 Home
Home
 Back
Back
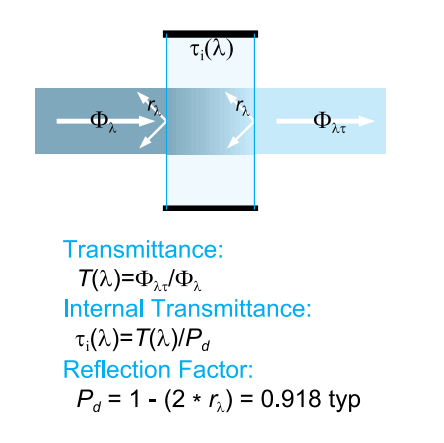
Definition: This calculator determines the transmittance and internal transmittance of a glass filter based on incident flux, transmitted flux, and reflection factor.
Purpose: Useful for analyzing optical filter performance.
The calculator uses the following steps:
Step 1: Transmittance
Step 2: Internal Transmittance
Steps:
Transmittance is crucial for:
Example 1: \( \Phi_\lambda = 100 \), \( \Phi_{\lambda t} = 90 \), \( P_d = 0.918 \):
Q: What if incident flux is zero?
A: The calculation cannot proceed; ensure a non-zero value.
Q: What is the reflection factor?
A: \( P_d \) accounts for losses due to reflection, typically around 0.918.
Q: Where to find flux values?
A: Refer to optical measurement data or manufacturer specs.