1. What is a Free Fall with Air Resistance Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the time of fall, maximum velocity, and terminal velocity of an object falling through the atmosphere under gravity, accounting for air resistance.
Purpose: It is used in physics, engineering, and activities like skydiving to predict the motion of falling objects, aiding in safety, design, and educational applications.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas, computed in SI units:
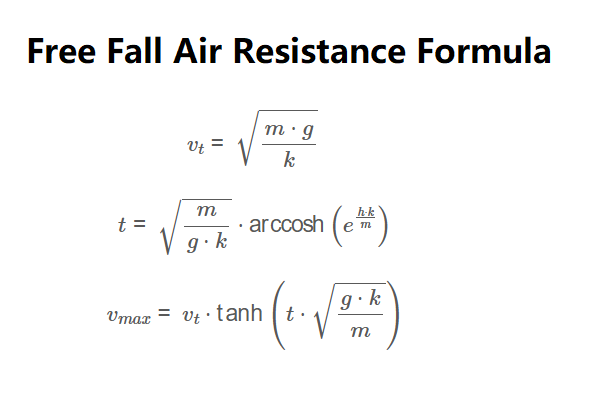
Terminal Velocity:
\[
v_t = \sqrt{\frac{m \cdot g}{k}}
\]
Time of Fall:
\[
t = \sqrt{\frac{m}{g \cdot k}} \cdot \text{arccosh}\left(e^{\frac{h \cdot k}{m}}\right)
\]
Maximum Velocity:
\[
v_{max} = v_t \cdot \tanh\left(t \cdot \sqrt{\frac{g \cdot k}{m}}\right)
\]
Where:
- \(m\): Mass (kg)
- \(h\): Altitude (m)
- \(g\): Gravitational acceleration (m/s²)
- \(k\): Air resistance coefficient (kg/m)
- \(t\): Time of fall (s)
- \(v_{max}\): Maximum velocity (m/s)
- \(v_t\): Terminal velocity (m/s)
Unit Conversions:
- Mass: kg, lb (1 lb = 0.453592 kg)
- Altitude: m, ft (1 ft = 0.3048 m), km (1 km = 1000 m), mi (1 mi = 1609.344 m)
- Gravitational Acceleration: m/s², ft/s² (1 ft/s² = 0.3048 m/s²)
- Air Resistance Coefficient: kg/m, lb/ft (1 lb/ft = 1.488164 kg/m)
- Time: s, min (1 min = 60 s)
- Velocities: m/s, km/h (1 km/h = 0.277778 m/s), ft/s (1 ft/s = 0.3048 m/s), mph (1 mph = 0.44704 m/s)
Steps:
- Enter the mass (m), selecting the unit (kg, lb)
- Enter the altitude (h), selecting the unit (m, ft, km, mi)
- Enter the gravitational acceleration (g), selecting the unit (m/s², ft/s²)
- Enter the air resistance coefficient (k), selecting the unit (kg/m, lb/ft)
- Convert all inputs to SI units (kg, m, m/s², kg/m)
- Calculate terminal velocity, time of fall, and maximum velocity
- Select desired units for results and view converted values
3. Importance of Free Fall with Air Resistance Calculation
Calculating these parameters is crucial for:
- Safety: Ensuring safe descent times and velocities for skydivers or equipment drops.
- Engineering: Designing aerodynamic systems like parachutes to achieve desired terminal velocities.
- Education: Understanding the effects of air resistance on free fall motion.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (Skydiver): For a skydiver with mass \(m = 176.37 \, \text{lb}\), altitude \(h = 1.864 \, \text{mi}\), gravitational acceleration \(g = 32.174 \, \text{ft/s}^2\), air resistance coefficient \(k = 0.167 \, \text{lb/ft}\):
- Mass: \( 176.37 \cdot 0.453592 = 80 \, \text{kg} \)
- Altitude: \( 1.864 \cdot 1609.344 = 3000 \, \text{m} \)
- Gravitational acceleration: \( 32.174 \cdot 0.3048 = 9.80665 \, \text{m/s}^2 \)
- Air resistance coefficient: \( 0.167 \cdot 1.488164 = 0.25 \, \text{kg/m} \)
- Terminal velocity: \( v_t = \sqrt{\frac{80 \cdot 9.80665}{0.25}} \approx 56.019 \, \text{m/s} = 56.019 \cdot 2.23694 \approx 125.329 \, \text{mph} \)
- Time of fall: \( t = \sqrt{\frac{80}{9.80665 \cdot 0.25}} \cdot \text{arccosh}(e^{\frac{3000 \cdot 0.25}{80}}) \approx 48.112 \, \text{s} = 48.112 / 60 \approx 0.802 \, \text{min} \)
- Maximum velocity: \( v_{max} = 56.019 \cdot \tanh(48.112 \cdot \sqrt{\frac{9.80665 \cdot 0.25}{80}}) \approx 56.019 \, \text{m/s} \approx 125.329 \, \text{mph} \)
- Example 2 (Small Object): For an object with mass \(m = 0.5 \, \text{kg}\), altitude \(h = 164.042 \, \text{ft}\), gravitational acceleration \(g = 9.80665 \, \text{m/s}^2\), air resistance coefficient \(k = 0.134 \, \text{lb/ft}\):
- Altitude: \( 164.042 \cdot 0.3048 = 50 \, \text{m} \)
- Air resistance coefficient: \( 0.134 \cdot 1.488164 = 0.2 \, \text{kg/m} \)
- Terminal velocity: \( v_t = \sqrt{\frac{0.5 \cdot 9.80665}{0.2}} \approx 4.951 \, \text{m/s} = 4.951 \cdot 3.6 \approx 17.824 \, \text{km/h} \)
- Time of fall: \( t = \sqrt{\frac{0.5}{9.80665 \cdot 0.2}} \cdot \text{arccosh}(e^{\frac{50 \cdot 0.2}{0.5}}) \approx 10.054 \, \text{s} \)
- Maximum velocity: \( v_{max} = 4.951 \cdot \tanh(10.054 \cdot \sqrt{\frac{9.80665 \cdot 0.2}{0.5}}) \approx 4.951 \, \text{m/s} \approx 17.824 \, \text{km/h} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is terminal velocity?
A: Terminal velocity (\(v_t\)) is the constant speed an object reaches when air resistance equals gravitational force, calculated as \(v_t = \sqrt{\frac{m \cdot g}{k}}\).
Q: How does unit conversion work in the calculator?
A: Inputs are converted to SI units (kg, m, m/s², kg/m) for calculations, and outputs are converted to the selected units (s, min, m/s, km/h, ft/s, mph) for display.
Q: What is the air resistance coefficient?
A: The air resistance coefficient (\(k\)) quantifies drag, combining air density, drag coefficient, and cross-sectional area, expressed in kg/m or lb/ft.
Free Fall with Air Resistance Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back