 Home
Home
 Back
Back
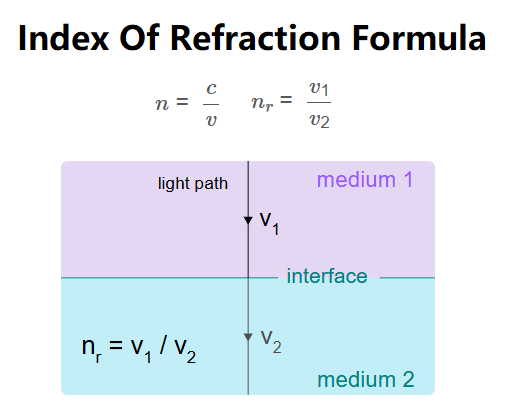
Definition: This calculator computes the refractive index of a medium, either absolute (relative to vacuum) or relative (between two media), based on the speed of light in the media.
Purpose: It is used in optics to determine how much light bends when passing through a medium, essential for designing lenses, prisms, and understanding light behavior.
The calculator uses two formulas depending on the mode:
Absolute Index of Refraction: \[ n = \frac{c}{v} \] Relative Index of Refraction: \[ n_r = \frac{v_1}{v_2} \] Where:
Steps:
Calculating the refractive index is crucial for:
Examples:
Q: What is the refractive index?
A: The refractive index measures how much light slows down in a medium compared to a vacuum (absolute) or another medium (relative). It determines how much light bends when entering the medium.
Q: Why is the refractive index always greater than 1 for absolute calculations?
A: The speed of light in any medium is less than in a vacuum, so \( n = \frac{c}{v} \) is always greater than 1 for absolute refractive indices.
Q: What does a relative refractive index less than 1 mean?
A: A relative refractive index less than 1 means light travels faster in Medium 1 than in Medium 2, causing it to bend away from the normal when transitioning between the media.