1. What is the Absolute Humidity Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the absolute humidity (\( AH \)) and actual vapor pressure (\( P_{\text{actual}} \)) of air based on the relative humidity (\( RH \)) and air temperature (\( T \)). Absolute humidity is the mass of water vapor per unit volume of air.
Purpose: It is used in meteorology, HVAC engineering, and environmental science to assess moisture content in the air for applications like weather forecasting, indoor climate control, and industrial processes.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Formulas:
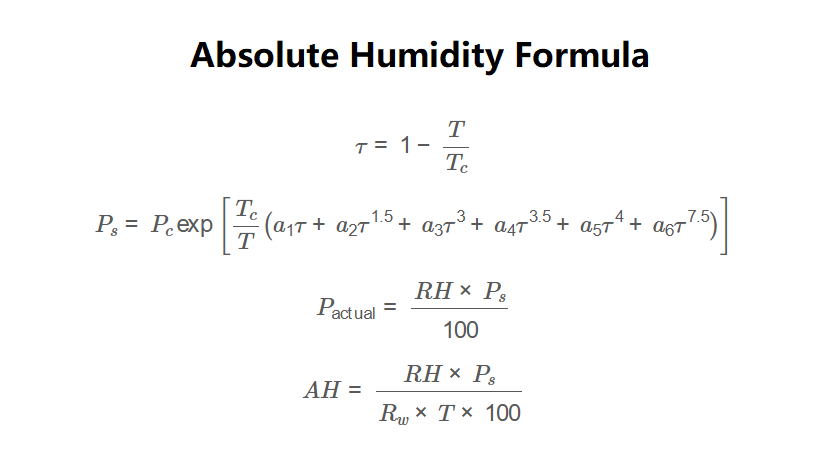
\[
\tau = 1 - \frac{T}{T_c}
\]
\[
P_s = P_c \exp \left[ \frac{T_c}{T} \left( a_1 \tau + a_2 \tau^{1.5} + a_3 \tau^3 + a_4 \tau^{3.5} + a_5 \tau^4 + a_6 \tau^{7.5} \right) \right]
\]
\[
P_{\text{actual}} = \frac{RH \times P_s}{100}
\]
\[
AH = \frac{RH \times P_s}{R_w \times T \times 100}
\]
where:
- \( P_{\text{actual}} \): Actual vapor pressure (Pa, bar, psi, at, atm, Torr, hPa, kPa, lb/ft²)
- \( AH \): Absolute humidity (kg/m³, g/m³, lb/ft³)
- \( RH \): Relative humidity (%)
- \( P_s \): Saturation vapor pressure (Pa)
- \( R_w \): Specific gas constant for water vapor, 461.5 J/(kg·K)
- \( T \): Temperature (K, °C, °F)
- \( P_c \): Critical pressure for water, 22.064 MPa
- \( T_c \): Critical temperature for water, 647.096 K
- Empirical constants: \( a_1 = -7.85951783 \), \( a_2 = 1.84408259 \), \( a_3 = -11.7866497 \), \( a_4 = 22.6807411 \), \( a_5 = -15.9618719 \), \( a_6 = 1.80122502 \)
Unit Conversions:
- Temperature (\( T \)):
- 1 °C = 273.15 K
- 1 °F = (T - 32) × 5/9 + 273.15 K
- 1 K = 1 K
- Actual Vapor Pressure (\( P_{\text{actual}} \)):
- 1 Pa = 1 Pa
- 1 bar = 100000 Pa
- 1 psi = 6894.76 Pa
- 1 at = 98066.5 Pa
- 1 atm = 101325 Pa
- 1 Torr = 133.322 Pa
- 1 hPa = 100 Pa
- 1 kPa = 1000 Pa
- 1 lb/ft² = 47.8803 Pa
- Absolute Humidity (\( AH \)):
- 1 kg/m³ = 1 kg/m³
- 1 g/m³ = 0.001 kg/m³
- 1 lb/ft³ = 16.0185 kg/m³
Steps:
- Enter the relative humidity (\( RH \)) as a percentage (default is 50%, step size 0.00001).
- Enter the air temperature (\( T \)) in °C, °F, or K (default is 25°C, step size 0.00001).
