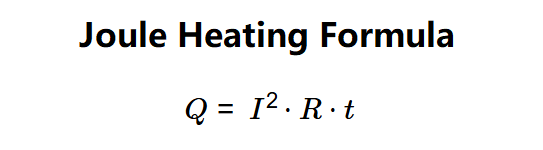1. What is Joule Heating Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the heat (\( Q \)) generated in a current-carrying cable using Joule's first law, which relates the heat produced to the current, resistance, and time.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to estimate the heat generated in wires, resistors, and other components, aiding in the design of safe and efficient electrical systems.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses Joule's first law:
- \( Q = I^2 \cdot R \cdot t \)
Where:
- \( I \): Current (A);
- \( R \): Resistance (Ω);
- \( t \): Current flow time (s);
- \( Q \): Heat generated (J).
Steps:
- Enter the current (\( I \)) and its unit (A, mA, or kA).
- Enter the resistance (\( R \)) and its unit (Ω, mΩ, or kΩ).
- Enter the current flow time (\( t \)) and its unit (s, min, or h).
- Convert all inputs to base units (A for current, Ω for resistance, s for time).
- Calculate the heat \( Q \) using Joule's first law.
- Convert the result to the selected output unit (J, kJ, MJ, Wh, kWh, cal, or kcal).
- Display the result, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Joule Heating Calculation
Calculating Joule heating is crucial for:
- Electrical Safety: Preventing overheating in wires and components, reducing the risk of fire hazards.
- System Design: Selecting appropriate wire gauges and materials to handle the expected heat generation.
- Energy Efficiency: Minimizing energy losses due to heat in electrical circuits.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Simple Circuit): Calculate the heat generated in a resistor with the following properties:
- Current: \( I = 2 \, \text{A} \);
- Resistance: \( R = 5 \, \text{Ω} \);
- Time: \( t = 10 \, \text{s} \);
- Heat: \( Q = 2^2 \times 5 \times 10 = 200 \, \text{J} \);
- Result in kJ: \( Q = 200 / 1000 = 0.2000 \, \text{kJ} \);
- Result in cal: \( Q = 200 / 4.184 \approx 47.8002 \, \text{cal} \).
Example 2 (Different Units): Calculate the heat generated with the following inputs:
- Current: \( I = 500 \, \text{mA} \);
- Resistance: \( R = 2 \, \text{kΩ} \);
- Time: \( t = 1 \, \text{min} \);
- Convert units: \( I = 500 / 1000 = 0.5 \, \text{A} \), \( R = 2 \times 1000 = 2000 \, \text{Ω} \), \( t = 1 \times 60 = 60 \, \text{s} \);
- Heat: \( Q = 0.5^2 \times 2000 \times 60 = 30000 \, \text{J} \);
- Result in kJ: \( Q = 30000 / 1000 = 30.0000 \, \text{kJ} \);
- Result in kWh: \( Q = 30000 / 3600000 \approx 0.0083 \, \text{kWh} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is Joule heating?
A: Joule heating, also known as resistive heating, is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor produces heat due to resistance.
Q: Can this calculator be used for alternating current (AC)?
A: This calculator assumes direct current (DC). For AC, you would need to use the RMS values of current and account for additional factors like impedance, which are not included here.
Q: How can I calculate the resistance for resistors in series or parallel?
A: For resistors in series, add their resistances: \( R = R_1 + R_2 + \cdots \). For resistors in parallel, use the formula: \( \frac{1}{R} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + \cdots \). You can use a separate resistance calculator to find the equivalent resistance.
Joule Heating Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back