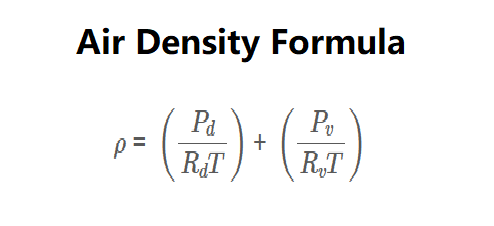1. What is the Air Density Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the air density (\( \rho \)) based on the total air pressure (\( P \)), air temperature (\( T \)), and a fixed relative humidity (\( RH \)) of 0.01%. Air density is the mass of air per unit volume.
Purpose: It is used in meteorology, aerodynamics, and engineering to determine air density for applications like aircraft performance, weather forecasting, and HVAC design.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Formulas:
\[
p_1 = 6.1078 \cdot 10^{\frac{7.5T}{243.12 + T}}
\]
\[
P_v = p_1 \cdot \frac{RH}{100}
\]
\[
P_d = P - P_v
\]
\[
\rho = \left( \frac{P_d}{R_d T} \right) + \left( \frac{P_v}{R_v T} \right)
\]
where:
- \( \rho \): Air density (kg/m³, g/m³, lb/ft³)
- \( p_1 \): Saturation vapor pressure (hPa)
- \( P_v \): Actual vapor pressure (Pa)
- \( P_d \): Pressure of dry air (Pa)
- \( P \): Total air pressure (Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, lb/ft²)
- \( RH \): Relative humidity, fixed at 0.01%
- \( T \): Air temperature (K, °C, °F)
- \( R_d \): Specific gas constant for dry air, 287.058 J/(kg·K)
- \( R_v \): Specific gas constant for water vapor, 461.495 J/(kg·K)
Unit Conversions:
- Pressure (\( P \)):
- 1 Pa = 1 Pa
- 1 bar = 100000 Pa
- 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa
- 1 at = 98066.5 Pa
- 1 atm = 101325 Pa
- 1 Torr = 133.322 Pa
- 1 hPa = 100 Pa
- 1 kPa = 1000 Pa
- 1 lb/ft² = 47.8803 Pa
- Temperature (\( T \)):
- 1 °C = 273.15 K
- 1 °F = (T - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 K
- 1 K = 1 K
- Air Density (\( \rho \)):
- 1 kg/m³ = 1 kg/m³
- 1 g/m³ = 0.001 kg/m³
- 1 lb/ft³ = 16.0185 kg/m³
Steps:
- Enter the total air pressure (\( P \)) in Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, or lb/ft² (default is 101325 Pa, step size 0.00001).
- Enter the air temperature (\( T \)) in °C, °F, or K (default is 25°C, step size 0.00001).
- Use a fixed relative humidity (\( RH \)) of 0.01%.
- Convert pressure to Pa and temperature to both Kelvin (K) and Celsius (°C).
- Calculate the saturation vapor pressure (\( p_1 \)) using the formula.
- Calculate the actual vapor pressure (\( P_v \)) using the fixed relative humidity.
- Calculate the pressure of dry air (\( P_d \)) by subtracting \( P_v \) from \( P \).
- Calculate the air density (\( \rho \)) using the formula.
- Convert the result to the selected unit and display it, using scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise rounded to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Air Density Calculation
Calculating air density is crucial for:
- Aerodynamics: Determining lift, drag, and engine performance in aircraft and vehicles, which depend on air density.
- Meteorology: Understanding atmospheric conditions for weather forecasting and climate studies.
- Engineering: Designing HVAC systems, wind turbines, and other systems where air density affects performance.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Calculate the air density for a total air pressure of 101325 Pa and temperature of 25°C, with air density in kg/m³:
- Enter \( P = 101325 \) Pa.
- Enter \( T = 25 \) °C, convert to K: \( 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 \, \text{K} \), and Celsius: \( T_C = 25 \).
- Relative humidity: \( RH = 0.01 \)%.
- Saturation vapor pressure: \( p_1 = 6.1078 \times 10^{\frac{7.5 \times 25}{243.12 + 25}} = 31.6829 \, \text{hPa} \), convert to Pa: \( 31.6829 \times 100 = 3168.29 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Actual vapor pressure: \( P_v = 3168.29 \times \frac{0.01}{100} = 0.3168 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Pressure of dry air: \( P_d = 101325 - 0.3168 = 101324.6832 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Air density: \( \rho = \left( \frac{101324.6832}{287.058 \times 298.15} \right) + \left( \frac{0.3168}{461.495 \times 298.15} \right) = 1.1839 + 0.0000023 = 1.1839 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \).
- Result: \( \rho = 1.1839 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \).
- Example 2: Calculate the air density for a total air pressure of 0.001 bar and temperature of -10°C, with air density in g/m³:
- Enter \( P = 0.001 \) bar, convert to Pa: \( 0.001 \times 100000 = 100 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Enter \( T = -10 \) °C, convert to K: \( -10 + 273.15 = 263.15 \, \text{K} \), and Celsius: \( T_C = -10 \).
- Relative humidity: \( RH = 0.01 \)%.
- Saturation vapor pressure: \( p_1 = 6.1078 \times 10^{\frac{7.5 \times (-10)}{243.12 + (-10)}} = 2.5935 \, \text{hPa} \), convert to Pa: \( 2.5935 \times 100 = 259.35 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Actual vapor pressure: \( P_v = 259.35 \times \frac{0.01}{100} = 0.0259 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Pressure of dry air: \( P_d = 100 - 0.0259 = 99.9741 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Air density: \( \rho = \left( \frac{99.9741}{287.058 \times 263.15} \right) + \left( \frac{0.0259}{461.495 \times 263.15} \right) = 0.0013 + 0.0000002 = 0.0013 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \).
- Convert to g/m³: \( 0.0013 \times 1000 = 1.3247 \), use scientific notation: \( 1.3247 \times 10^{-3} \).
- Result: \( \rho = 1.3247 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{g/m}^3 \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is air density?
A: Air density is the mass of air per unit volume, typically measured in kg/m³ or g/m³. It depends on temperature, pressure, and humidity.
Q: Why is relative humidity fixed at 0.01% in this calculator?
A: The relative humidity is fixed at 0.01% to simplify the calculation while still accounting for a minimal amount of water vapor, which has a small but non-zero effect on air density.
Q: How does temperature affect air density?
A: Higher temperatures decrease air density because the air expands, reducing the mass per unit volume. Conversely, lower temperatures increase air density.
 Home
Home
 Back
Back