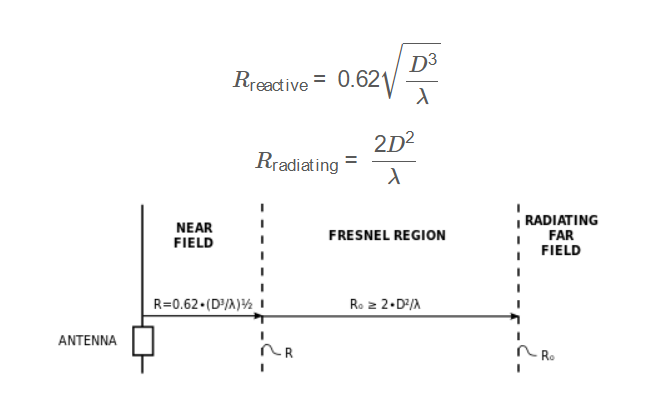
1. What is Antenna Near-Field Distance Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the reactive and radiating near-field distances of an antenna based on its largest dimension and operating frequency.
Purpose: It is used in RF engineering to understand the near-field regions of an antenna, which is critical for antenna design, testing, and placement.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Formulas:
\[
R_{\text{reactive}} = 0.62 \sqrt{\frac{D^3}{\lambda}}
\]
\[
R_{\text{radiating}} = \frac{2 D^2}{\lambda}
\]
\[
\lambda = \frac{c}{f}
\]
Where:
- \( R_{\text{reactive}} \): Reactive Near-Field Distance (m, km, ft, mi)
- \( R_{\text{radiating}} \): Radiating Near-Field Distance (m, km, ft, mi)
- \( D \): Largest Dimension of the Antenna (m)
- \( \lambda \): Wavelength (m)
- \( c \): Speed of Light (299,792,458 m/s)
- \( f \): Frequency (Hz)
Unit Conversions:
- Largest Dimension:
- 1 m = 1 meter
- 1 cm = 0.01 m
- 1 mm = 0.001 m
- 1 ft = 0.3048 m
- 1 in = 0.0254 m
- Frequency:
- 1 Hz = 1 Hertz
- 1 kHz = 1,000 Hz
- 1 MHz = 1,000,000 Hz
- 1 GHz = 1,000,000,000 Hz
- 1 THz = 1,000,000,000,000 Hz
- Distances:
- 1 m = 1 meter
- 1 km = 1,000 m
- 1 ft = 0.3048 m
- 1 mi = 1,609.344 m
Steps:
- Enter the Largest Dimension of the antenna and select the unit (m, cm, mm, ft, in).
- Enter the Frequency and select the unit (Hz, kHz, MHz, GHz, THz).
- Convert Largest Dimension to meters and Frequency to Hz.
- Calculate the wavelength \( \lambda = \frac{c}{f} \).
- Calculate \( R_{\text{reactive}} \) and \( R_{\text{radiating}} \) in meters.
- Convert the results to the selected unit (m, km, ft, mi).
- Display the results, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Antenna Near-Field Distance Calculation
Calculating the Antenna Near-Field Distances is crucial for:
- Antenna Design: Understanding the near-field regions to optimize antenna performance and placement.
- Testing: Determining the appropriate distance for measurements in antenna testing setups.
- RF Engineering: Ensuring proper electromagnetic field behavior in applications like wireless communication and radar systems.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( D = 0.5 \, \text{m} \), \( f = 2.4 \, \text{GHz} \), results in meters:
- Convert to Hz: \( f = 2.4 \times 10^9 \, \text{Hz} \)
- \( \lambda = \frac{299,792,458}{2.4 \times 10^9} \approx 0.125 \, \text{m} \)
- \( R_{\text{reactive}} = 0.62 \sqrt{\frac{0.5^3}{0.125}} \approx 0.62 \sqrt{1} = 0.6200 \, \text{m} \)
- \( R_{\text{radiating}} = \frac{2 \times 0.5^2}{0.125} = \frac{0.5}{0.125} = 4.0000 \, \text{m} \)
- Example 2: For \( D = 12 \, \text{in} \), \( f = 900 \, \text{MHz} \), results in feet:
- Convert to meters: \( D = 12 \times 0.0254 = 0.3048 \, \text{m} \)
- Convert to Hz: \( f = 900 \times 10^6 = 9 \times 10^8 \, \text{Hz} \)
- \( \lambda = \frac{299,792,458}{9 \times 10^8} \approx 0.3331 \, \text{m} \)
- \( R_{\text{reactive}} = 0.62 \sqrt{\frac{0.3048^3}{0.3331}} \approx 0.2354 \, \text{m} \)
- \( R_{\text{radiating}} = \frac{2 \times 0.3048^2}{0.3331} \approx 0.5577 \, \text{m} \)
- Convert to feet: \( R_{\text{reactive}} \approx 0.7723 \, \text{ft} \), \( R_{\text{radiating}} \approx 1.8297 \, \text{ft} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the near-field region of an antenna?
A: The near-field region is the area close to the antenna where the electromagnetic field does not yet resemble a plane wave, divided into reactive and radiating near-field zones.
Q: Why calculate near-field distances?
A: These distances help determine where to place measurement equipment and understand field behavior near the antenna, crucial for design and testing.
Q: How does frequency affect the near-field distance?
A: Higher frequency means shorter wavelength, which reduces the near-field distance for a given antenna size.
Antenna Near-Field Distance Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back