 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator converts between physical measurements (e.g., temperature, pressure) and 4-20 mA current loop signals, commonly used in industrial instrumentation to transmit process variables. It also calculates the percentage of the signal within the 4-20 mA range.
Purpose: It is used in industrial automation, process control, and engineering to scale sensor readings to current signals or vice versa, ensuring accurate monitoring and control.
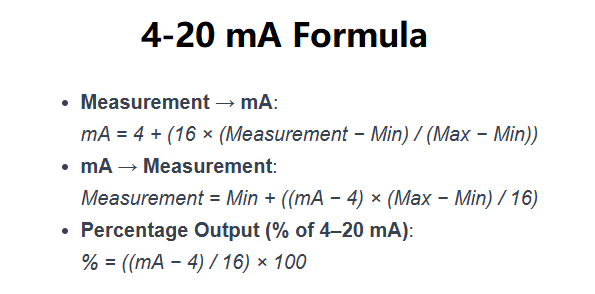
The calculator uses the following formulas:
Formulas: \[ \text{Current (mA)} = 4 + \left(16 \times \frac{\text{Measurement} - \text{Min}}{\text{Max} - \text{Min}}\right) \] \[ \text{Measurement} = \text{Min} + \left(\frac{\text{Current (mA)} - 4}{16} \times (\text{Max} - \text{Min})\right) \] \[ \text{Percentage (\%)} = \frac{\text{Current (mA)} - 4}{16} \times 100 \] where:
Steps:
Calculating 4-20 mA conversions is crucial for:
Examples:
Q: What is a 4-20 mA current loop?
A: It's a standard for transmitting analog signals in industrial environments, where 4 mA represents the minimum value and 20 mA the maximum.
Q: Why use 4-20 mA instead of 0-20 mA?
A: Starting at 4 mA allows detection of faults like broken wires (0 mA indicates error).
Q: What are common applications?
A: Used in sensors for temperature, pressure, flow, and level in industries like manufacturing and oil & gas.