1. What is Helical Coil Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the coil height (\( H \)), wire length (\( L_w \)), volume of wire used (\( V \)), inductance (\( L \)), and resonant frequency (\( R_f \)) of a helical coil based on its geometric parameters and capacitance.
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering and physics to design helical coils for applications such as inductors, antennas, and resonant circuits, ensuring the coil meets the desired electrical and physical specifications.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
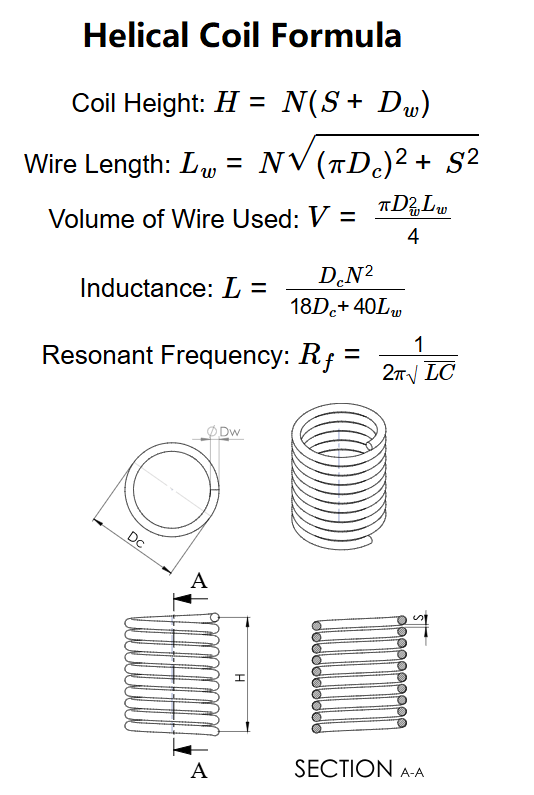
- Coil Height: \( H = N(S + D_w) \)
- Wire Length: \( L_w = N \sqrt{(\pi D_c)^2 + S^2} \)
- Volume of Wire Used: \( V = \frac{\pi D_w^2 L_w}{4} \)
- Inductance: \( L = \frac{D_c N^2}{18 D_c + 40 L_w} \) (where \( D_c \) and \( L_w \) are in mm, \( L \) is in µH)
- Resonant Frequency: \( R_f = \frac{1}{2\pi \sqrt{L C}} \)
Where:
- \( D_c \): Coil diameter (m)
- \( R_c \): Coil radius (m), where \( R_c = D_c / 2 \)
- \( D_w \): Wire diameter (m)
- \( N \): Number of turns
- \( S \): Coil spacing (m)
- \( H \): Coil height (m)
- \( L_w \): Wire length (m)
- \( V \): Volume of wire used (m³)
- \( L \): Inductance (H)
- \( C \): Capacitance (F)
- \( R_f \): Resonant frequency (Hz)
Steps:
- Enter the coil diameter (\( D_c \)), coil radius (\( R_c \)), wire diameter (\( D_w \)), number of turns (\( N \)), coil spacing (\( S \)), and capacitance (\( C \)) with their units.
- Convert all inputs to base units (m, F).
- Calculate the coil height, wire length, volume of wire used, inductance, and resonant frequency using the formulas.
- For inductance, convert \( D_c \) and \( L_w \) to millimeters before applying the formula, as the result will be in microhenries (µH).
- Convert the results to the selected output units.
- Display the results: if a value is less than 0.001 in the selected unit, use scientific notation; otherwise, display with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Helical Coil Calculation
Calculating the parameters of a helical coil is crucial for:
- Inductor Design: Ensuring the coil has the desired inductance for use in circuits like filters or oscillators.
- Resonant Circuits: Determining the resonant frequency for applications like radio frequency (RF) circuits or antennas.
