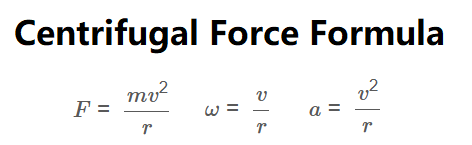1. What is a Centrifugal Force Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the centrifugal force, angular velocity, and centrifugal acceleration for an object in circular motion using mass, velocity, and radius.
Purpose: It is used in physics to analyze forces and motion in rotational systems, such as vehicles in turns or rotating machinery.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Centrifugal Force:
\[
F = \frac{m v^2}{r}
\]
Angular Velocity:
\[
\omega = \frac{v}{r}
\]
Centrifugal Acceleration:
\[
a = \frac{v^2}{r}
\]
Where:
- \( F \): Centrifugal force (N, kN, pdl, lbf)
- \( \omega \): Angular velocity (rpm, rad/s, Hz)
- \( a \): Centrifugal acceleration (m/s², g)
- \( m \): Mass (mg, g, dag, kg, oz, lb, st, Earth)
- \( v \): Velocity (m/s, km/h, ft/s, mph, km/s, mi/s)
- \( r \): Radius (mm, cm, m, km, in, ft, yd, mi)
Unit Conversions:
- Mass (\( m \)): mg (1 mg = 0.000001 kg), g (1 g = 0.001 kg), dag (1 dag = 0.01 kg), kg, oz (1 oz = 0.028349523125 kg), lb (1 lb = 0.45359237 kg), st (1 st = 6.35029318 kg), Earth (1 Earth = 5.972 × 10²⁴ kg)
- Velocity (\( v \)): m/s, km/h (1 km/h = \( \frac{1000}{3600} \) m/s ≈ 0.277777778 m/s), ft/s (1 ft/s = 0.3048 m/s), mph (1 mph = 0.44704 m/s), km/s (1 km/s = 1000 m/s), mi/s (1 mi/s = 1609.344 m/s)
- Radius (\( r \)): mm (1 mm = 0.001 m), cm (1 cm = 0.01 m), m, km (1 km = 1000 m), in (1 in = 0.0254 m), ft (1 ft = 0.3048 m), yd (1 yd = 0.9144 m), mi (1 mi = 1609.344 m)
- Angular Velocity (\( \omega \)): rpm, rad/s, Hz (1 rad/s = \( \frac{60}{2\pi} \) rpm ≈ 9.549296596 rpm, 1 rad/s = \( \frac{1}{2\pi} \) Hz ≈ 0.159154943 Hz)
- Centrifugal Force (\( F \)): N, kN (1 kN = 1000 N), pdl (1 N = 7.233013851209894 pdl), lbf (1 N = 0.224808943 lbf)
- Centrifugal Acceleration (\( a \)): m/s², g (1 g = 9.80665 m/s²)
Steps:
- Enter the mass, velocity, and radius, and select their units.
- Convert all inputs to base units (kg, m/s, m).
- Calculate the angular velocity, centrifugal force, and centrifugal acceleration.
- Convert the results to the selected units in the result form.
- Display results, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with specified decimal places.
3. Importance of Centrifugal Force Calculation
Calculating these values is crucial for:
- Physics Education: Understanding forces and motion in circular systems.
- Engineering: Designing safe vehicles, roads, and rotating machinery.
- Safety Analysis: Ensuring stability in high-speed turns or rotating systems.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( m = 82.36 \, \text{kg} \), \( v = 15 \, \text{m/s} \), \( r = 10 \, \text{m} \), angular velocity in rpm, force in N, acceleration in m/s²:
- Angular Velocity: \( \omega = \frac{15}{10} = 1.5 \, \text{rad/s} \), \( \omega = 1.5 \times \frac{60}{2\pi} = 14.324 \, \text{rpm} \)
- Centrifugal Force: \( F = \frac{82.36 \times 15^2}{10} = 1853.1 \, \text{N} \)
- Centrifugal Acceleration: \( a = \frac{15^2}{10} = 22.5 \, \text{m/s}^2 \)
- Example 2: For \( m = 500 \, \text{g} \), \( v = 36 \, \text{km/h} \), \( r = 50 \, \text{cm} \), angular velocity in Hz, force in lbf, acceleration in g:
- Convert: \( m = 500 \times 0.001 = 0.5 \, \text{kg} \), \( v = 36 \times \frac{1000}{3600} = 10 \, \text{m/s} \), \( r = 50 \times 0.01 = 0.5 \, \text{m} \)
- Angular Velocity: \( \omega = \frac{10}{0.5} = 20 \, \text{rad/s} \), \( \omega = \frac{20}{2\pi} = 3.183 \, \text{Hz} \)
- Centrifugal Force: \( F = \frac{0.5 \times 10^2}{0.5} = 100.0 \, \text{N} \), \( F = 100.0 \times 0.224808943 = 22.5 \, \text{lbf} \)
- Centrifugal Acceleration: \( a = \frac{10^2}{0.5} = 200.0 \, \text{m/s}^2 \), \( a = \frac{200.0}{9.80665} = 20.4 \, \text{g} \)
- Example 3 (Small Value): For \( m = 1 \, \text{mg} \), \( v = 0.1 \, \text{m/s} \), \( r = 100 \, \text{m} \), angular velocity in rad/s, force in kN, acceleration in m/s²:
- Convert: \( m = 1 \times 0.000001 = 0.000001 \, \text{kg} \)
- Angular Velocity: \( \omega = \frac{0.1}{100} = 0.001 \, \text{rad/s} \)
- Centrifugal Force: \( F = \frac{0.000001 \times 0.1^2}{100} = 1.000 \times 10^{-10} \, \text{N} \), \( F = 1.000 \times 10^{-10} \times 0.001 = 1.000 \times 10^{-13} \, \text{kN} \)
- Centrifugal Acceleration: \( a = \frac{0.1^2}{100} = 0.0001 \, \text{m/s}^2 \), display as \( 1.000 \times 10^{-4} \, \text{m/s}^2 \)
- Example 4: For \( m = 2 \, \text{oz} \), \( v = 20 \, \text{m/s} \), \( r = 5 \, \text{m} \), angular velocity in rad/s, force in pdl, acceleration in g:
- Convert: \( m = 2 \times 0.028349523125 = 0.05669904625 \, \text{kg} \)
- Angular Velocity: \( \omega = \frac{20}{5} = 4 \, \text{rad/s} \)
- Centrifugal Force: \( F = \frac{0.05669904625 \times 20^2}{5} = 4.536 \, \text{N} \), \( F = 4.536 \times 7.233013851209894 = 32.809 \, \text{pdl} \)
- Centrifugal Acceleration: \( a = \frac{20^2}{5} = 80 \, \text{m/s}^2 \), \( a = \frac{80}{9.80665} = 8.2 \, \text{g} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is centrifugal force?
A: Centrifugal force is a fictitious force experienced in a non-inertial reference frame during circular motion, directed outward from the center of rotation.
Q: How is angular velocity related to velocity?
A: Angular velocity \(\omega\) is the linear velocity \(v\) divided by the radius \(r\): \(\omega = \frac{v}{r}\). It can be expressed in rpm, rad/s, or Hz.
Q: What is centrifugal acceleration?
A: It’s the acceleration due to circular motion, calculated as \(a = \frac{v^2}{r}\). It can be expressed in m/s² or in g (where 1 g = 9.80665 m/s²).
Centrifugal Force Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back