1. What is an Effective Antenna Aperture Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the effective aperture \( A_e \) (or effective area) of an antenna based on the frequency \( f \) and antenna gain \( G \). The effective aperture quantifies the antenna's ability to capture radio waves.
Purpose: It helps RF engineers and antenna designers evaluate an antenna's performance in receiving signals, which is critical for applications like wireless communication, radar, and satellite systems.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula to compute the effective aperture:
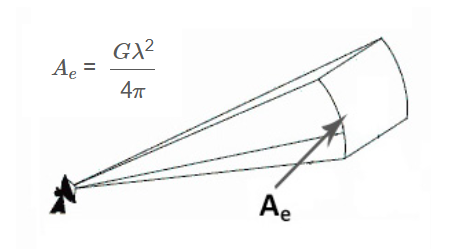
Effective Aperture \( A_e \):
\[
A_e = \frac{G \lambda^2}{4 \pi}
\]
Where:
\[
\lambda = \frac{c}{f}
\]
If gain is in dB:
\[
G = 10^{\frac{G_{dB}}{10}}
\]
Where:
- \( A_e \): Effective aperture in square meters (m²)
- \( G \): Antenna gain (linear)
- \( \lambda \): Wavelength in meters
- \( c \): Speed of light (\( 3 \times 10^8 \) m/s)
- \( f \): Frequency in Hz
Unit Conversions:
- Input Frequency (\( f \)):
- 1 kHz = 1000 Hz
- 1 MHz = \( 10^6 \) Hz
- 1 GHz = \( 10^9 \) Hz
- Input Gain (\( G \)):
- \( G_{\text{linear}} = 10^{\frac{G_{dB}}{10}} \)
- Output Aperture (\( A_e \)):
- 1 m² = \( 10^4 \) cm²
- 1 m² = \( 10^6 \) mm²
Steps:
- Enter the frequency \( f \) and select the unit (Hz, kHz, MHz, or GHz).
- Enter the antenna gain \( G \) and select the unit (dB or linear).
- Click "Calculate" to compute \( A_e \).
- The result is initially displayed in square meters (m²).
- Select a different unit for \( A_e \) (m², cm², or mm²) from the dropdown after the result to convert the displayed value.
3. Importance of Effective Antenna Aperture Calculation
Calculating the effective aperture of an antenna is essential for:
- Antenna Performance: Determines how effectively an antenna captures incoming signals, impacting received power.
- System Design: Helps in designing wireless communication systems, radar, and satellite links by optimizing antenna size and gain.
- Link Budget Analysis: Provides critical input for calculating signal strength in RF systems.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: \( f = 1 \) GHz, \( G = 10 \) dB, Result in m²
- Convert: \( f = 1 \times 10^9 = 10^9 \, \text{Hz} \), \( G = 10^{\frac{10}{10}} = 10 \)
- Wavelength: \( \lambda = \frac{3 \times 10^8}{10^9} = 0.3 \, \text{m} \)
- \( A_e = \frac{10 \times (0.3)^2}{4 \pi} \approx \frac{10 \times 0.09}{12.566} \approx 0.0716 \, \text{m²} \)
- Example 2: \( f = 1000 \) MHz, \( G = 10 \) linear, Result in cm²
- Convert: \( f = 1000 \times 10^6 = 10^9 \, \text{Hz} \), \( G = 10 \)
- Same as Example 1: \( A_e \approx 0.0716 \, \text{m²} \)
- Result in cm²: \( A_e = 0.0716 \times 10^4 = 716 \, \text{cm²} \)
- Example 3: \( f = 1 \) GHz, \( G = 10 \) dB, Result in mm²
- Same as Example 1: \( A_e \approx 0.0716 \, \text{m²} \)
- Result in mm²: \( A_e = 0.0716 \times 10^6 = 71600 \, \text{mm²} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is effective antenna aperture?
A: Effective antenna aperture (or area) is a measure of an antenna's ability to capture radio waves, directly related to its gain and the wavelength of the signal.
Q: Why does the effective aperture depend on frequency?
A: The effective aperture depends on the wavelength, which is inversely proportional to frequency (\( \lambda = \frac{c}{f} \)). Higher frequencies (shorter wavelengths) result in smaller apertures for the same gain.
Q: Can this calculator be used for any antenna type?
A: The formula applies to antennas where the gain and frequency are known. It assumes isotropic conditions and may need adjustments for specific antenna types or non-ideal environments.
Effective Antenna Aperture Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back