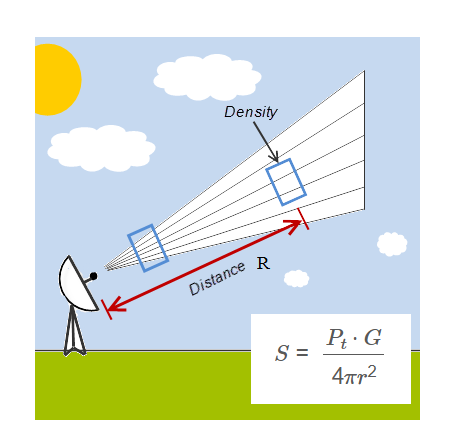
1. What is Antenna Power Density Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the power density of an antenna at a given distance, based on the transmitted power and antenna gain.
Purpose: It is used in RF engineering to assess the intensity of electromagnetic radiation from an antenna, important for safety, coverage, and system design.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula:
Formula:
\[
S = \frac{P_t \cdot G}{4 \pi r^2}
\]
Where:
- \( S \): Power Density (W/m², mW/m², W/cm², mW/cm²)
- \( P_t \): Transmitted Power (W)
- \( G \): Antenna Gain (linear)
- \( r \): Distance (m)
Unit Conversions:
- Transmitted Power:
- 1 W = 1 Watt
- 1 mW = 0.001 W
- 1 kW = 1,000 W
- 1 dBm = \( 10^{\frac{\text{dBm} - 30}{10}} \) W
- Antenna Gain:
- Linear: No conversion
- dBi: \( G = 10^{\frac{G_{\text{dBi}}}{10}} \)
- Distance:
- 1 m = 1 meter
- 1 km = 1,000 m
- 1 ft = 0.3048 m
- 1 mi = 1,609.344 m
- Power Density:
- 1 W/m² = 1 Watt per square meter
- 1 mW/m² = 0.001 W/m²
- 1 W/cm² = 10,000 W/m²
- 1 mW/cm² = 10 W/m²
Steps:
- Enter the Transmitted Power (positive value) and select the unit (W, mW, kW, dBm).
- Enter the Antenna Gain (positive value) and select the unit (linear, dBi).
- Enter the Distance (positive value) and select the unit (m, km, ft, mi).
- Convert Transmitted Power to watts, Antenna Gain to linear, and Distance to meters.
- Calculate \( S \) in W/m² using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit (W/m², mW/m², W/cm², mW/cm²).
- Display the result, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Antenna Power Density Calculation
Calculating Antenna Power Density is crucial for:
- Safety: Ensuring electromagnetic radiation levels are within safe limits for human exposure.
- Coverage: Assessing the signal strength at various distances for effective communication system design.
- RF Engineering: Optimizing antenna placement and power settings for desired coverage and performance.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( P_t = 100 \, \text{W} \), \( G = 10 \, \text{(linear)} \), \( r = 10 \, \text{m} \), results in W/m²:
- \( S = \frac{100 \times 10}{4 \pi \times 10^2} \approx \frac{1000}{1256.637} \approx 0.7958 \, \text{W/m}^2 \)
- Example 2: For \( P_t = 30 \, \text{dBm} \), \( G = 15 \, \text{dBi} \), \( r = 1 \, \text{km} \), results in mW/m²:
- Convert power: \( P_t = 10^{\frac{30 - 30}{10}} = 1 \, \text{W} \)
- Convert gain: \( G = 10^{\frac{15}{10}} \approx 31.6228 \)
- Convert distance: \( r = 1 \times 1000 = 1000 \, \text{m} \)
- \( S = \frac{1 \times 31.6228}{4 \pi \times 1000^2} \approx \frac{31.6228}{12566370} \approx 0.000002516 \, \text{W/m}^2 \)
- Convert to mW/m²: \( 0.000002516 \times 1000 \approx 0.0025 \, \text{mW/m}^2 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is power density?
A: Power density is the amount of power per unit area, typically measured in watts per square meter, indicating the intensity of electromagnetic radiation.
Q: Why does distance affect power density?
A: Power density decreases with the square of the distance due to the inverse square law, as the energy spreads over a larger area.
Q: How is this calculation used in real life?
A: It is used in RF system design, safety assessments for electromagnetic exposure, and ensuring adequate signal strength for communication systems.
Antenna Power Density Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back