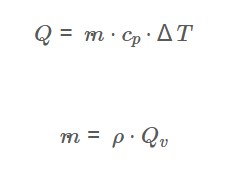1. What is a Heat Exchanger Power Dissipation Calculator?
Definition: This calculator estimates the power dissipated (heat transfer rate) in a heat exchanger using the mass flow rate of a liquid fluid, its specific heat capacity, and the temperature difference across the exchanger.
Purpose: It helps engineers and designers estimate the heat transfer rate in a heat exchanger for system sizing, performance evaluation, and optimization.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the mass flow rate method to compute the heat transfer rate:
Formulas:
\[
Q = \dot{m} \cdot c_p \cdot \Delta T
\]
If mass flow rate is unknown:
\[
\dot{m} = \rho \cdot Q_v
\]
Where:
- \( Q \): Power dissipated (W)
- \( \dot{m} \): Mass flow rate (kg/s)
- \( c_p \): Specific heat capacity (J/kg·K)
- \( \Delta T \): \( T_{\text{hot,in}} - T_{\text{hot,out}} \) (K or °C)
- \( \rho \): Density (kg/m³)
- \( Q_v \): Volumetric flow rate (m³/s)
Liquid Substance Properties (at 25 °C):
- Water: Specific Heat = 4184 J/kg·K (4.184 J/g·°C), Density = 997 kg/m³
- Ethanol: Specific Heat = 2450 J/kg·K (2.450 J/g·°C), Density = 789 kg/m³
- Mercury: Specific Heat = 140 J/kg·K (0.140 J/g·°C), Density = 13546 kg/m³
Unit Conversions:
- Volumetric Flow Rate (\( Q_v \)):
- 1 cm³/s = 0.000001 m³/s
- 1 m³/h = 0.000277778 m³/s
- 1 m³/min = 0.0166667 m³/s
- 1 fpm (ft³/min) = 0.000471947 m³/s
- 1 ft³/s = 0.0283168 m³/s
- 1 in³/s = 0.0000163871 m³/s
- Temperature:
- \( T_{\text{°C}} = (T_{\text{°F}} - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} \)
- Power:
- 1 W = 0.001 kW
- 1 W = 3.41214 BTU/h
- 1 W = 0.00134102 hp
Steps:
- Select a liquid substance from the dropdown to auto-fill the specific heat capacity (\( c_p \)) and density (\( \rho \)), or choose "Custom" to enter your own values.
- Choose whether you know the mass flow rate (\( \dot{m} \)).
- If "Yes," enter the mass flow rate directly.
- If "No," enter the density (\( \rho \)) and volumetric flow rate (\( Q_v \)), selecting the unit, and compute \( \dot{m} = \rho \cdot Q_v \).
- Enter the hot fluid inlet and outlet temperatures, selecting the unit (°C or °F).
- Compute the temperature difference \( \Delta T = T_{\text{hot,in}} - T_{\text{hot,out}} \) (in °C).
- Calculate the power dissipated using \( Q = \dot{m} \cdot c_p \cdot \Delta T \).
- Display the result in Watts (W), kilowatts (kW), BTU/h, and horsepower (hp), rounded to 2 decimal places.
3. Importance of Heat Exchanger Power Calculations
Accurate heat transfer calculations are crucial for:
- Efficiency: Ensuring the heat exchanger meets thermal performance requirements.
- Design: Sizing the exchanger appropriately for the application.
- Cost: Avoiding over- or under-sizing, which impacts material and operational costs.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (Known Mass Flow Rate): Substance = Water (\( c_p = 4184 \, \text{J/kg·K} \)), Mass Flow Rate Known, \( \dot{m} = 2 \, \text{kg/s} \), \( T_{\text{hot,in}} = 176 \, \text{°F} \), \( T_{\text{hot,out}} = 140 \, \text{°F} \):
- \( T_{\text{hot,in}} = (176 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} = 80 \, \text{°C} \)
- \( T_{\text{hot,out}} = (140 - 32) \times \frac{5}{9} = 60 \, \text{°C} \)
- \( \Delta T = 80 - 60 = 20 \, \text{°C} \)
- \( Q = 2 \times 4184 \times 20 = 167360 \, \text{W} = 167.36 \, \text{kW} = 570888.54 \, \text{BTU/h} = 224.39 \, \text{hp} \)
- Example 2 (Calculate Mass Flow Rate): Substance = Ethanol (\( c_p = 2450 \, \text{J/kg·K} \), \( \rho = 789 \, \text{kg/m³} \)), Mass Flow Rate Unknown, \( Q_v = 7200 \, \text{cm³/s} \), \( T_{\text{hot,in}} = 70 \, \text{°C} \), \( T_{\text{hot,out}} = 50 \, \text{°C} \):
- \( Q_v = 7200 \div 1000000 = 0.0072 \, \text{m³/s} \)
- \( \dot{m} = 789 \times 0.0072 = 5.6808 \, \text{kg/s} \)
- \( \Delta T = 70 - 50 = 20 \, \text{°C} \)
- \( Q = 5.6808 \times 2450 \times 20 = 278359.20 \, \text{W} = 278.36 \, \text{kW} = 949524.93 \, \text{BTU/h} = 373.23 \, \text{hp} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Why are only liquid substances listed?
A: This calculator focuses on liquid fluids commonly used in heat exchangers. Use the "Custom" option for other fluids or states.
Q: What if I don’t know the specific heat capacity or density?
A: Select a liquid substance from the dropdown to use predefined values, or choose "Custom" and enter the specific heat capacity and density manually after consulting fluid property tables.
Q: What if I don’t know the mass flow rate?
A: Select "No" for the mass flow rate option, and enter the density and volumetric flow rate (in your preferred unit) to calculate \( \dot{m} = \rho \cdot Q_v \).
Q: Is this calculator sufficient for designing a heat exchanger?
A: No, this is an estimate. Professional design requires detailed analysis, including flow arrangement, fouling factors, and fluid properties.
Heat Exchanger Power Dissipation Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back