1. What is Gas Velocities Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the root mean square velocity (\( v_{rms} \)), average velocity (\( v_{ave} \)), and median velocity (\( v_m \)) of gas molecules based on their temperature and molar mass, derived from the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Purpose: It is used in physics and chemistry to understand the kinetic behavior of gas molecules, which is essential for applications like gas dynamics, thermodynamics, and chemical kinetics.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas derived from the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution:
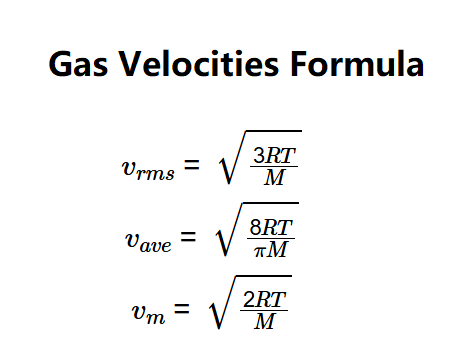
- \( v_{rms} = \sqrt{\frac{3RT}{M}} \)
- \( v_{ave} = \sqrt{\frac{8RT}{\pi M}} \)
- \( v_m = \sqrt{\frac{2RT}{M}} \)
Where:
- \( R = 8.314 \, \text{J/(K·mol)} \): Gas constant;
- \( T \): Temperature of the gas (K);
- \( M \): Molar mass of the gas (kg/mol);
- \( v_{rms} \): Root mean square velocity (m/s);
- \( v_{ave} \): Average velocity (m/s);
- \( v_m \): Median (most probable) velocity (m/s).
Steps:
- Enter the temperature (\( T \)) and its unit (K, °C, or °F).
- Choose to select a gas from the list or input a custom molar mass (\( M \)).
- If selecting a gas, choose from the predefined list with associated molar masses.
- If entering a custom value, provide the molar mass and its unit (kg/mol or g/mol).
- Convert temperature to Kelvin and molar mass to kg/mol.
- Calculate the three velocities using the formulas.
- Convert the velocities to the selected output unit (m/s, km/h, or mph).
- Display the results, formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Gas Velocities Calculation
Calculating the velocities of gas molecules is crucial for:
- Gas Dynamics: Understanding the motion of gas molecules, which affects diffusion, viscosity, and thermal conductivity.
- Thermodynamics: Relating the kinetic energy of gas molecules to temperature and pressure in the ideal gas law.
- Chemical Reactions: Estimating collision rates between gas molecules, which influence reaction rates.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1 (Nitrogen Gas at Room Temperature): Calculate the velocities of nitrogen molecules:
- Temperature: \( T = 300 \, \text{K} \);
- Gas: Nitrogen (\( M = 0.02801 \, \text{kg/mol} \));
- Root Mean Square Velocity: \( v_{rms} = \sqrt{\frac{3 \times 8.314 \times 300}{0.02801}} \approx \sqrt{266862.5484} \approx 516.5887 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Average Velocity: \( v_{ave} = \sqrt{\frac{8 \times 8.314 \times 300}{\pi \times 0.02801}} \approx \sqrt{226929.408} \approx 476.3732 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Median Velocity: \( v_m = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 8.314 \times 300}{0.02801}} \approx \sqrt{177908.3656} \approx 421.7942 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Result: \( v_{rms} = 516.5887 \, \text{m/s} \), \( v_{ave} = 476.3732 \, \text{m/s} \), \( v_m = 421.7942 \, \text{m/s} \).
Example 2 (Custom Molar Mass, Different Units): Calculate the velocities with a custom molar mass:
- Temperature: \( T = 77 \, \text{°F} \);
- Molar Mass: \( M = 28 \, \text{g/mol} = 0.028 \, \text{kg/mol} \);
- Convert temperature: \( T = (77 - 32) \times 5/9 + 273.15 = 298.15 \, \text{K} \);
- Root Mean Square Velocity: \( v_{rms} \approx \sqrt{265336.3982} \approx 515.1062 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Average Velocity: \( v_{ave} \approx \sqrt{225452.6874} \approx 474.8204 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Median Velocity: \( v_m \approx \sqrt{176890.9321} \approx 420.5842 \, \text{m/s} \);
- Result in km/h: \( v_{rms} = 1854.3823 \, \text{km/h} \), \( v_{ave} = 1709.3534 \, \text{km/h} \), \( v_m = 1514.1031 \, \text{km/h} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What do the different velocities represent?
A: The root mean square velocity (\( v_{rms} \)) is the square root of the average squared velocity, the average velocity (\( v_{ave} \)) is the mean speed, and the median velocity (\( v_m \)) is the most probable speed in the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution.
Q: Why is the gas constant used?
A: The gas constant (\( R \)) relates the temperature and molar mass to the kinetic energy of gas molecules, a fundamental constant in the ideal gas law.
Q: How does temperature affect the velocities?
A: All velocities are proportional to the square root of the temperature; as temperature increases, the molecules move faster due to increased kinetic energy.
Gas Velocities Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back