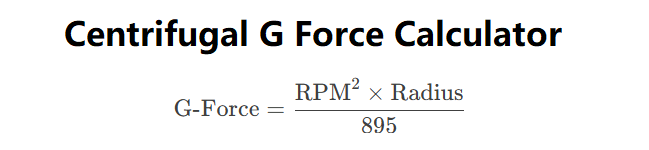G Force Calculation for Centrifuge
How to Calculate Centrifugal G-Force
Centrifugal G-Force measures the acceleration experienced by an object in circular motion, expressed as a multiple of Earth’s gravity (g = 9.81 m/s²). It is crucial in fields like engineering, physics, and centrifugation. The formula is:
\( \text{G-Force} = \frac{\text{RPM}^2 \cdot \text{Radius}}{895} \)
Where:
- \( \text{RPM} \): Revolutions per minute.
- \( \text{Radius} \): Distance from the center of rotation in meters (converted from cm, in, or ft).
- \( 895 \): Constant derived from the relationship between RPM, radius in meters, and gravitational acceleration.
Enter the RPM and radius with the appropriate unit to calculate the G-Force in g units.
Using the Centrifugal G-Force Calculator
This calculator determines the centrifugal G-force for applications like centrifuges, rotating machinery, or amusement rides.
Input the RPM and radius with their units. The calculator will display the G-Force in multiples of g.
Example: Calculate for 3500 RPM and 10 cm radius.
- RPM: \( 3500 \)
- Radius: \( 10 \, \text{cm} = 0.1 \, \text{m} \)
- G-Force: \( \frac{3500^2 \times 0.1}{895} \approx 13.72 \, \text{g} \)
- Result: G-Force ≈ 13.72 g
Use this tool for lab centrifugation, engineering design, or safety assessments.
Common G-Force Table
The following table provides G-Force values for common centrifuge configurations:
| RPM |
Radius (m) |
G-Force (g) |
| 1000 |
0.1 |
1.12 |
| 3500 |
0.1 |
13.72 |
| 5000 |
0.15 |
41.90 |
| 8000 |
0.2 |
143.01 |
| 10000 |
0.25 |
279.33 |
Use this table for quick reference or to verify calculator results.
Common FAQ
Below are frequently asked questions about Centrifugal G-Force:
- Q: What does G-Force measure?
A: G-Force measures the acceleration an object experiences due to rotation, relative to Earth’s gravity.
- Q: Why are unit conversions needed?
A: The formula requires radius in meters, so inputs in cm, in, or ft are converted internally.
- Q: How accurate is this calculator?
A: The calculator uses precise conversion factors and rounds results to 2 decimal places, assuming accurate inputs.
- Q: Can this be used for any rotating system?
A: Yes, as long as RPM and radius are provided, it applies to centrifuges, rides, or machinery.
- Q: What is a typical G-Force in a centrifuge?
A: Lab centrifuges often range from 1 to 10,000 g, depending on RPM and radius.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back