1. What is Generator Power Supply Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the apparent power (kVA), active power (kW), and motor output horsepower (HP) for a generator based on its power supply type (single-phase, three-phase, or direct current).
Purpose: It is used in electrical engineering to determine the power characteristics of a generator, which is essential for selecting the appropriate generator for a given load, such as in industrial, commercial, or residential applications.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses different formulas based on the power supply type:
Single-Phase Power Supply:
- Apparent Power: \( \text{kVA} = \frac{V \cdot I}{1000} \)
- Power: \( \text{kW} = \frac{V \cdot I \cdot \text{PF}}{1000} \)
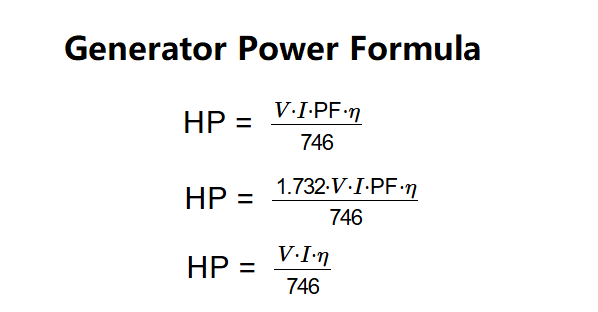
- Motor Output Horsepower: \( \text{HP} = \frac{V \cdot I \cdot \text{PF} \cdot \eta}{746} \)
Three-Phase Power Supply:
- Apparent Power: \( \text{kVA} = \frac{1.732 \cdot V \cdot I}{1000} \)
- Power: \( \text{kW} = \frac{1.732 \cdot V \cdot I \cdot \text{PF}}{1000} \)
- Motor Output Horsepower: \( \text{HP} = \frac{1.732 \cdot V \cdot I \cdot \text{PF} \cdot \eta}{746} \)
Direct Current (DC) Power Supply:
- Apparent Power: Not applicable
- Power: \( \text{kW} = \frac{V \cdot I}{1000} \)
- Motor Output Horsepower: \( \text{HP} = \frac{V \cdot I \cdot \eta}{746} \)
Where:
- \( V \): Voltage (V)
- \( I \): Current (A)
- \( \text{PF} \): Power factor (unitless, between 0 and 1)
- \( \eta \): Efficiency (unitless, between 0 and 1)
- 1.732: The square root of 3 (\( \sqrt{3} \)), used for three-phase calculations
- 1000: Conversion factor from VA/W to kVA/kW
- 746: Conversion factor from watts to horsepower (1 HP = 746 W)
Steps:
- Select the power supply type (single-phase, three-phase, or direct current).
- Enter the voltage (\( V \)), current (\( I \)), power factor (\( \text{PF} \)) (if applicable), and efficiency (\( \eta \)) with their units.
- Convert all inputs to base units (V, A).
- Calculate the apparent power (kVA), power (kW), and motor output horsepower (HP) using the appropriate formulas.
- Display the results: if a value is less than 0.001, use scientific notation; otherwise, display with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Generator Power Calculation
Calculating the power parameters of a generator is crucial for:
- Generator Sizing: Ensuring the generator can handle the required load without overloading.
- Efficiency Optimization: Understanding the impact of power factor and efficiency on the generator’s performance.
- Motor Applications: Determining the mechanical power output (HP) for motors connected to the generator, which is essential for industrial applications.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Single-Phase): Calculate the power parameters for a single-phase generator with \( V = 230 \, \text{V} \), \( I = 10 \, \text{A} \), \( \text{PF} = 0.8 \), and \( \eta = 0.9 \):
- Voltage (\( V \)): 230 V
- Current (\( I \)): 10 A
- Power Factor (\( \text{PF} \)): 0.8
- Efficiency (\( \eta \)): 0.9
- Apparent Power (\( \text{kVA} \)): \( \frac{230 \cdot 10}{1000} = 2.3 \, \text{kVA} \)
- Power (\( \text{kW} \)): \( \frac{230 \cdot 10 \cdot 0.8}{1000} = 1.84 \, \text{kW} \)
- Motor Output Horsepower (\( \text{HP} \)): \( \frac{230 \cdot 10 \cdot 0.8 \cdot 0.9}{746} \approx 2.2212 \, \text{HP} \)
- Result: \( \text{kVA} = 2.3000 \), \( \text{kW} = 1.8400 \), \( \text{HP} = 2.2212 \)
Example 2 (Three-Phase, Demonstrating Scientific Notation): Calculate the power parameters for a three-phase generator with \( V = 400 \, \text{V} \), \( I = 0.001 \, \text{A} \), \( \text{PF} = 0.85 \), and \( \eta = 0.95 \):
- Voltage (\( V \)): 400 V
- Current (\( I \)): 0.001 A
- Power Factor (\( \text{PF} \)): 0.85
- Efficiency (\( \eta \)): 0.95
- Apparent Power (\( \text{kVA} \)): \( \frac{1.732 \cdot 400 \cdot 0.001}{1000} \approx 0.0006928 \, \text{kVA} \)
- Power (\( \text{kW} \)): \( \frac{1.732 \cdot 400 \cdot 0.001 \cdot 0.85}{1000} \approx 0.0005889 \, \text{kW} \)
- Motor Output Horsepower (\( \text{HP} \)): \( \frac{1.732 \cdot 400 \cdot 0.001 \cdot 0.85 \cdot 0.95}{746} \approx 0.0007495 \, \text{HP} \)
- Result: \( \text{kVA} = 6.9280 \times 10^{-4} \), \( \text{kW} = 5.8888 \times 10^{-4} \), \( \text{HP} = 7.4946 \times 10^{-4} \)
Example 3 (Direct Current): Calculate the power parameters for a DC generator with \( V = 12 \, \text{V} \), \( I = 5 \, \text{A} \), and \( \eta = 0.9 \):
- Voltage (\( V \)): 12 V
- Current (\( I \)): 5 A
- Efficiency (\( \eta \)): 0.9
- Apparent Power (\( \text{kVA} \)): Not applicable
- Power (\( \text{kW} \)): \( \frac{12 \cdot 5}{1000} = 0.06 \, \text{kW} \)
- Motor Output Horsepower (\( \text{HP} \)): \( \frac{12 \cdot 5 \cdot 0.9}{746} \approx 0.0724 \, \text{HP} \)
- Result: \( \text{kVA} = \text{N/A} \), \( \text{kW} = 0.0600 \), \( \text{HP} = 0.0724 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between apparent power (kVA) and active power (kW)?
A: Apparent power (kVA) is the total power supplied, including both active (real) and reactive components. Active power (kW) is the real power that does useful work, calculated by multiplying the apparent power by the power factor.
Q: Why is apparent power not applicable for DC generators?
A: In DC systems, there is no reactive power component (since there is no phase difference), so the concept of apparent power (kVA) does not apply. The power is simply the product of voltage and current (kW).
Q: What is the significance of the power factor?
A: The power factor (\( \text{PF} \)) indicates the efficiency of power usage. A lower power factor means more reactive power is present, reducing the effective power delivered to the load and increasing losses.
Generator Power Supply Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back