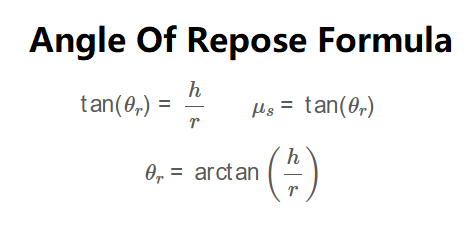1. What is Angle of Repose Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the angle of repose (\( \theta_r \)), the steepest angle at which a sloping surface formed of loose material is stable, and the static friction coefficient (\( \mu_s \)) of the material.
Purpose: It is used in engineering, geology, and material science to determine the stability of granular materials like sand, gravel, or soil, and to understand their frictional properties.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Formulas:
\[
\tan(\theta_r) = \frac{h}{r}
\]
\[
\theta_r = \arctan\left(\frac{h}{r}\right)
\]
\[
\mu_s = \tan(\theta_r)
\]
Where:
- \( \theta_r \): Angle of repose (deg, rad, gon, tr, arcmin, arcsec, mrad, μrad, x π rad)
- \( h \): Height of the heap (mm, cm, dm, m, in, ft, yd)
- \( r \): Radius of the heap (mm, cm, dm, m, in, ft, yd)
- \( \mu_s \): Static friction coefficient (dimensionless)
Unit Conversions:
- Height (\( h \)) and Radius (\( r \)):
- 1 mm = 0.001 m
- 1 cm = 0.01 m
- 1 dm = 0.1 m
- 1 m = 1 m
- 1 in = 0.0254 m
- 1 ft = 0.3048 m
- 1 yd = 0.9144 m
- Angle (\( \theta_r \)):
- 1 deg = \( \frac{\pi}{180} \) rad
- 1 rad = 1 rad
- 1 gon = \( \frac{\pi}{200} \) rad
- 1 tr = \( 2\pi \) rad
- 1 arcmin = \( \frac{\pi}{180 \times 60} \) rad
- 1 arcsec = \( \frac{\pi}{180 \times 3600} \) rad
- 1 mrad = 0.001 rad
- 1 μrad = 0.000001 rad
- 1 x π rad = \( x \times \pi \) rad
- Static Friction Coefficient (\( \mu_s \)): Dimensionless (no unit conversion needed)
Steps:
- Enter the height of the heap (\( h \)) and the radius of the heap (\( r \)) with their respective units.
- Convert the height and radius to meters.
- Calculate \( \theta_r = \arctan\left(\frac{h}{r}\right) \) in radians.
- Calculate \( \mu_s = \tan(\theta_r) \).
- Convert the angle to the selected unit.
- Display the results, using scientific notation for values less than 0.001, otherwise with 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Angle of Repose Calculation
Calculating the angle of repose is crucial for:
- Engineering: Designing stable slopes, embankments, and storage piles for granular materials.
- Geology: Understanding the stability of natural slopes and predicting landslides.
- Material Science: Analyzing the frictional properties of materials for industrial applications.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: For \( h = 200 \, \text{cm} \), \( r = 400 \, \text{cm} \), angle in degrees:
- Convert to meters: \( h = 2 \, \text{m} \), \( r = 4 \, \text{m} \)
- \( \theta_r = \arctan\left(\frac{2}{4}\right) = \arctan(0.5) \approx 0.4636 \, \text{rad} \)
- Convert to degrees: \( \theta_r = 0.4636 \times \frac{180}{\pi} \approx 26.5651^\circ \)
- \( \mu_s = \tan(0.4636) \approx 0.5000 \)
- Example 2: For \( h = 1.5 \, \text{ft} \), \( r = 3 \, \text{ft} \), angle in gradians:
- Convert to meters: \( h = 1.5 \times 0.3048 = 0.4572 \, \text{m} \), \( r = 3 \times 0.3048 = 0.9144 \, \text{m} \)
- \( \theta_r = \arctan\left(\frac{0.4572}{0.9144}\right) = \arctan(0.5) \approx 0.4636 \, \text{rad} \)
- Convert to gradians: \( \theta_r = 0.4636 \times \frac{200}{\pi} \approx 29.5168 \, \text{gon} \)
- \( \mu_s = \tan(0.4636) \approx 0.5000 \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the angle of repose?
A: The angle of repose is the steepest angle at which a sloping surface formed of loose material, such as sand or gravel, remains stable without sliding.
Q: How does the static friction coefficient relate to the angle of repose?
A: The static friction coefficient (\( \mu_s \)) is equal to the tangent of the angle of repose (\( \theta_r \)), as \( \mu_s = \tan(\theta_r) \). It represents the frictional resistance between particles.
Q: How is the angle of repose used in real life?
A: It is used in designing storage silos, analyzing slope stability in mining, and understanding the behavior of granular materials in construction and agriculture.
Angle of Repose Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back