- Material Estimation: Calculating the volume and length of wire needed for manufacturing the coil, aiding in cost and resource planning.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the parameters for a helical coil with \( D_c = 10 \, \text{mm} \), \( R_c = 5 \, \text{mm} \), \( D_w = 1 \, \text{mm} \), \( N = 10 \), \( S = 2 \, \text{mm} \), and \( C = 100 \, \text{pF} \):
- Coil Diameter (\( D_c \)): 10 mm = 0.01 m
- Coil Radius (\( R_c \)): 5 mm = 0.005 m
- Wire Diameter (\( D_w \)): 1 mm = 0.001 m
- Number of Turns (\( N \)): 10
- Coil Spacing (\( S \)): 2 mm = 0.002 m
- Capacitance (\( C \)): 100 pF = \( 100 \times 10^{-12} \) F
- Coil Height (\( H \)): \( 10(0.002 + 0.001) = 0.03 \, \text{m} \), in mm: \( 0.03 \times 1000 = 30 \, \text{mm} \)
- Wire Length (\( L_w \)): \( 10 \sqrt{(\pi \cdot 0.01)^2 + 0.002^2} \approx 10 \sqrt{0.000986 + 0.000004} \approx 10 \cdot 0.0315 \approx 0.315 \, \text{m} \), in mm: \( 0.315 \times 1000 = 315 \, \text{mm} \)
- Volume of Wire Used (\( V \)): \( \frac{\pi (0.001)^2 \cdot 0.315}{4} \approx 2.477 \times 10^{-7} \, \text{m}^3 \), in mm³: \( 2.477 \times 10^{-7} \times 10^9 = 0.2477 \, \text{mm}^3 \)
- Inductance (\( L \)): \( \frac{10 \cdot 10^2}{18 \cdot 10 + 40 \cdot 315} = \frac{1000}{180 + 12600} \approx \frac{1000}{12780} \approx 0.07825 \, \text{µH} \), in µH: \( 0.07825 \, \text{µH} \)
- Resonant Frequency (\( R_f \)): \( \frac{1}{2\pi \sqrt{(0.07825 \times 10^{-6}) \cdot (100 \times 10^{-12})}} \approx \frac{1}{2\pi \sqrt{7.825 \times 10^{-15}}} \approx 568000 \, \text{Hz} \), in kHz: \( 568 \, \text{kHz} \)
- Result: \( H = 30.0000 \, \text{mm} \), \( L_w = 315.0000 \, \text{mm} \), \( V = 0.2477 \, \text{mm}^3 \), \( L = 0.0783 \, \text{µH} \), \( C = 100.0000 \, \text{pF} \), \( R_f = 568.0000 \, \text{kHz} \)
Example 2 (Demonstrating Scientific Notation): Calculate the parameters for a helical coil with \( D_c = 1 \, \text{in} \), \( R_c = 0.5 \, \text{in} \), \( D_w = 0.01 \, \text{in} \), \( N = 5 \), \( S = 0.01 \, \text{in} \), and \( C = 10 \, \text{pF} \):
- Coil Diameter (\( D_c \)): 1 in = 0.0254 m = 25.4 mm
- Coil Radius (\( R_c \)): 0.5 in = 0.0127 m = 12.7 mm
- Wire Diameter (\( D_w \)): 0.01 in = 0.000254 m = 0.254 mm
- Number of Turns (\( N \)): 5
- Coil Spacing (\( S \)): 0.01 in = 0.000254 m = 0.254 mm
- Capacitance (\( C \)): 10 pF = \( 10 \times 10^{-12} \) F
- Coil Height (\( H \)): \( 5(0.000254 + 0.000254) = 0.00254 \, \text{m} \), in in: \( 0.00254 / 0.0254 = 0.1 \, \text{in} \)
- Wire Length (\( L_w \)): \( 5 \sqrt{(\pi \cdot 0.0254)^2 + 0.000254^2} \approx 5 \sqrt{0.006366 + 0.0000000645} \approx 5 \cdot 0.0798 \approx 0.399 \, \text{m} \), in in: \( 0.399 / 0.0254 \approx 15.71 \, \text{in} \), in mm: \( 0.399 \times 1000 = 399 \, \text{mm} \)
- Volume of Wire Used (\( V \)): \( \frac{\pi (0.000254)^2 \cdot 0.399}{4} \approx 2.021 \times 10^{-8} \, \text{m}^3 \), in cuin: \( 2.021 \times 10^{-8} \times 61023.7441 \approx 1.233 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{cuin} \)
- Inductance (\( L \)): \( \frac{25.4 \cdot 5^2}{18 \cdot 25.4 + 40 \cdot 399} = \frac{635}{457.2 + 15960} \approx \frac{635}{16417.2} \approx 0.03868 \, \text{µH} \), in µH: \( 0.03868 \, \text{µH} \)
- Resonant Frequency (\( R_f \)): \( \frac{1}{2\pi \sqrt{(0.03868 \times 10^{-6}) \cdot (10 \times 10^{-12})}} \approx 80800 \, \text{Hz} \), in kHz: \( 80.8 \, \text{kHz} \)
- Result: \( H = 0.1000 \, \text{in} \), \( L_w = 15.7100 \, \text{in} \), \( V = 1.2330 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{cuin} \), \( L = 0.0387 \, \text{µH} \), \( C = 10.0000 \, \text{pF} \), \( R_f = 80.8000 \, \text{kHz} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a helical coil?
A: A helical coil is a type of coil where the wire is wound in a spiral (helix) shape around a central axis. It is commonly used in inductors, antennas, and resonant circuits due to its ability to store magnetic energy.
Q: Why is the resonant frequency important?
A: The resonant frequency (\( R_f \)) is the frequency at which the coil’s inductance and capacitance resonate, resulting in high impedance. This is critical for applications like RF circuits, where the coil must operate at a specific frequency.
Q: How does the number of turns affect the inductance?
A: The inductance (\( L \)) is proportional to the square of the number of turns (\( N^2 \)). Increasing the number of turns significantly increases the inductance, which can enhance the coil’s ability to store magnetic energy.
Helical Coil Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back