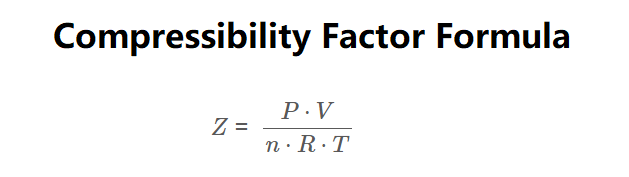1. What is the Compressibility Factor Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the compressibility factor (\( Z \)) of a gas, which measures how much a real gas deviates from ideal gas behavior. It uses the formula \( Z = \frac{P \cdot V}{n \cdot R \cdot T} \), where a \( Z \) value of 1 indicates ideal gas behavior, \( Z < 1 \) indicates attractive forces dominate, and \( Z > 1 \) indicates repulsive forces dominate.
Purpose: It is used in thermodynamics and engineering to correct for non-ideal gas behavior in applications like gas storage, pipeline design, and chemical processes.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the compressibility factor formula:
Formula:
\[
Z = \frac{P \cdot V}{n \cdot R \cdot T}
\]
where:
- \( P \): Pressure (Pa, bar, atm, psi, kPa, mmHg)
- \( V \): Volume (mm³, cm³, in³, L, mL, ft³, yd³, m³)
- \( n \): Number of moles (mol, mmol, μmol, nmol, pmol)
- \( R \): Universal gas constant (\( 8.314 \, \text{J}/(\text{K} \cdot \text{mol}) \))
- \( T \): Temperature (K, °C, °F)
Unit Conversions:
- Pressure (\( P \)):
- 1 Pa = 1 Pa
- 1 bar = 100,000 Pa
- 1 atm = 101,325 Pa
- 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa
- 1 kPa = 1000 Pa
- 1 mmHg = 133.322 Pa
- Volume (\( V \)):
- 1 mm³ = \( 1 \times 10^{-9} \, \text{m}^3 \)
- 1 cm³ = \( 1 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m}^3 \)
- 1 in³ = \( 1.63871 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{m}^3 \)
- 1 L = 0.001 m³
- 1 mL = \( 1 \times 10^{-6} \, \text{m}^3 \)
- 1 ft³ = 0.0283168 m³
- 1 yd³ = 0.764555 m³
- 1 m³ = 1 m³
- Number of Moles (\( n \)):
- 1 mol = 1 mol
- 1 mmol = \( 1 \times 10^{-3} \) mol
- 1 μmol = \( 1 \times 10^{-6} \) mol
- 1 nmol = \( 1 \times 10^{-9} \) mol
- 1 pmol = \( 1 \times 10^{-12} \) mol
- Temperature (\( T \)):
- Kelvin (K): No conversion needed
- Celsius (°C) to Kelvin: \( T_K = T_C + 273.15 \)
- Fahrenheit (°F) to Kelvin: \( T_K = (T_F - 32) \cdot \frac{5}{9} + 273.15 \)
Steps:
- Enter the pressure (\( P \)) in Pa, bar, atm, psi, kPa, or mmHg (step size 0.00001).
- Enter the volume (\( V \)) in mm³, cm³, in³, L, mL, ft³, yd³, or m³ (step size 0.00001).
- Enter the number of moles (\( n \)) in mol, mmol, μmol, nmol, or pmol (step size 0.01).
- Enter the temperature (\( T \)) in K, °C, or °F (step size 0.01).
- Convert pressure to Pa, volume to m³, number of moles to mol, and temperature to K.
- Calculate the compressibility factor using the formula \( Z = \frac{P \cdot V}{n \cdot R \cdot T} \).
- Display the result, using scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise rounded to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Compressibility Factor Calculation
Calculating the compressibility factor is crucial for:
- Real Gas Behavior: It corrects for deviations from ideal gas behavior, improving accuracy in gas law calculations.
- Engineering Applications: It is used in designing gas storage systems, pipelines, and compressors where real gas effects are significant.
- Chemical Processes: It helps in predicting gas behavior under high pressure or low temperature conditions in industrial processes.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Calculate the compressibility factor for air with \( P = 1 \, \text{bar} \), \( V = 1 \, \text{m}^3 \), \( n = 44.6 \, \text{moles} \), and \( T = 293 \, \text{K} \):
- Enter Pressure = 1 bar, convert to Pa: \( 1 \times 100,000 = 100,000 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Enter Volume = 1 m³.
- Enter Number of Moles = 44.6 mol.
- Enter Temperature = 293 K.
- Compressibility Factor: \( Z = \frac{P \cdot V}{n \cdot R \cdot T} = \frac{100,000 \cdot 1}{44.6 \cdot 8.314 \cdot 293} \approx 0.9204 \).
- Result: \( Z = 0.9204 \).
- Example 2: Calculate the compressibility factor for a gas with \( P = 2 \, \text{atm} \), \( V = 500 \, \text{L} \), \( n = 20,000 \, \text{mmol} \), and \( T = 25 \, \text{°C} \):
- Enter Pressure = 2 atm, convert to Pa: \( 2 \times 101,325 = 202,650 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Enter Volume = 500 L, convert to m³: \( 500 \times 0.001 = 0.5 \, \text{m}^3 \).
- Enter Number of Moles = 20,000 mmol, convert to mol: \( 20,000 \times 10^{-3} = 20 \, \text{mol} \).
- Enter Temperature = 25 °C, convert to K: \( 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 \, \text{K} \).
- Compressibility Factor: \( Z = \frac{P \cdot V}{n \cdot R \cdot T} = \frac{202,650 \cdot 0.5}{20 \cdot 8.314 \cdot 298.15} \approx 2.0439 \).
- Result: \( Z = 2.0439 \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What does the compressibility factor indicate?
A: The compressibility factor \( Z \) indicates how much a real gas deviates from ideal gas behavior. A value of \( Z = 1 \) means the gas behaves ideally, \( Z < 1 \) indicates attractive forces dominate, and \( Z > 1 \) indicates repulsive forces dominate.
Q: Why must temperature be in Kelvin?
A: The ideal gas law requires absolute temperature (Kelvin) because it involves temperature ratios, and Kelvin ensures positive values with a true zero point, avoiding negative values that would occur with Celsius or Fahrenheit.
Q: What are some real-world applications of the compressibility factor?
A: The compressibility factor is used in natural gas pipeline design, gas storage calculations, and chemical engineering processes where gases are under high pressure or low temperature, such as in LNG production.
Compressibility Factor Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back