Deflection Calculator - Calculate Deflection in mm, m, in, ft
Unit Converter ▲
Unit Converter ▼
1. What is the Deflection Calculator?
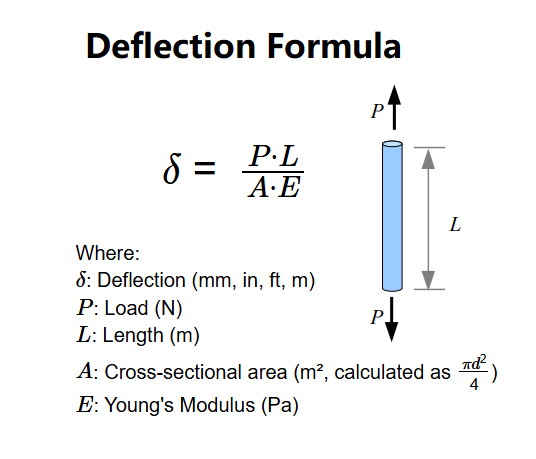
Definition: The Deflection Calculator determines the deflection (\(\delta\)) of a tensile bar using the formula \(\delta = \frac{P \cdot L}{A \cdot E}\), converting the result to millimeters (mm), inches (in), feet (ft), and meters (m).
Purpose: Assists engineers in analyzing material deformation under load.
Reference:Applied Strength of Materials for Engineering Technology
http://www.etcs.pfw.edu/~dupenb/ET_200/Applied%20Str%20of%20Mat%20for%20ET%20v14%20July%202018.pdf
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
Formula:
\(\delta = \frac{P \cdot L}{A \cdot E}\)
Where:
- \(\delta\): Deflection (mm, in, ft, m)
- \(P\): Load (N)
- \(L\): Length (m)
- \(A\): Cross-sectional area (m², calculated as \(\frac{\pi d^2}{4}\))
- \(E\): Young's Modulus (Pa)
Steps:
- Step 1: Input Load. Enter the load value (e.g., 30 kN, 6744 lb).
- Step 2: Input Length. Enter the length (e.g., 80 cm, 31.5 in, 2.62 ft).
- Step 3: Input Diameter. Enter the diameter (e.g., 6 mm, 0.236 in).
- Step 4: Input Young's Modulus. Enter the modulus (e.g., 207 GPa, 30e6 psi).
- Step 5: Calculate. The calculator converts units and computes deflection in multiple units.
3. Importance of Deflection Calculation
Calculating deflection is crucial for:
- Material Deformation: Ensures materials stretch within safe limits.
- Design Safety: Prevents excessive deformation or failure.
- Unit Consistency: Supports conversions from kN/lb, cm/in/ft/m, mm/cm/in, and GPa/psi/Pa.
4. Using the Calculator
Example (SI):
Load = 30 kN, Length = 80 cm, Diameter = 6 mm, Young's Modulus = 207 GPa:
- Step 1: \( P = 30,000 \, \text{N} \).
- Step 2: \( L = 0.8 \, \text{m} \).
- Step 3: \( d = 0.006 \, \text{m}, A \approx 2.83 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Step 4: \( E = 207 \times 10^9 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Step 5: \(\delta \approx 4.1 \, \text{mm}, 0.16 \, \text{in}, 0.013 \, \text{ft}, 0.0041 \, \text{m}\).
Example (Imperial):
Load = 6744 lb, Length = 2.62 ft, Diameter = 0.236 in, Young's Modulus = 30e6 psi:
- Step 1: \( P = 30,000 \, \text{N} \).
- Step 2: \( L = 0.8 \, \text{m} \).
- Step 3: \( d = 0.006 \, \text{m}, A \approx 2.83 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{m}^2 \).
- Step 4: \( E = 207 \times 10^9 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Step 5: \(\delta \approx 4.1 \, \text{mm}, 0.16 \, \text{in}, 0.013 \, \text{ft}, 0.0041 \, \text{m}\).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is deflection?
A: Deflection is the amount a material stretches under load.
Q: Why convert units?
A: The calculator ensures consistent SI units (N, m, Pa) for accurate results and provides multiple output units.
Q: Is this accurate for all materials?
A: Yes, if the load, length, diameter, and modulus are correctly measured.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back