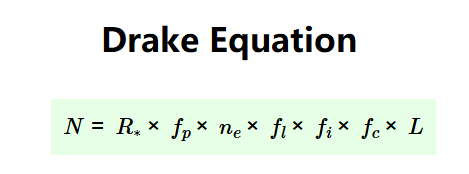1. What is the Drake Equation Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the number of expected alien civilizations (\( N \)) in our galaxy that might be capable of communicating with us, based on the Drake Equation developed by Frank Drake in 1961.
Purpose: It is used in the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI) to estimate the potential number of communicative alien civilizations, helping to guide research and exploration efforts.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equation to compute the number of expected alien civilizations:
- \( N = R_* \times f_p \times n_e \times f_l \times f_i \times f_c \times L \)
Where:
- \( N \): Number of expected alien civilizations
- \( R_* \): Rate of stellar formation in our galaxy (stars per year)
- \( f_p \): Fraction of stars with a planetary system (0 to 1)
- \( n_e \): Number of Earth-like planets, or planets able to sustain life, in an average planetary system
- \( f_l \): Fraction of planets able to sustain life where life actually develops (0 to 1)
- \( f_i \): Fraction of planets with life where intelligent life eventually emerges (0 to 1)
- \( f_c \): Fraction of intelligent civilizations that manage to develop a way to communicate beyond the planetary boundary (0 to 1)
- \( L \): Average lifespan of such a civilization (years)
Steps:
- Enter the values for \( R_* \), \( f_p \), \( n_e \), \( f_l \), \( f_i \), \( f_c \), and \( L \).
- Validate the inputs to ensure they are within acceptable ranges.
- Calculate \( N \) using the Drake Equation.
- If the result is less than 0.0001 or greater than 1,000,000, display it in scientific notation; otherwise, display it with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of the Drake Equation Calculation
Calculating the number of expected alien civilizations is crucial for:
- Guiding SETI Research: The Drake Equation helps prioritize efforts in the search for extraterrestrial intelligence by estimating the likelihood of communicative alien life.
- Understanding Galactic Habitability: It provides insights into the factors that influence the development of life and intelligence in the galaxy.
- Philosophical Implications: The equation encourages discussion about humanity’s place in the universe and the potential for other intelligent life forms.
4. Using the Calculator
Example:
Calculate the number of expected alien civilizations using the following values:
- \( R_* = 1 \) star per year
- \( f_p = 0.5 \)
- \( n_e = 1 \)
- \( f_l = 0.1 \)
- \( f_i = 0.01 \)
- \( f_c = 0.01 \)
- \( L = 100 \) years
- Enter the values into the form.
- The calculator computes:
- \( N = R_* \times f_p \times n_e \times f_l \times f_i \times f_c \times L \)
- \( N = 1 \times 0.5 \times 1 \times 0.1 \times 0.01 \times 0.01 \times 100 \)
- \( N = 0.0005 \)
- Since \( 0.0005 < 0.0001 \), the result is displayed in scientific notation: \( 5.0000 \times 10^{-4} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the Drake Equation?
A: The Drake Equation, developed by Frank Drake in 1961, is a probabilistic formula used to estimate the number of communicative alien civilizations in our galaxy.
Q: Why are the fractions in the equation so uncertain?
A: Many factors in the Drake Equation, such as the fraction of planets where life develops (\( f_l \)) or intelligent life emerges (\( f_i \)), are speculative because we lack direct evidence of extraterrestrial life.
Q: Why is scientific notation used for the result?
A: For results less than 0.0001 or greater than 1,000,000, scientific notation is used to make the values more readable and to handle extremely small or large numbers effectively.
Drake Equation Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back