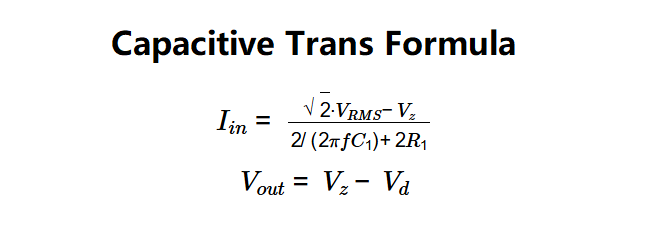1. What is Capacitive Transformerless Power Supply Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the input current and output voltage for a capacitive transformerless power supply, which converts high AC input voltage to low DC voltage using a voltage divider circuit with a capacitor.
Purpose: It is used in electronics to design transformerless power supplies for low-power applications, such as LED drivers or small electronic devices, ensuring proper current and voltage levels.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
\( I_{in} = \frac{\sqrt{2} \cdot V_{RMS} - V_z}{2/(2 \pi f C_1 )+ 2 R_1} \)
\( V_{out} = V_z - V_d \)
Where:
- \( I_{in} \): Input current (A)
- \( V_{RMS} \): RMS value of the input AC voltage (V)
- \( V_z \): Zener voltage (regulated DC output voltage, V)
- \( f \): Frequency of the AC input voltage (Hz)
- \( C_1 \): Capacitance of the voltage-dropping capacitor (F)
- \( R_1 \): Resistance (Ω)
- \( V_{out} \): Output voltage (V)
- \( V_d \): Forward bias voltage of the second diode (V)
Steps:
- Enter the RMS input voltage (\( V_{RMS} \)) with its unit (V, mV, kV).
- Enter the Zener voltage (\( V_z \)) with its unit (V, mV, kV).
- Enter the frequency (\( f \)) with its unit (Hz, kHz, MHz).
- Enter the capacitance (\( C_1 \)) with its unit (F, mF, µF).
- Enter the resistance (\( R_1 \)) with its unit (Ω, kΩ, MΩ).
- Enter the forward bias voltage of the second diode (\( V_d \)) with its unit (V, mV, kV).
- Convert all inputs to base units (V, Hz, F, Ω).
- Calculate the input current and output voltage using the formulas.
- Convert the results to the selected output units.
- Display the results with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Capacitive Transformerless Power Supply Calculation
Calculating these parameters is crucial for:
- Electronics Design: Ensuring the power supply delivers the correct DC voltage and current for the load.
- Safety: Properly sizing components to handle the input current and voltage, avoiding overheating or failure.
- Efficiency: Optimizing the circuit for minimal power loss in low-power applications.
4. Using the Calculator
Example: A capacitive transformerless power supply with an RMS input voltage of 230 V, a Zener voltage of 5 V, a frequency of 50 Hz, a capacitance of 1 µF, a resistance of 100 Ω, and a forward bias voltage of 0.7 V:
- RMS Input Voltage (\( V_{RMS} \)): 230 V
- Zener Voltage (\( V_z \)): 5 V
- Frequency (\( f \)): 50 Hz
- Capacitance (\( C_1 \)): 1 µF = \( 1 \times 10^{-6} \) F
- Resistance (\( R_1 \)): 100 Ω
- Forward Bias Voltage (\( V_d \)): 0.7 V
- Input Current (\( I_{in} \)): \( \frac{\sqrt{2} \times 230 - 5}{2 \pi \times 50 \times 10^{-6} + 2 \times 100} \approx \frac{325.2691 - 5}{0.0003142 + 200} \approx 1.6010 \) A
- Output Voltage (\( V_{out} \)): \( 5 - 0.7 = 4.3 \) V
- Result: \( I_{in} = 1.6010 \) A (or 1601.0000 mA), \( V_{out} = 4.3000 \) V
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a capacitive transformerless power supply?
A: It is a circuit that converts high AC voltage to low DC voltage using a voltage-dropping capacitor and a Zener diode, without a bulky transformer, often used in low-power applications.
Q: Why is the output voltage less than the Zener voltage?
A: The output voltage is reduced by the forward bias voltage (\( V_d \)) of the second diode, as per the formula \( V_{out} = V_z - V_d \).
Q: What is the role of the capacitor in this circuit?
A: The capacitor (\( C_1 \)) acts as a voltage-dropping element, limiting the current and reducing the high AC voltage to a lower level before rectification.
Capacitive Transformerless Power Supply Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back