 Home
Home
 Back
Back
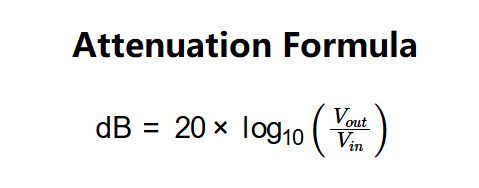
Definition: This calculator computes the attenuation (\( \text{dB} \)) of a signal given the input voltage (\( V_{in} \)) and output voltage (\( V_{out} \)).
Purpose: It is used in electronics and signal processing to quantify how much a signal weakens as it travels through a circuit or medium.
The calculator uses the following equation:
Where:
Steps:
Calculating attenuation is crucial for:
Example 1: Calculate the attenuation when the input voltage is 2 V and the output voltage is 0.5 V:
Example 2: Calculate the attenuation when the input voltage is 100 mV and the output voltage is 10 mV:
Q: What does a negative attenuation value mean?
A: A negative value indicates that the output voltage is less than the input voltage, meaning the signal has been attenuated (weakened).
Q: Why do we use decibels for attenuation?
A: Decibels provide a logarithmic scale that makes it easier to represent large changes in signal strength and compare ratios in a more intuitive way.
Q: Can this calculator be used for power attenuation?
A: This calculator is designed for voltage attenuation. For power attenuation, the formula is different: \( \text{dB} = 10 \times \log_{10} \left( \frac{P_{out}}{P_{in}} \right) \).