 Home
Home
 Back
Back
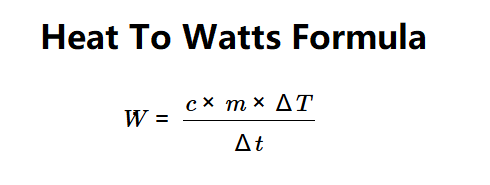
Definition: This calculator computes the power (\( \dot{W} \)) required to heat a given mass of a substance by a specified temperature change over a given time, based on the material's specific heat capacity.
Purpose: It is used in thermodynamics and engineering to determine the power needed for heating processes, such as in material processing, HVAC systems, or laboratory experiments.
The calculator uses the following equation:
Formula:
Unit Conversions:
Steps:
Calculating the power required to heat a substance is crucial for:
Examples:
Q: What is specific heat capacity?
A: Specific heat capacity (\( c \)) is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 Kelvin (or 1°C), typically measured in J/g·K.
Q: Why does the calculator require the time to heat?
A: The time (\( \Delta t \)) is needed to calculate the rate of energy transfer (power), as power is defined as energy per unit time (\( \dot{W} = Q / \Delta t \)).
Q: What are some real-world applications of this calculator?
A: It’s used for determining the power requirements of heaters (e.g., for water heating), designing industrial furnaces, and calculating energy needs for scientific experiments involving temperature changes.