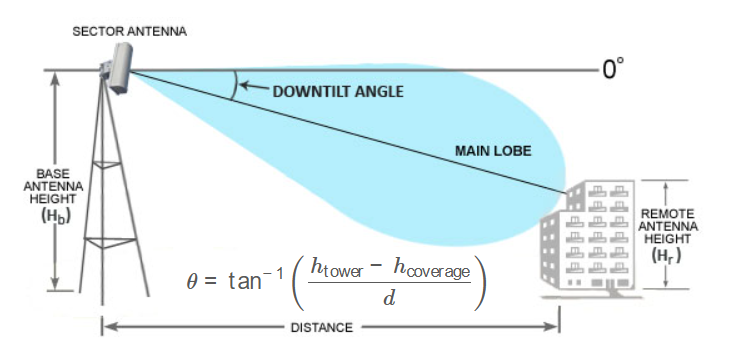
1. What is Antenna Downtilt Angle Calculator?
Definition: This calculator determines the downtilt angle of an antenna to aim at a specific coverage area, based on the tower height, distance to the coverage area, and the height of the coverage area.
Purpose: It is used in RF engineering and telecommunications to optimize antenna coverage in cellular networks, ensuring signals reach the intended area effectively.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formula:
Formula:
\[
\theta = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{h_{\text{tower}} - h_{\text{coverage}}}{d}\right)
\]
Where:
- \( \theta \): Downtilt Angle (degrees)
- \( h_{\text{tower}} \): Tower Height (m)
- \( h_{\text{coverage}} \): Height of Coverage Area (m)
- \( d \): Distance to Coverage Area (m)
Unit Conversions:
- Tower Height, Height of Coverage Area, Distance:
- 1 m = 1 meter
- 1 km = 1,000 m
- 1 ft = 0.3048 m
- 1 mi = 1,609.344 m
- Downtilt Angle: Measured in degrees, no conversion needed
Steps:
- Enter the Tower Height (non-negative value) and select the unit (m, km, ft, mi).
- Enter the Height of Coverage Area (non-negative value) and select the unit (m, km, ft, mi).
- Enter the Distance to Coverage Area (positive value) and select the unit (m, km, ft, mi).
- Convert all measurements to meters.
- Calculate \( \theta = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{h_{\text{tower}} - h_{\text{coverage}}}{d}\right) \) in degrees.
- Display the result, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Antenna Downtilt Angle Calculation
Calculating the Antenna Downtilt Angle is crucial for:
- RF Engineering: Optimizing signal coverage in cellular networks to reduce interference and improve signal quality.
- Telecommunications: Ensuring base stations cover the intended area effectively, especially in urban environments.
- Network Planning: Enhancing network performance by directing antenna beams precisely to target areas.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( h_{\text{tower}} = 30 \, \text{m} \), \( h_{\text{coverage}} = 1.5 \, \text{m} \), \( d = 500 \, \text{m} \):
- Height difference: \( 30 - 1.5 = 28.5 \, \text{m} \)
- \( \theta = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{28.5}{500}\right) \)
- \( \frac{28.5}{500} = 0.057 \)
- \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(0.057) \approx 3.2636 \, \text{degrees} \)
- Example 2: For \( h_{\text{tower}} = 100 \, \text{ft} \), \( h_{\text{coverage}} = 5 \, \text{ft} \), \( d = 1 \, \text{km} \):
- Convert to meters: \( h_{\text{tower}} = 100 \times 0.3048 = 30.48 \, \text{m} \), \( h_{\text{coverage}} = 5 \times 0.3048 = 1.524 \, \text{m} \), \( d = 1 \times 1000 = 1000 \, \text{m} \)
- Height difference: \( 30.48 - 1.524 = 28.956 \, \text{m} \)
- \( \theta = \tan^{-1}\left(\frac{28.956}{1000}\right) \)
- \( \frac{28.956}{1000} = 0.028956 \)
- \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(0.028956) \approx 1.6590 \, \text{degrees} \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is antenna downtilt?
A: Antenna downtilt is the angle at which an antenna is tilted downward to direct its beam towards a specific coverage area.
Q: Why is downtilt angle important?
A: It ensures optimal signal coverage, reduces interference, and improves signal quality in the target area, especially in cellular networks.
Q: Can I use different units for the inputs?
A: Yes, the calculator converts all measurements to meters before calculation, allowing flexibility with units like meters, kilometers, feet, and miles.
Antenna Downtilt Angle Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back