Hoop Stress Calculator
Unit Converter ▲
Unit Converter ▼
1. What is the Hoop Stress Calculator?
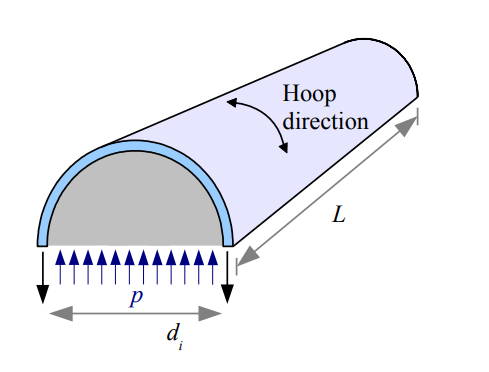
Definition: This calculator determines the hoop stress in a thin-walled pipe carrying pressurized fluid, using the formula \(\sigma_{hoop} = \frac{p d_i}{2 t}\).
Purpose: Helps assess the stress in pipes under internal pressure.
Reference:Applied Strength of Materials for Engineering Technology
http://www.etcs.pfw.edu/~dupenb/ET_200/Applied%20Str%20of%20Mat%20for%20ET%20v14%20July%202018.pdf
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
Formula:
\(\sigma_{hoop} = \frac{p d_i}{2 t}\)
Where:
- \(\sigma_{hoop}\): Hoop stress
- \(p\): Internal pressure
- \(d_i\): Inside diameter
- \(t\): Wall thickness
Steps:
- Step 1: Input Inside Diameter. Enter the internal diameter (e.g., 14 in).
- Step 2: Input Wall Thickness. Enter the wall thickness (e.g., 0.5 in).
- Step 3: Input Internal Pressure. Enter the pressure (e.g., 110 psi).
- Step 4: Calculate. The calculator checks if the pipe is thin-walled and computes the hoop stress.
3. Importance of Hoop Stress Calculation
Calculating hoop stress is crucial for:
- Structural Integrity: Prevents pipe failure under pressure.
- Design Safety: Ensures the pipe can withstand internal pressure.
- Unit Consistency: Supports conversions across units (e.g., in to cm, psi to Pa).
4. Using the Calculator
Example:
\( d_i = 14 \, in \), \( t = 0.5 \, in \), \( p = 110 \, psi \):
- Step 1: Ratio \( \frac{t}{r_i} = \frac{0.5}{7} \approx 0.071 < 0.1 \), so thin-walled.
- Step 2: \(\sigma_{hoop} = \frac{110 \cdot 14}{2 \cdot 0.5} = 1540 \, psi\).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a thin-walled pipe?
A: A pipe is thin-walled if the wall thickness to internal radius ratio is less than 0.1.
Q: Can I use metric units?
A: Yes, the calculator converts cm, m, mm, Pa, and bar to inches and psi internally.
Q: What if the pipe is not thin-walled?
A: The calculation is not valid; use a thick-walled pipe formula instead.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back