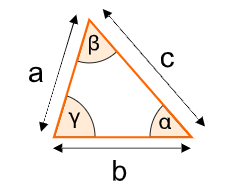
1. What is a Triangle Angle Calculator?
Definition: This calculator computes the angles of a triangle using different input methods: three sides, an angle and two sides, or two angles.
Purpose: It is used in geometry to determine triangle angles, useful in education, design, and engineering.
2. How Does the Calculator Work?
The calculator operates in three modes:
Three Sides (SSS) Mode:
- Angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \arccos\left(\frac{b^2 + c^2 - a^2}{2bc}\right) \)
- Angle \( \beta \): \( \beta = \arccos\left(\frac{a^2 + c^2 - b^2}{2ac}\right) \)
- Angle \( \gamma \): \( \gamma = \arccos\left(\frac{a^2 + b^2 - c^2}{2ab}\right) \)
Angle and Two Sides (SAS) Mode:
- If given \( \alpha \), \( a \), \( b \):
- Side \( c \): \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(\alpha)} \)
- Angle \( \beta \): \( \beta = \arcsin\left(\frac{b \sin(\alpha)}{c}\right) \)
- Angle \( \gamma \): \( \gamma = 180^\circ - \alpha - \beta \)
- If given \( \beta \), \( a \), \( b \):
- Side \( c \): \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(\beta)} \)
- Angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \arcsin\left(\frac{a \sin(\beta)}{c}\right) \)
- Angle \( \gamma \): \( \gamma = 180^\circ - \alpha - \beta \)
- If given \( \gamma \), \( a \), \( b \):
- Side \( c \): \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(\gamma)} \)
- Angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \arccos\left(\frac{b^2 + c^2 - a^2}{2bc}\right) \)
- Angle \( \beta \): \( \beta = 180^\circ - \alpha - \gamma \)
Two Angles (AA) Mode:
- Angle \( \gamma \): \( \gamma = 180^\circ - \alpha - \beta \)
Unit Conversions:
- Input Dimensions: m, cm (1 m = 100 cm), mm (1 m = 1000 mm), in (1 m = 39.3701 in), ft (1 m = 3.28084 ft), yd (1 m = 1.09361 yd)
- Output Dimensions: m, cm, mm, in, ft, yd
Steps:
- Select the mode (Three Sides, Angle and Two Sides, or Two Angles).
- View the corresponding triangle diagram for the selected mode.
- For Angle and Two Sides mode, choose the known angle (\( \alpha \), \( \beta \), or \( \gamma \)).
- Input the required values with their units.
- Convert all dimensions to meters for calculation.
- Validate the inputs (e.g., triangle inequality, angle constraints).
- Calculate the outputs based on the mode's formulas, formatted to 4 decimal places.
3. Importance of Triangle Angle Calculations
Calculating triangle angles is crucial for:
- Geometry Education: Understanding trigonometric laws and triangle properties.
- Engineering Design: Analyzing angular relationships in structures.
- Construction: Ensuring accurate angular measurements for layouts.
4. Using the Calculator
Examples:
- Example 1 (Three Sides Mode): For a triangle with \( a = 3 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 4 \, \text{cm} \), \( c = 5 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.03 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 0.04 \, \text{m} \), \( c = 0.05 \, \text{m} \)
- Angle \( \alpha \): \( \alpha = \arccos\left(\frac{0.04^2 + 0.05^2 - 0.03^2}{2 \times 0.04 \times 0.05}\right) \approx 36.8699^\circ \)
- Angle \( \beta \): \( \beta = \arccos\left(\frac{0.03^2 + 0.05^2 - 0.04^2}{2 \times 0.03 \times 0.05}\right) \approx 53.1301^\circ \)
- Angle \( \gamma \): \( \gamma = \arccos\left(\frac{0.03^2 + 0.04^2 - 0.05^2}{2 \times 0.03 \times 0.04}\right) = 90^\circ \)
- Example 2 (Angle and Two Sides Mode, Angle \( \alpha \)): For a triangle with \( \alpha = 30^\circ \), \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 6 \, \text{cm} \):
- Convert: \( a = 0.05 \, \text{m} \), \( b = 0.06 \, \text{m} \)
- Side \( c \): \( c = \sqrt{0.05^2 + 0.06^2 - 2 \times 0.05 \times 0.06 \times \cos(30^\circ)} \approx 0.0312 \, \text{m} \)
- Angle \( \beta \): \( \beta = \arcsin\left(\frac{0.06 \times \sin(30^\circ)}{0.0312}\right) \approx 66.9725^\circ \)
- Angle \( \gamma \): \( \gamma = 180 - 30 - 66.9725 \approx 83.0275^\circ \)
- Convert: \( c \approx 3.12 \, \text{cm} \)
- Example 3 (Two Angles Mode): For a triangle with \( \alpha = 50^\circ \), \( \beta = 60^\circ \):
- Angle \( \gamma \): \( \gamma = 180 - 50 - 60 = 70^\circ \)
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How do you find the angles of a triangle?
A: Depending on the given data, you can use the law of cosines (for three sides), a combination of the law of cosines and law of sines (for an angle and two sides), or the triangle angle sum theorem (for two angles).
Q: Why is calculating triangle angles important?
A: It is essential for solving problems in geometry, engineering, and physics involving triangular shapes.
Triangle Angle Calculator© - All Rights Reserved 2025
 Home
Home
 Back
Back