1. What is Buck Converter Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the duty cycle and required inductance for a DC-to-DC buck converter, which steps down an input voltage to a lower output voltage.
Purpose: It is used in electronics to design buck converters for applications like power supplies, battery chargers, and LED drivers, ensuring proper operation and efficiency.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
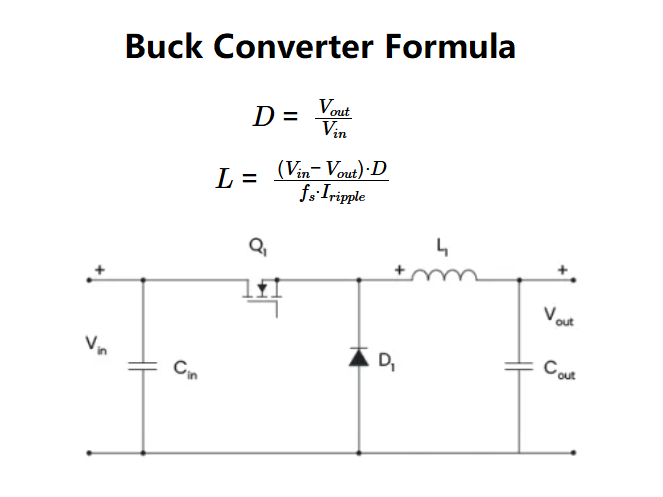
\( D = \frac{V_{out}}{V_{in}} \)
\( L = \frac{(V_{in} - V_{out}) \cdot D}{f_s \cdot I_{ripple}} \)
Where:
- \( D \): Duty cycle (as a percentage)
- \( V_{in} \): Input voltage (V)
- \( V_{out} \): Output voltage (V)
- \( L \): Inductance (H)
- \( f_s \): Switching frequency (Hz)
- \( I_{ripple} \): Maximum ripple current (A)
Steps:
- Enter the input voltage (\( V_{in} \)) with its unit (V, mV, kV).
- Enter the output voltage (\( V_{out} \)) with its unit (V, mV, kV).
- Enter the switching frequency (\( f_s \)) with its unit (Hz, kHz, MHz).
- Enter the maximum ripple current (\( I_{ripple} \)) with its unit (A, mA, µA, kA).
- Convert all inputs to base units (V, Hz, A).
- Calculate the duty cycle and inductance using the formulas.
- Convert the inductance to the selected output unit (H, mH, µH).
- Display the results with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Buck Converter Calculation
Calculating the duty cycle and inductance is crucial for:
- Electronics Design: Ensuring the buck converter operates in the correct mode (e.g., continuous conduction mode) and achieves the desired voltage step-down.
- Efficiency: Optimizing the balance between energy efficiency and the step-down ratio.
- Stability: Selecting the proper inductance to maintain stable operation and minimize ripple current.
4. Using the Calculator
Example: A buck converter has an input voltage of 12 V, an output voltage of 5 V, a switching frequency of 50 kHz, and a maximum ripple current of 200 mA:
- Input Voltage (\( V_{in} \)): 12 V
- Output Voltage (\( V_{out} \)): 5 V
- Switching Frequency (\( f_s \)): 50 kHz = 50,000 Hz
- Maximum Ripple Current (\( I_{ripple} \)): 200 mA = 0.2 A
- Duty Cycle (\( D \)): \( \frac{5}{12} \approx 0.4167 \) (41.67%)
- Inductance (\( L \)): \( \frac{(12 - 5) \times 0.4167}{50,000 \times 0.2} = \frac{7 \times 0.4167}{10,000} \approx 0.0002917 \) H = 0.2917 mH
- Result: \( D = 41.6700 \) %, \( L = 0.2917 \) mH
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is a buck converter?
A: A buck converter is a DC-to-DC converter that steps down an input voltage to a lower output voltage, commonly used in power electronics.
Q: Why is the duty cycle important?
A: The duty cycle determines the fraction of time the switch is on, directly affecting the voltage step-down ratio and the converter’s efficiency.
Q: How does inductance affect the buck converter?
A: The inductance value influences the ripple current and the converter’s operating mode. A proper inductance ensures stable operation and minimizes current ripple.
Buck Converter Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back