 Home
Home
 Back
Back
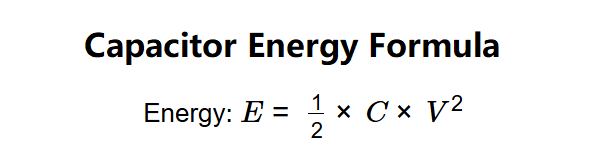
Definition: This calculator computes the energy (\( E \)) stored in a capacitor based on its capacitance (\( C \)), voltage (\( V \)), or charge (\( Q \)).
Purpose: It is used in electronics to determine the energy storage capacity of capacitors, which is essential for designing power supplies, energy storage systems, and circuits involving capacitors.
The calculator supports three modes:
Mode 1: Using Capacitance and Voltage (\( C \) and \( V \))
Mode 2: Using Charge and Capacitance (\( Q \) and \( C \))
Mode 3: Using Charge and Voltage (\( Q \) and \( V \))
Where:
Steps:
Calculating the energy stored in a capacitor is crucial for:
Example 1 (Mode 1: Capacitance and Voltage): A capacitor with a capacitance of 100 µF and a voltage of 10 V:
Example 2 (Mode 2: Charge and Capacitance): A capacitor with a charge of 0.001 C and capacitance of 100 µF:
Example 3 (Mode 3: Charge and Voltage): A capacitor with a charge of 0.001 C and a voltage of 10 V:
Q: Why is the energy formula for a capacitor \( E = \frac{1}{2} \times C \times V^2 \)?
A: The energy stored in a capacitor is the work done to charge it. As the voltage increases linearly with charge (\( V = Q / C \)), the average voltage during charging is \( V/2 \), so the work done is \( E = Q \times (V/2) \), which simplifies to \( \frac{1}{2} \times C \times V^2 \).
Q: Can a capacitor store energy indefinitely?
A: No, capacitors can lose energy over time due to leakage currents or dielectric losses, especially in non-ideal capacitors.
Q: How does the energy change if the voltage doubles?
A: Since \( E \propto V^2 \), doubling the voltage quadruples the energy stored in the capacitor.