- Convert the temperature to Kelvin (K).
- Calculate the saturation vapor pressure (\( P_s \)) using the Wagner-Pruss equation.
- Calculate the actual vapor pressure (\( P_{\text{actual}} \)) using \( P_{\text{actual}} = \frac{RH \times P_s}{100} \).
- Calculate the absolute humidity (\( AH \)) using \( AH = \frac{RH \times P_s}{R_w \times T \times 100} \).
- Convert the results to the selected units and display them, using scientific notation if the absolute value is less than 0.001, otherwise rounded to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Absolute Humidity Calculation
Calculating absolute humidity is crucial for:
- Meteorology: Understanding the moisture content in the air for weather prediction and climate studies.
- HVAC Systems: Designing and optimizing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for comfort and energy efficiency.
- Industrial Processes: Controlling humidity levels in processes like drying, storage, and manufacturing to ensure product quality.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1: Calculate the absolute humidity and actual vapor pressure for air with a relative humidity of 50% and temperature of 25°C, with actual vapor pressure in Pa and absolute humidity in kg/m³:
- Enter \( RH = 50 \) %.
- Enter \( T = 25 \) °C, convert to K: \( 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 \, \text{K} \).
- Calculate \( \tau \): \( \tau = 1 - \frac{298.15}{647.096} = 0.5392 \).
- Calculate \( P_s \): \( P_s = 22.064 \times 10^6 \times \exp \left( \frac{647.096}{298.15} \left( -7.85951783 \times 0.5392 + 1.84408259 \times 0.5392^{1.5} + \ldots \right) \right) \approx 3168.29 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Actual vapor pressure: \( P_{\text{actual}} = \frac{50 \times 3168.29}{100} = 1584.15 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Absolute humidity: \( AH = \frac{50 \times 3168.29}{461.5 \times 298.15 \times 100} = 0.0115 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \).
- Result: \( P_{\text{actual}} = 1584.1450 \, \text{Pa} \), \( AH = 0.0115 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \).
- Example 2: Calculate the absolute humidity and actual vapor pressure for air with a relative humidity of 0.1% and temperature of -10°C, with actual vapor pressure in psi and absolute humidity in g/m³:
- Enter \( RH = 0.1 \) %.
- Enter \( T = -10 \) °C, convert to K: \( -10 + 273.15 = 263.15 \, \text{K} \).
- Calculate \( \tau \): \( \tau = 1 - \frac{263.15}{647.096} = 0.5933 \).
- Calculate \( P_s \): \( P_s = 22.064 \times 10^6 \times \exp \left( \frac{647.096}{263.15} \left( -7.85951783 \times 0.5933 + \ldots \right) \right) \approx 259.35 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Actual vapor pressure: \( P_{\text{actual}} = \frac{0.1 \times 259.35}{100} = 0.2594 \, \text{Pa} \).
- Convert to psi: \( 0.2594 \times 0.000145038 = 0.0000376 \), use scientific notation: \( 3.7615 \times 10^{-5} \).
- Absolute humidity: \( AH = \frac{0.1 \times 259.35}{461.5 \times 263.15 \times 100} = 0.000002134 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \).
- Convert to g/m³: \( 0.000002134 \times 1000 = 0.002134 \), use scientific notation: \( 2.1340 \times 10^{-3} \).
- Result: \( P_{\text{actual}} = 3.7615 \times 10^{-5} \, \text{psi} \), \( AH = 2.1340 \times 10^{-3} \, \text{g/m}^3 \).
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is absolute humidity?
A: Absolute humidity is the mass of water vapor per unit volume of air, typically measured in kg/m³ or g/m³. It represents the actual amount of moisture in the air, independent of temperature.
Q: How does relative humidity affect absolute humidity?
A: Relative humidity determines the fraction of the saturation vapor pressure that is present as actual vapor pressure. Higher relative humidity increases the absolute humidity for a given temperature.
Q: Why use the Wagner-Pruss equation for saturation vapor pressure?
A: The Wagner-Pruss equation provides a highly accurate approximation for the saturation vapor pressure of water over a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for precise humidity calculations.
Absolute Humidity Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back