1. What is a Car Crash Force Calculator?
Definition: This calculator estimates the average impact force, stopping time, deceleration, and equivalent mass sensation experienced during a car crash, comparing scenarios with and without a seatbelt.
Purpose: It helps in understanding the forces involved in a car crash, demonstrating the protective effect of seatbelts and aiding in safety analysis and vehicle design.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator computes results for two scenarios:
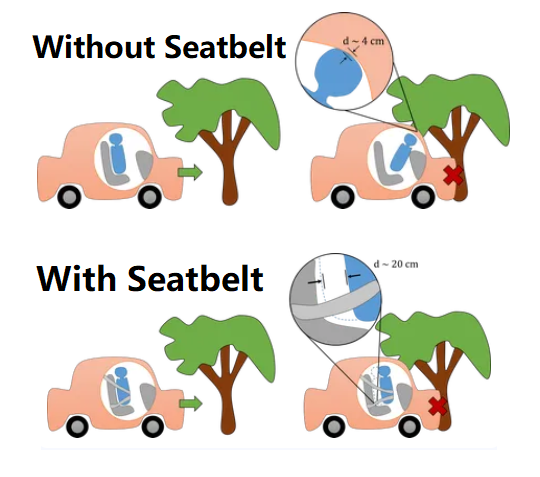
- Without Seatbelt: Stopping distance is 4 cm (0.04 m).
- With Seatbelt: Stopping distance is 20 cm (0.2 m).
It uses the following formulas:
Stopping Time:
\[
t = \frac{2d}{v}
\]
Deceleration:
\[
a = \frac{v^2}{2d}
\]
Average Impact Force:
\[
F = m \cdot a = m \cdot \frac{v^2}{2d}
\]
Equivalent Mass Sensation:
\[
m_{\text{eq}} = \frac{F}{g}
\]
Where:
- \(v\): Car speed (m/s)
- \(m\): Your weight (kg)
- \(d\): Stopping distance (m)
- \(g\): Gravitational acceleration (9.80665 m/s²)
- \(t\): Stopping time (s)
- \(a\): Deceleration (m/s²)
- \(F\): Average impact force (N)
- \(m_{\text{eq}}\): Equivalent mass (kg)
Unit Conversions:
- Speed: m/s, km/h (1 km/h = 0.277778 m/s), mph (1 mph = 0.44704 m/s), kn (1 kn = 0.514444 m/s)
- Weight: kg, lb (1 lb = 0.453592 kg)
- Force: N, kN (1 kN = 1000 N), lbf (1 N = 0.224809 lbf)
- Time: s, ms (1 s = 1000 ms)
- Deceleration: m/s², ft/s² (1 ft/s² = 0.3048 m/s²), g (1 g = 9.80665 m/s²)
- Mass: kg, lb (1 kg = 2.20462 lb)
Steps:
- Enter the car speed (v), selecting the unit (m/s, km/h, mph, kn)
- Enter your weight (m), selecting the unit (kg, lb)
- Convert inputs to SI units (m/s, kg)
- Calculate stopping time, deceleration, impact force, and equivalent mass for both scenarios
- Select desired units for each result in each scenario and view converted values
3. Importance of Car Crash Force Calculation
Calculating car crash forces is crucial for:
- Safety: Highlighting the importance of seatbelts in reducing impact forces.
- Design: Engineering vehicles with better safety features like crumple zones and seatbelts.
- Education: Raising awareness about the physics of car crashes and the benefits of safety measures.
4. Using the Calculator
Example: For a car speed \( v = 160 \, \text{km/h} \), your weight \( m = 70 \, \text{kg} \), and gravitational acceleration \( g = 9.80665 \, \text{m/s}^2 \):
- Speed: \( 160 \cdot 0.277778 = 44.444 \, \text{m/s} \)
- Without Seatbelt (d = 0.04 m):
- Stopping time: \( t = \frac{2 \cdot 0.04}{44.444} \approx 0.002 \, \text{s} = 1.800 \, \text{ms} \)
- Deceleration: \( a = \frac{44.444^2}{2 \cdot 0.04} \approx 24691.358 \, \text{m/s}^2 \approx 2518.519 \, \text{g} \)
- Impact force: \( F = 70 \cdot 24691.358 \approx 1728395.062 \, \text{N} \approx 1728.395 \, \text{kN} \)
- Equivalent mass: \( m_{\text{eq}} = \frac{1728395.062}{9.80665} \approx 176279.533 \, \text{kg} \)
- With Seatbelt (d = 0.2 m):
- Stopping time: \( t = \frac{2 \cdot 0.2}{44.444} \approx 0.009 \, \text{s} = 9.000 \, \text{ms} \)
- Deceleration: \( a = \frac{44.444^2}{2 \cdot 0.2} \approx 4938.272 \, \text{m/s}^2 \approx 503.704 \, \text{g} \)
- Impact force: \( F = 70 \cdot 4938.272 \approx 345679.012 \, \text{N} \approx 345.679 \, \text{kN} \)
- Equivalent mass: \( m_{\text{eq}} = \frac{345679.012}{9.80665} \approx 35255.907 \, \text{kg} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is average impact force?
A: Average impact force is the force exerted on your body during a car crash, calculated as \( F = m \cdot \frac{v^2}{2d} \).
Q: Why is stopping time longer with a seatbelt?
A: A seatbelt increases the stopping distance, allowing the car to decelerate over a longer time, which reduces the impact force and deceleration.
Q: What does the equivalent mass sensation mean?
A: It represents the mass that would exert the same force on you under Earth’s gravity, illustrating the intensity of the crash force.
Car Crash Force Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back