1. What is Forward Converter Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the output voltage (\( V_{\text{out}} \)) and ripple current (\( I_{\text{ripple}} \)) for a forward converter, a type of DC-DC converter.
Purpose: It is used in power electronics to design forward converters, which are commonly used in applications requiring isolated DC-DC conversion, such as in power supplies for telecommunications, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
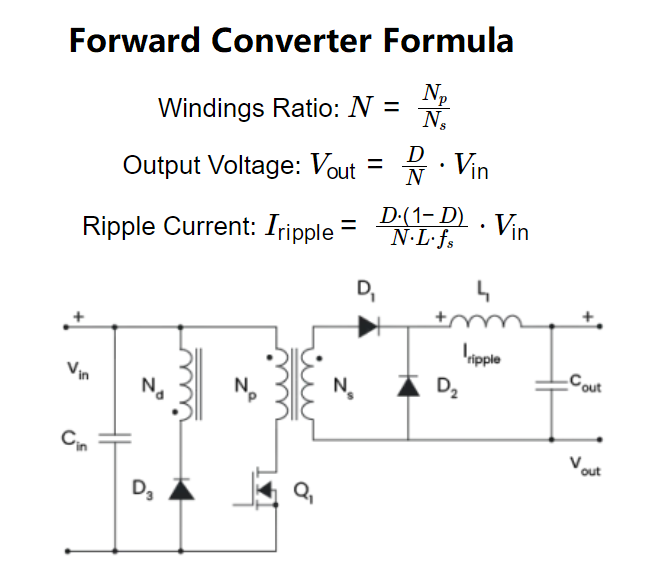
- Windings Ratio: \( N = \frac{N_p}{N_s} \)
- Output Voltage: \( V_{\text{out}} = \frac{D}{N} \cdot V_{\text{in}} \)
- Ripple Current: \( I_{\text{ripple}} = \frac{D \cdot (1 - D)}{N \cdot L \cdot f_s} \cdot V_{\text{in}} \)
Where:
- \( V_{\text{in}} \): Input voltage (V)
- \( V_{\text{out}} \): Output voltage (V)
- \( D \): Duty cycle (unitless, between 0 and 1)
- \( N_p \): Number of turns in the primary winding
- \( N_s \): Number of turns in the secondary winding
- \( N \): Windings ratio (\( N_p / N_s \), unitless)
- \( f_s \): Switching frequency (Hz)
- \( L \): Inductance of the \( L_1 \) inductor (H)
- \( I_{\text{ripple}} \): Ripple current (A)
Steps:
- Enter the input voltage (\( V_{\text{in}} \)), duty cycle (\( D \)), primary winding (\( N_p \)), secondary winding (\( N_s \)), switching frequency (\( f_s \)), and inductance (\( L \)) with their units.
- Convert all inputs to base units (V, Hz, H).
- Calculate the windings ratio, output voltage, and ripple current using the formulas.
- Convert the results to the selected output units.
- Display the results: if a value is less than 0.001 in the selected unit, use scientific notation; otherwise, display with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Forward Converter Calculation
Calculating the parameters of a forward converter is crucial for:
- Power Supply Design: Ensuring the forward converter delivers the required output voltage for applications like telecommunications or industrial equipment.
- Efficiency: Optimizing the duty cycle and inductance to minimize ripple current and improve efficiency.
- Component Selection: Determining the appropriate transformer windings and inductor to handle the voltage and current requirements.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate the parameters for a forward converter with \( V_{\text{in}} = 48 \, \text{V} \), \( D = 0.4 \), \( N_p = 20 \), \( N_s = 10 \), \( f_s = 100 \, \text{kHz} \), and \( L = 200 \, \mu\text{H} \):
- Input Voltage (\( V_{\text{in}} \)): 48 V
- Duty Cycle (\( D \)): 0.4
- Primary Winding (\( N_p \)): 20
- Secondary Winding (\( N_s \)): 10
- Switching Frequency (\( f_s \)): 100 kHz = \( 100 \times 10^3 \) Hz
- Inductance (\( L \)): 200 µH = \( 200 \times 10^{-6} \) H
- Windings Ratio (\( N \)): \( \frac{20}{10} = 2 \)
- Output Voltage (\( V_{\text{out}} \)): \( \frac{0.4}{2} \cdot 48 = 0.2 \cdot 48 = 9.6 \, \text{V} \)
- Ripple Current (\( I_{\text{ripple}} \)): \( \frac{0.4 \cdot (1 - 0.4)}{2 \cdot 200 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 100 \times 10^3} \cdot 48 = \frac{0.4 \cdot 0.6}{2 \cdot 200 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 100 \times 10^3} \cdot 48 = \frac{0.24}{0.04} \cdot 48 = 6 \cdot 48 = 288 \, \text{A} \)
- Result: \( V_{\text{out}} = 9.6000 \, \text{V} \), \( I_{\text{ripple}} = 288.0000 \, \text{A} \)
Example 2 (Demonstrating Scientific Notation): Calculate the parameters for a forward converter with \( V_{\text{in}} = 12 \, \text{V} \), \( D = 0.3 \), \( N_p = 100 \), \( N_s = 50 \), \( f_s = 1 \, \text{MHz} \), and \( L = 1 \, \text{mH} \):
- Input Voltage (\( V_{\text{in}} \)): 12 V
- Duty Cycle (\( D \)): 0.3
- Primary Winding (\( N_p \)): 100
- Secondary Winding (\( N_s \)): 50
- Switching Frequency (\( f_s \)): 1 MHz = \( 1 \times 10^6 \) Hz
- Inductance (\( L \)): 1 mH = \( 1 \times 10^{-3} \) H
- Windings Ratio (\( N \)): \( \frac{100}{50} = 2 \)
- Output Voltage (\( V_{\text{out}} \)): \( \frac{0.3}{2} \cdot 12 = 0.15 \cdot 12 = 1.8 \, \text{V} \)
- Ripple Current (\( I_{\text{ripple}} \)): \( \frac{0.3 \cdot (1 - 0.3)}{2 \cdot 1 \times 10^{-3} \cdot 1 \times 10^6} \cdot 12 = \frac{0.3 \cdot 0.7}{2 \cdot 10^{-3} \cdot 10^6} \cdot 12 = \frac{0.21}{2 \times 10^3} \cdot 12 = 0.000105 \cdot 12 = 0.00126 \, \text{A} \), in mA: \( 0.00126 \times 10^3 = 1.26 \, \text{mA} \), in µA: \( 0.00126 \times 10^6 = 1260 \, \text{µA} \)
- Result: \( V_{\text{out}} = 1.8000 \, \text{V} \), \( I_{\text{ripple}} = 1.2600 \, \text{mA} \) (or \( 1260.0000 \, \text{µA} \))
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a forward converter?
A: A forward converter is a type of DC-DC converter that uses a transformer to step down voltage and provide galvanic isolation. It is commonly used in applications requiring efficient power conversion with isolation, such as in power supplies for industrial equipment.
Q: Why must the duty cycle be between 0 and 1?
A: The duty cycle represents the fraction of time the switch is on during one switching cycle. A value greater than 1 would imply the switch is on for longer than the cycle period, which is physically impossible.
Q: What is the significance of the ripple current?
A: The ripple current represents the AC component of the current through the inductor. Minimizing ripple current is important for reducing output voltage ripple and ensuring stable operation of the converter.
Forward Converter Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back