^2 = 1.5 \), \( \lambda = 1 \, \text{μm} \), \( f = 50 \, \text{cm} \), \( d = 5 \, \text{mm} \), spot size in mm, depth of focus in cm:
- Convert: \( \lambda = 1 \times 10^{-6} = 10^{-6} \, \text{m} \), \( f = 50 \times 0.01 = 0.5 \, \text{m} \), \( d = 5 \times 0.001 = 0.005 \, \text{m} \)
- Spot Size: \( S = \frac{4 \times (1.5)^2 \times 10^{-6} \times 0.5}{\pi \times 0.005} \approx 2.8648 \times 10^{-4} \, \text{m} \), in mm: \( 2.8648 \times 10^{-4} \times 1000 \approx 0.2865 \, \text{mm} \)
- Depth of Focus: \( \text{DOF} = 2 \times \pi \times \frac{(2.8648 \times 10^{-4})^2}{(1.5)^2 \times 10^{-6}} \approx 0.2292 \, \text{m} \), in cm: \( 0.2292 \times 100 \approx 22.9183 \, \text{cm} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the laser spot size?
A: The laser spot size (\( S \)) is the diameter of the laser beam at the focal point of a lens, representing the smallest achievable beam size after focusing.
Q: What is the depth of focus?
A: The depth of focus (\( \text{DOF} \)) is the distance along the beam axis over which the beam remains focused, defined as twice the Rayleigh range (\( z_R \)), the distance from the focal point where the beam area doubles.
Q: How does the beam quality parameter affect the spot size and depth of focus?
A: A higher \( M^2 \) value indicates a less ideal Gaussian beam, increasing the spot size (\( S \)) and depth of focus (\( \text{DOF} \)), as the beam spreads more and focuses less tightly.
Laser Spot Size Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back