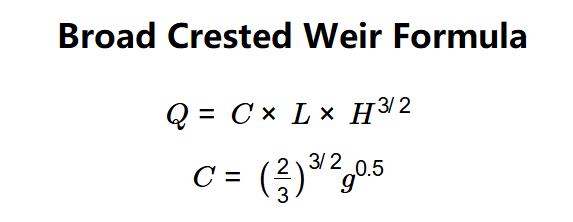1. What is Broad-Crested Weir Calculator?
Definition: This calculator uses the broad-crested weir equation to compute the discharge (\( Q \)) over a broad-crested weir and the weir coefficient (\( C \)).
Purpose: It is used in hydraulics and civil engineering to measure and predict the flow rate of water over a weir, which is essential for designing spillways, dams, and irrigation systems.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following equations:
- \( Q = C \times L \times H^{3/2} \)
- \( C = \left( \frac{2}{3} \right)^{3/2} g^{0.5} \)
Where:
- \( Q \): Discharge (m³/s);
- \( C \): Weir coefficient (dimensionless);
- \( L \): Length of the weir (m);
- \( H \): Upstream head (m);
- \( g \): Acceleration due to gravity (m/s²).
Steps:
- Enter the upstream head (\( H \)) with its unit.
- Enter the length of the weir (\( L \)) with its unit.
- Enter the acceleration due to gravity (\( g \)) with its unit (default is 9.80665 m/s²).
- Convert all inputs to base units (m for length, m/s² for gravity).
- Calculate the weir coefficient: \( C = \left( \frac{2}{3} \right)^{3/2} g^{0.5} \).
- Calculate the discharge: \( Q = C \times L \times H^{3/2} \).
- Convert the discharge to the selected output unit and display both \( C \) and \( Q \), formatted in scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Broad-Crested Weir Calculation
Calculating the discharge over a broad-crested weir is crucial for:
- Water Management: Measuring flow rates in rivers, canals, and irrigation systems to manage water resources effectively.
- Dam and Spillway Design: Ensuring safe and efficient design of spillways to handle flood flows.
- Environmental Engineering: Monitoring and controlling water flow to maintain ecological balance in aquatic systems.
4. Using the Calculator
Example 1: Calculate \( C \) and \( Q \) for a broad-crested weir with the following properties:
- Upstream Head: \( H = 0.5 \, \text{m} \);
- Length of Weir: \( L = 2 \, \text{m} \);
- Acceleration due to Gravity: \( g = 9.80665 \, \text{m/s}^2 \);
- Weir Coefficient: \( C = \left( \frac{2}{3} \right)^{3/2} \times 9.80665^{0.5} \approx 1.7048 \);
- Discharge: \( Q = 1.7048 \times 2 \times 0.5^{3/2} \approx 1.2047 \, \text{m}^3/\text{s} \);
- Result: \( C = 1.7048 \), \( Q = 1.2047 \, \text{m}^3/\text{s} \).
Example 2 (Different Units): Calculate \( C \) and \( Q \) with the following properties:
- Upstream Head: \( H = 1.5 \, \text{ft} \);
- Length of Weir: \( L = 10 \, \text{ft} \);
- Acceleration due to Gravity: \( g = 32.174 \, \text{ft/s}^2 \);
- Convert units: \( H = 1.5 \times 0.3048 = 0.4572 \, \text{m} \), \( L = 10 \times 0.3048 = 3.048 \, \text{m} \), \( g = 32.174 \times 0.3048 = 9.8066 \, \text{m/s}^2 \);
- Weir Coefficient: \( C = \left( \frac{2}{3} \right)^{3/2} \times 9.8066^{0.5} \approx 1.7048 \);
- Discharge: \( Q = 1.7048 \times 3.048 \times 0.4572^{3/2} \approx 1.6042 \, \text{m}^3/\text{s} \);
- Result (in selected units, e.g., ft³/s): \( C = 1.7048 \), \( Q = 56.6319 \, \text{ft}^3/\text{s} \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the significance of the weir coefficient \( C \)?
A: The weir coefficient \( C \) accounts for the weir's geometry and the effects of gravity on the flow. It adjusts the theoretical flow rate to match real-world conditions.
Q: Why does the discharge depend on \( H^{3/2} \)?
A: The \( H^{3/2} \) term arises from the physics of open-channel flow over a weir, reflecting the relationship between the head and the velocity of the water as it passes over the weir.
Q: Can this calculator be used for other types of weirs?
A: This calculator is specific to broad-crested weirs. Other types of weirs (e.g., sharp-crested weirs) use different equations and coefficients, which this calculator does not account for.
Broad-Crested Weir Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back