1. What is Brinell Hardness Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the hardness of a material based on the Brinell hardness test, where a spherical indenter is pressed into the material under a specified load, and the resulting indentation is measured.
Purpose: It is used in material science and engineering to assess the hardness of metals, helping to determine their suitability for specific applications.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula:
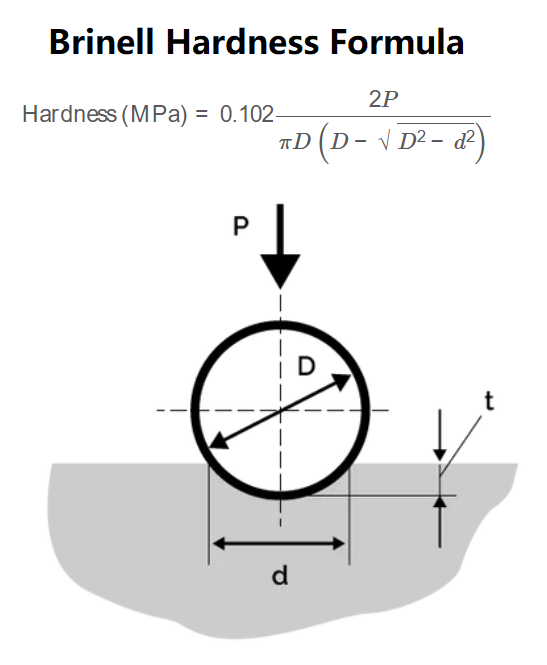
Formula:
\[
\text{Hardness (MPa)} = 0.102 \frac{2P}{\pi D \left(D - \sqrt{D^2 - d^2}\right)}
\]
Where:
- \( \text{Hardness} \): Hardness value (kgf/mm², psi, kPa, MPa, GPa)
- \( P \): Test force (N, kN, lbf)
- \( D \): Indenter diameter (mm, cm, in)
- \( d \): Indentation diameter (mm, cm, in)
Unit Conversions:
- Test Force (\( P \)):
- 1 N = 1 N
- 1 kN = 1000 N
- 1 lbf = 4.44822 N
- Indenter Diameter (\( D \)), Indentation Diameter (\( d \)):
- 1 mm = 1 mm
- 1 cm = 10 mm
- 1 in = 25.4 mm
- Hardness:
- 1 MPa = 1 MPa
- 1 MPa = 1000 kPa
- 1 MPa = 0.001 GPa
- 1 MPa = 145.0377 psi
- 1 MPa = 0.101971621 kgf/mm²
Steps:
- Enter the test force (\( P \)), indenter diameter (\( D \)), and indentation diameter (\( d \)) with their respective units.
- Convert the test force to Newtons and the diameters to millimeters.
- Calculate the hardness in MPa using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (kgf/mm², psi, kPa, MPa, GPa).
- Display the result with 6 decimal places to match the precision in the image, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001.
3. Importance of Brinell Hardness Calculation
Calculating the Brinell hardness is crucial for:
- Material Selection: Determining the hardness of metals to ensure they meet the requirements for specific applications.
- Quality Control: Verifying the consistency of material properties in manufacturing.
- Engineering Design: Assessing the wear resistance and durability of materials in mechanical components.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( P = 22 \, \text{N} \), \( D = 51 \, \text{mm} \), \( d = 12 \, \text{mm} \), result in MPa:
- \( \text{Hardness (MPa)} = 0.102 \frac{2 \times 22}{\pi \times 51 \left(51 - \sqrt{51^2 - 12^2}\right)} \)
- \( \text{Hardness (MPa)} \approx 0.102 \frac{44}{\pi \times 51 \left(51 - \sqrt{2457}\right)} \)
- \( \text{Hardness (MPa)} \approx 0.102 \frac{44}{\pi \times 51 \times 1.4329} \approx 0.019563 \, \text{MPa} \)
- Example 2: For \( P = 1 \, \text{kN} \), \( D = 0.5 \, \text{in} \), \( d = 2 \, \text{mm} \), result in psi:
- Convert: \( P = 1 \times 1000 = 1000 \, \text{N} \), \( D = 0.5 \times 25.4 = 12.7 \, \text{mm} \)
- \( \text{Hardness (MPa)} = 0.102 \frac{2 \times 1000}{\pi \times 12.7 \left(12.7 - \sqrt{12.7^2 - 2^2}\right)} \)
- \( \text{Hardness (MPa)} \approx 0.102 \frac{2000}{\pi \times 12.7 \left(12.7 - \sqrt{157.29}\right)} \approx 0.102 \frac{2000}{\pi \times 12.7 \times 0.3155} \approx 0.016208 \, \text{MPa} \)
- Convert to psi: \( 0.016208 \times 145.0377 \approx 2.350771 \, \text{psi} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the Brinell hardness test?
A: The Brinell hardness test involves pressing a spherical indenter into a material under a specified load and measuring the diameter of the resulting indentation to calculate hardness. Details can be found in the international standard ISO 6506-1 for metallic testing.
Q: How is the Brinell hardness used in real life?
A: It is used in material testing to evaluate the hardness of metals, in quality control to ensure material consistency, and in engineering to select materials for components requiring specific hardness levels.
Brinell Hardness Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back